MySQL中LAG()函数和LEAD()函数的使用
目录
- 一、窗口函数的基本用法
- 二、LAG()和LEAD()函数介绍
- 三、数据准备(建表sql在最后)
- 四、建表数据sql
一、窗口函数的基本用法
从MySQL8之后才开始支持窗口函数
<窗口函数> OVER ([PARTITION BY <用于分组的列>] ORDER BY <用于排序的列>)
二、LAG()和LEAD()函数介绍
- lag和lead分别是向前向后的意思
- 参数有三个。expression:列名;offset:偏移量;default_value:超出记录窗口的默认值(默认为null,可以设置为0)
三、数据准备(建表sql在最后)
1、LAG()函数:统计与前一天相比温度更高的日期Id
我们先按照日期进行排序,然后找到当天比前一天温度高的id;使用lag()函数,将温度向后推一天。
select id, date, temperature, LAG(temperature, 1, 0) OVER (order by date) as temp FROM weather
查询结果:

然后将temperature大于temp 并且temp不等于0的数据挑选出来
select id from (select id, date, temperature, LAG(temperature, 1, 0) OVER (order by date) as temp FROM weather) tmp where temperature>temp and temp != 0;
结果如下:

2、LEAD()函数:统计与后一天相比温度更高的日期Id
我们还是先按照日期进行排序,然后找到当天比后一天温度高的id;使用lead()函数,将温度向后推一天。
select id, date, temperature, LEAD(temperature, 1, 0) OVER (order by date) as temp FROM weather
查询结果:
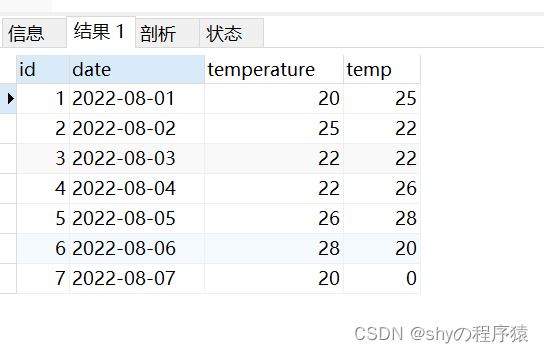
然后将temperature大于temp 并且temp不等于0的数据挑选出来
select id from (select id, date, temperature, LEAD(temperature, 1, 0) OVER (order by date) as temp FROM weather) tmp where temperature>temp and temp != 0;
查询结果:

四、建表数据sql
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `weather`; CREATE TABLE `weather` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL, `date` date NULL DEFAULT NULL, `temperature` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of weather -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `weather` VALUES (1, '2022-08-01', 20); INSERT INTO `weather` VALUES (2, '2022-08-02', 25); INSERT INTO `weather` VALUES (3, '2022-08-03', 22); INSERT INTO `weather` VALUES (4, '2022-08-04', 22); INSERT INTO `weather` VALUES (5, '2022-08-05', 26); INSERT INTO `weather` VALUES (6, '2022-08-06', 28); INSERT INTO `weather` VALUES (7, '2022-08-07', 20); SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
到此这篇关于MySQL中LAG()函数和LEAD()函数的使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关mysql LAG()和LEAD()函数内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!
赞 (0)

