Python实现病毒仿真器的方法示例(附demo)
最近新冠在神州大陆横行,全国上下一心抗击疫情。作为一枚程序员,我也希望可以为抗击疫情做出自己的贡献,钟院士一直劝说大家不要出门,减少人口间的流动。对此,我特意做了一个病毒仿真器,探询冠状病毒传播。
1. 仿真效果
仿真开始,一开始只有5个发病者,传播率为0.8,潜伏期为14天

由于人口的流动,以及医院床位的隔离,一开始病毒扩撒不是很速度
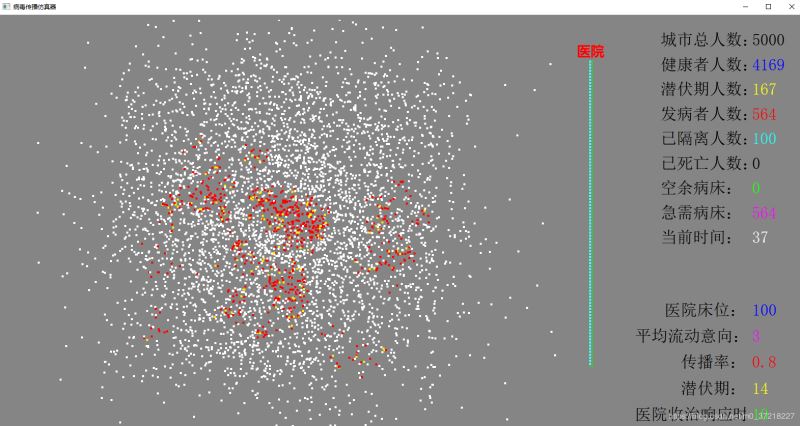
随着医院床位满了,隔离失败,加上人口的流动,病患数开始几何式的增加
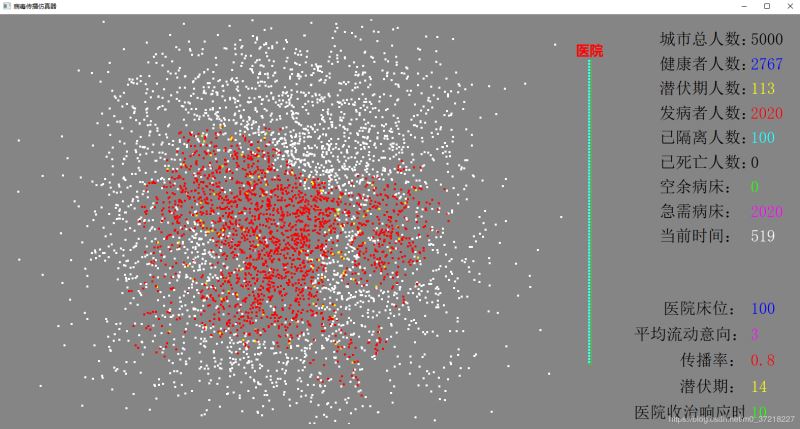
2. 什么是仿真器
仿真器(emulator)以某一系统复现另一系统的功能。与计算机模拟系统(Computer Simulation)的区别在于,仿真器致力于模仿系统的外在表现、行为,而不是模拟系统的抽象模型。
3. python如何实现仿真器
现在来谈谈仿真器实现的原理。仿真器使用Python和PyQt5实现。PyQt5是封装了Qt library的跨平台GUI开发库,基于Python语言。
这里主要涉及到仿真器效果绘制,以及如何模拟多个参数。先来说一下绘制市民的状态。绘制的工作通过drawing.py文件的Drawing类来完成。该类是QWidget的子类,这也就意味着Drawing类本身是PyQt5的一个组件。与按钮、标签类似。只是并不需要往Drawing上放置任何子组件。只要在Drawing上绘制各种图形即可。
在PyQt5中,任何一个QWidget的子类,都可以实现一个paintEvent方法,当组件每次刷新时,就会调用paintEvent方法重新绘制组件的内容。Drawing类中paintEvent方法的代码如下:
# 每次Drawing刷新,都会调用该方法
def paintEvent(self,event):
qp = QPainter()
qp.begin(self)
self.drawing(qp) # 绘制城市的各种状态的市民
qp.end()
在绘制图像前,需要创建QPainter对象,然后调用QPainter对象的begin方法,结束绘制后,需要调用QPainter对象的end方法。上面代码中的drawing方法用于完成具体的绘制工作。
仿真器设置一个人员池,来进行人员的流动性
class Persons(metaclass=Singleton):
def __init__(self):
self.persons = [] # 保存所有的人员
self.latency_persons = [] # 保存处于潜伏期的人员
city = City(Params.city_center_x,Params.city_center_y)
for value in range(0, Params.city_person_count):
x = Params.person_position_scale * next_gaussian() + city.center_x
y = Params.person_position_scale * next_gaussian() + city.center_y
if x > Params.city_width:
x = Params.city_width
if y > Params.city_height:
y = Params.city_height
self.persons.append(Person(city,x,y))
# 获取特定人群的数量
def get_person_size(self,state):
if state == -1:
return len(self.persons)
count = 0
for person in self.persons:
if person.state == state:
count += 1
return count
仿真代码
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
from socket import *
class Transmission:
def __init__(self,ui):
self.ui = ui
self.host = 'localhost'
self.port = 5678
self.addr = (self.host,self.port)
def send_command(self,command,value=None):
tcp_client_socket = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)
tcp_client_socket.connect(self.addr)
if value == None:
value = 0
data = command + ':' + str(value)
tcp_client_socket.send(('%s\r\n' % data).encode(encoding='utf-8'))
data = tcp_client_socket.recv(1024)
result = data.decode('utf-8').strip()
tcp_client_socket.close()
return result
def setup(self):
self.ui.horizontalSliderBedCount.valueChanged.connect(self.bed_count_value_change)
self.ui.pushButtonUpdateBedCount.clicked.connect(self.update_bed_count)
self.ui.horizontalSliderFlowIntention.valueChanged.connect(self.flow_intention_value_change)
self.ui.pushButtonFlowIntention.clicked.connect(self.update_flow_intention)
self.ui.horizontalSliderBroadRate.valueChanged.connect(self.broad_rate_value_change)
self.ui.pushButtonBroadRate.clicked.connect(self.update_broad_rate)
self.ui.horizontalSliderLatency.valueChanged.connect(self.latency_value_change)
self.ui.pushButtonLatency.clicked.connect(self.update_latency)
self.ui.pushButtonClose.clicked.connect(self.close_virus_simulation)
