关于keras多任务多loss回传的思考
如果有一个多任务多loss的网络,那么在训练时,loss是如何工作的呢?
比如下面:
model = Model(inputs = input, outputs = [y1, y2]) l1 = 0.5 l2 = 0.3 model.compile(loss = [loss1, loss2], loss_weights=[l1, l2], ...)
其实我们最终得到的loss为
final_loss = l1 * loss1 + l2 * loss2
我们最终的优化效果是最小化final_loss。
问题来了,在训练过程中,是否loss2只更新得到y2的网络通路,还是loss2会更新所有的网络层呢?
此问题的关键在梯度回传上,即反向传播算法。
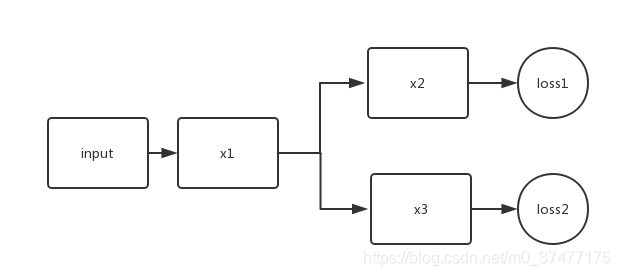

所以loss1只对x1和x2有影响,而loss2只对x1和x3有影响。
补充:keras 多个LOSS总和定义
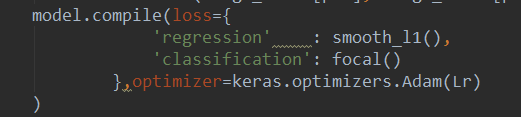
用字典形式,名字是模型中输出那一层的名字,这里的loss可以是自己定义的,也可是自带的
补充:keras实战-多类别分割loss实现
本文样例均为3d数据的onehot标签形式,即y_true(batch_size,x,y,z,class_num)
1、dice loss
def dice_coef_fun(smooth=1):
def dice_coef(y_true, y_pred):
#求得每个sample的每个类的dice
intersection = K.sum(y_true * y_pred, axis=(1,2,3))
union = K.sum(y_true, axis=(1,2,3)) + K.sum(y_pred, axis=(1,2,3))
sample_dices=(2. * intersection + smooth) / (union + smooth) #一维数组 为各个类别的dice
#求得每个类的dice
dices=K.mean(sample_dices,axis=0)
return K.mean(dices) #所有类别dice求平均的dice
return dice_coef
def dice_coef_loss_fun(smooth=0):
def dice_coef_loss(y_true,y_pred):
return 1-1-dice_coef_fun(smooth=smooth)(y_true=y_true,y_pred=y_pred)
return dice_coef_loss
2、generalized dice loss
def generalized_dice_coef_fun(smooth=0):
def generalized_dice(y_true, y_pred):
# Compute weights: "the contribution of each label is corrected by the inverse of its volume"
w = K.sum(y_true, axis=(0, 1, 2, 3))
w = 1 / (w ** 2 + 0.00001)
# w为各个类别的权重,占比越大,权重越小
# Compute gen dice coef:
numerator = y_true * y_pred
numerator = w * K.sum(numerator, axis=(0, 1, 2, 3))
numerator = K.sum(numerator)
denominator = y_true + y_pred
denominator = w * K.sum(denominator, axis=(0, 1, 2, 3))
denominator = K.sum(denominator)
gen_dice_coef = numerator / denominator
return 2 * gen_dice_coef
return generalized_dice
def generalized_dice_loss_fun(smooth=0):
def generalized_dice_loss(y_true,y_pred):
return 1 - generalized_dice_coef_fun(smooth=smooth)(y_true=y_true,y_pred=y_pred)
return generalized_dice_loss
3、tversky coefficient loss
# Ref: salehi17, "Twersky loss function for image segmentation using 3D FCDN"
# -> the score is computed for each class separately and then summed
# alpha=beta=0.5 : dice coefficient
# alpha=beta=1 : tanimoto coefficient (also known as jaccard)
# alpha+beta=1 : produces set of F*-scores
# implemented by E. Moebel, 06/04/18
def tversky_coef_fun(alpha,beta):
def tversky_coef(y_true, y_pred):
p0 = y_pred # proba that voxels are class i
p1 = 1 - y_pred # proba that voxels are not class i
g0 = y_true
g1 = 1 - y_true
# 求得每个sample的每个类的dice
num = K.sum(p0 * g0, axis=( 1, 2, 3))
den = num + alpha * K.sum(p0 * g1,axis= ( 1, 2, 3)) + beta * K.sum(p1 * g0, axis=( 1, 2, 3))
T = num / den #[batch_size,class_num]
# 求得每个类的dice
dices=K.mean(T,axis=0) #[class_num]
return K.mean(dices)
return tversky_coef
def tversky_coef_loss_fun(alpha,beta):
def tversky_coef_loss(y_true,y_pred):
return 1-tversky_coef_fun(alpha=alpha,beta=beta)(y_true=y_true,y_pred=y_pred)
return tversky_coef_loss
4、IoU loss
def IoU_fun(eps=1e-6):
def IoU(y_true, y_pred):
# if np.max(y_true) == 0.0:
# return IoU(1-y_true, 1-y_pred) ## empty image; calc IoU of zeros
intersection = K.sum(y_true * y_pred, axis=[1,2,3])
union = K.sum(y_true, axis=[1,2,3]) + K.sum(y_pred, axis=[1,2,3]) - intersection
#
ious=K.mean((intersection + eps) / (union + eps),axis=0)
return K.mean(ious)
return IoU
def IoU_loss_fun(eps=1e-6):
def IoU_loss(y_true,y_pred):
return 1-IoU_fun(eps=eps)(y_true=y_true,y_pred=y_pred)
return IoU_loss
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。
赞 (0)

