Android自定义VIew实现卫星菜单效果浅析
一 概述:
最近一直致力于Android自定义VIew的学习,主要在看《android群英传》,还有CSDN博客鸿洋大神和wing大神的一些文章,写的很详细,自己心血来潮,学着写了个实现了类似卫星效果的一个自定义的View,分享到博客上,望各位指点一二。写的比较粗糙,见谅。(因为是在Linux系统下写的,效果图我直接用手机拍的,难看,大家讲究下就看个效果,勿喷)。
先来看个效果图,有点不忍直视:
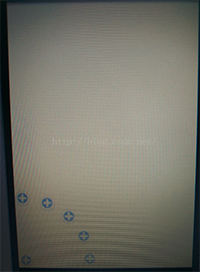
自定义VIew准备:
(1)创建继承自View的类;
(2)重写构造函数;
(3)定义属性。
(4)重写onMeasure(),onLayout()方法。
好了,废话不说了,准备上菜。
二 相关实现
首先是自定义的View,重写构造函数,我这里是直接继承的VIewGroup,贴上代码:
public MoonView(Context context) {
this(context,null);
}
public MoonView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs,0);
}
public MoonView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
这里需要读取自定义的属性,所以调用含三个参数的构造函数。
自定义的属性,我这里知定义了两个,一个是菜单弧形的半径,还有个是菜单在屏幕的位置,这里可以设置在左上角,左下角,右上角,右下角。代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <declare-styleable name="MoonAttrs"> <attr name="mRadius" format="integer"></attr><!--菜单圆形半径--> <attr name="mPosition"><!--卫星菜单屏幕所在位置--> <enum name="leftTop" value="-2"></enum><!--左上角--> <enum name="leftBottom" value="-1"></enum><!--左下角--> <enum name="rightTop" value="-3"></enum><!--右上角--> <enum name="rightBottom" value="-4"></enum><!--右下角--> </attr> </declare-styleable> </resources>
然后在布局文件里面引用自定义的View,配置属性:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <com.example.liujibin.testmyview3.myView.MoonView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:custom="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.example.liujibin.testmyview3" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" custom:mRadius="400" custom:mPosition="rightBottom" > <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="@mipmap/sapi_icon_add_account"/> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="@mipmap/sapi_icon_add_account"/> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="@mipmap/sapi_icon_add_account"/> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="@mipmap/sapi_icon_add_account"/> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="@mipmap/sapi_icon_add_account"/> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="@mipmap/sapi_icon_add_account"/> </com.example.liujibin.testmyview3.myView.MoonView>
最后我们需要在自定义的View类中的构造函数里,获取相关的属性值:
public MoonView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
//获取相关属性
TypedArray ta = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MoonAttrs,
defStyleAttr,0);
mRaius = ta.getInt(R.styleable.MoonAttrs_mRadius,500);
position = ta.getInt(R.styleable.MoonAttrs_mPosition,-1);
}
做完以上的准备工作,我们就可以对组件进行测量,布局。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
count = getChildCount()-1;
angle = 90/(count-1);
int count = getChildCount();
for(int i =0;i< count;i++){
measureChild(getChildAt(i),widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
count获取按钮的数量,有一个是中心点,不参与计算,angle是每个按钮离基准线的角度,这里以90度为准,固定在这个范围里面均匀分配。
首先先把中心点固定好位置:
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean b, int i, int i1, int i2, int i3) {
if(isChanged){
layoutBottom();
}
}
private void layoutBottom(){
View view = getChildAt(0);
switch (position){
case -1:
btml = 0;
btmt = getMeasuredHeight() - view.getMeasuredHeight();
btmr = view.getMeasuredWidth();
btmb = getMeasuredHeight();
break;
case -2:
btml = 0;
btmt = 0;
btmr = view.getMeasuredWidth();
btmb = view.getMeasuredHeight();
break;
case -3:
btml = getMeasuredWidth() - view.getMeasuredWidth();
btmt = 0;
btmr = getMeasuredWidth();
btmb = view.getMeasuredHeight();
break;
case -4:
btml = getMeasuredWidth() - view.getMeasuredWidth();
btmt = getMeasuredHeight() - view.getMeasuredHeight();
btmr = getMeasuredWidth();
btmb = getMeasuredHeight();
break;
}
btmWidth = view.getMeasuredWidth();
btmHeight = view.getMeasuredHeight();
view.setOnClickListener(this);
view.layout(btml,btmt,btmr,btmb);
}
position的值看属性就明白了,对中心点进行固定位置。并且注册点击事件。
现在开始给剩下的按钮布局,并隐藏按钮:
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean b, int i, int i1, int i2, int i3) {
if(isChanged){
layoutBottom();
int count = getChildCount();
for(int k = 0;k < count - 1;k++){
View view = getChildAt(k+1);
int childWidth = view.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = view.getMeasuredHeight();
int childX = (int)(mRaius*(Math.sin(angle*(k)*Math.PI/180)));
int childY = (int)(mRaius*(Math.cos(angle*(k)*Math.PI/180)));
int left = 0;