def bed_count_value_change(self):
self.ui.labelBedIncrement.setText(
f'<html><head/><body><p><span style=\" font-size:24pt; color:#0000ff;\">{self.ui.horizontalSliderBedCount.value()}</span></p></body></html>')
def update_bed_count(self):
print(self.ui.horizontalSliderBedCount.value())
result = self.send_command('add_bed_count', self.ui.horizontalSliderBedCount.value())
if result == 'ok':
QMessageBox.information(self.ui.centralwidget, '消息', f'成功添加了{self.ui.horizontalSliderBedCount.value()}张床位',
QMessageBox.Ok)
def flow_intention_value_change(self):
self.ui.labelFlowIntention.setText(
f'<html><head/><body><p><span style=\" font-size:24pt; color:#fc02ff;\">{self.ui.horizontalSliderFlowIntention.value() / 100}</span></p></body></html>')
def update_flow_intention(self):
result = self.send_command('set_flow_intention', self.ui.horizontalSliderFlowIntention.value())
if result == 'ok':
QMessageBox.information(self.ui.centralwidget, '消息',
f'成功设置流动意向为{self.ui.horizontalSliderFlowIntention.value() / 100}', QMessageBox.Ok)
def broad_rate_value_change(self):
self.ui.labelBroadRate.setText(
f'<html><head/><body><p><span style=\" font-size:24pt; color:#fc0107;\">{self.ui.horizontalSliderBroadRate.value() / 100}</span></p></body></html>')
def update_broad_rate(self):
result = self.send_command('set_broad_rate', self.ui.horizontalSliderBroadRate.value())
if result == 'ok':
QMessageBox.information(self.ui.centralwidget, '消息',
f'成功设置传播率为{self.ui.horizontalSliderBroadRate.value() / 100}', QMessageBox.Ok)
def latency_value_change(self):
self.ui.labelLatency.setText(
f'<html><head/><body><p><span style=\" font-size:24pt; color:#ffff0a;\">{self.ui.horizontalSliderLatency.value()}</span></p></body></html>')
def update_latency(self):
result = self.send_command('set_latency', self.ui.horizontalSliderLatency.value())
if result == 'ok':
QMessageBox.information(self.ui.centralwidget, '消息', f'成功设置传播率为{self.ui.horizontalSliderLatency.value()}',
QMessageBox.Ok)
def close_virus_simulation(self):
reply = QMessageBox.information(self.ui.centralwidget, "请问", "是否真的要关闭病毒扩散仿真器?",
QMessageBox.Yes | QMessageBox.No, QMessageBox.No)
if reply == QMessageBox.Yes:
result = self.send_command('close')
if result == 'ok':
QMessageBox.information(self.ui.centralwidget, '消息', '已经成功关闭病毒扩散仿真器', QMessageBox.Ok)
设置变量
class Params: success = False # 初始感染人数 original_infected_count = 50 # 病毒传播率 broad_rate = 0.8 # 病毒潜伏期,14天 virus_latency = 140 # 医院收治响应时间 hospital_receive_time = 10 # 医院床位 hospital_bed_count = 100 # 安全距离 safe_distance = 2 # 平均流动意向[-3,3] 值越大,流动意向越强 average_flow_intention = 3 # 城市总人口数量 city_person_count = 5000 # 病死率 fatality_rate = 0.02 # 死亡时间 dead_time = 30 # 死亡时间方差 dead_variance = 30 # 城市宽度 city_width = 1100 # 城市高度 city_height = 800 # 医院宽度(需要计算获得) hospial_width = 0 # 城市中心x坐标 city_center_x = 550 # 城市中心y坐标 city_center_y = 400 # 用于计算城市中每个人随机位置的scale(用于正态分布) person_position_scale = 200 current_time = 1 # 当前时间
我们可以根据这些修改仿真页面

完整代码
以上就是Python实现病毒仿真器的方法示例的详细内容,更多关于请关注我们其它相关文章!