int top = 0;
int right = 0;
int bottom = 0;
switch(position){
case -1:
left = childX+btmWidth/2-childWidth/2;
top =getMeasuredHeight() - (childY+childHeight/2+btmHeight/2);
right = childX+btmWidth/2+childWidth/2;
bottom =getMeasuredHeight() - (childY + btmHeight/2) + childHeight/2;
break;
case -2:
left = childX+btmWidth/2-childWidth/2;
top =childY-childHeight/2+btmHeight/2;
right = childX+btmWidth/2+childWidth/2;
bottom = childY + btmHeight/2 + childHeight/2;
break;
case -3:
left = getMeasuredWidth() - (childX+btmWidth/2+childWidth/2);
top =childY-childHeight/2+btmHeight/2;
right = getMeasuredWidth() - (childX+btmWidth/2+childWidth/2)+childWidth;
bottom = childY + btmHeight/2 + childHeight/2;
break;
case -4:
left = getMeasuredWidth() - (childX+btmWidth/2+childWidth/2);
top =getMeasuredHeight() - (childY+childHeight/2+btmHeight/2);
right = getMeasuredWidth() - (childX+btmWidth/2+childWidth/2)+childWidth;
bottom =getMeasuredHeight() - (childY + btmHeight/2) + childHeight/2;
break;
}
view.layout(left,top,right,bottom);
view.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
}
}
现在我们实现点击事件:
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
if(isChanged){
int count = getChildCount();
for(int i = 0;i < count - 1;i++){
View childView = getChildAt(i+1);
int childX = (int)(mRaius*(Math.sin(angle*(i)*Math.PI/180)));
int childY = (int)(mRaius*(Math.cos(angle*(i)*Math.PI/180)));
int childWidth = view.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = view.getMeasuredHeight();
int left = 0;
int top = 0;
TranslateAnimation ta = null;
switch(position){
case -1:
left = childX+btmWidth/2-childWidth/2;
top =getMeasuredHeight() - (childY+childHeight/2+btmHeight/2);
ta = new TranslateAnimation(-(left+childView.getMeasuredWidth()),0,getMeasuredHeight()-top,0);
break;
case -2:
left = childX+btmWidth/2-childWidth/2;
top =childY-childHeight/2+btmHeight/2;
ta = new TranslateAnimation(-(left+childView.getMeasuredWidth()),0,-top,0);
break;
case -3:
left = getMeasuredWidth() - (childX+btmWidth/2+childWidth/2);
top =childY-childHeight/2+btmHeight/2;
ta = new TranslateAnimation(getMeasuredWidth()-(left+childView.getMeasuredWidth()),0,-top,0);
break;
case -4:
left = getMeasuredWidth() - (childX+btmWidth/2+childWidth/2);
top =getMeasuredHeight() - (childY+childHeight/2+btmHeight/2);
ta = new TranslateAnimation(getMeasuredWidth()-(left+childView.getMeasuredWidth()),0,getMeasuredHeight()-top,0);
break;
}
ta.setDuration(500);
childView.setAnimation(ta);
childView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
isChanged = false;
}else{
int count = getChildCount();
for(int i = 0;i < count - 1;i++){
View childView = getChildAt(i+1);
int childX = (int)(mRaius*(Math.sin(angle*(i)*Math.PI/180)));
int childY = (int)(mRaius*(Math.cos(angle*(i)*Math.PI/180)));
int childWidth = view.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = view.getMeasuredHeight();
int left = 0;
int top = 0;
TranslateAnimation ta = null;
switch(position){
case -1:
left = childX+btmWidth/2-childWidth/2;
top =getMeasuredHeight() - (childY+childHeight/2+btmHeight/2);
ta = new TranslateAnimation(0,-(left+childView.getMeasuredWidth()),0,getMeasuredHeight()-top);
break;
case -2:
left = childX+btmWidth/2-childWidth/2;
top =childY-childHeight/2+btmHeight/2;
ta = new TranslateAnimation(0,-(left+childView.getMeasuredWidth()),0,-top);
break;
case -3:
left = getMeasuredWidth() - (childX+btmWidth/2+childWidth/2);
top =childY-childHeight/2+btmHeight/2;
ta = new TranslateAnimation(0,getMeasuredWidth()-(left+childView.getMeasuredWidth()),0,-top);
break;
case -4:
left = getMeasuredWidth() - (childX+btmWidth/2+childWidth/2);
top =getMeasuredHeight() - (childY+childHeight/2+btmHeight/2);
ta = new TranslateAnimation(0,getMeasuredWidth()-(left+childView.getMeasuredWidth()),0,getMeasuredHeight()-top);
break;
}
ta.setDuration(500);
childView.setAnimation(ta);
childView.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
isChanged = true;
}
}
设置点击显示以及隐藏,并且带飘动的动画效果。
四个角落效果如下:


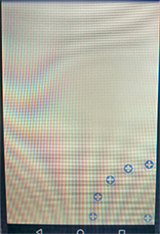
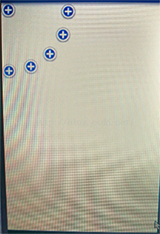
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的Android自定义VIew实现卫星菜单效果浅析,希望对大家有所帮助,如果大家有任何疑问请给我留言,小编会及时回复大家的。在此也非常感谢大家对我们网站的支持!

