C#多线程Thread使用示例详解
本文实例为大家分享了C#多线程Thread使用的示例代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
多线程:
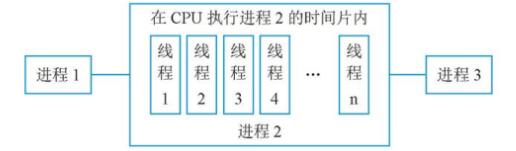
线程生命周期状态图:

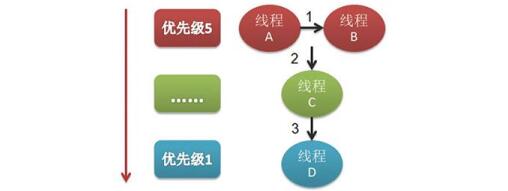
C#线程优先级(概率高低):

基本使用示例:
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace month_9_10._1009
{
class Run5
{
/* 测试线程的调用过程
* 主线程输出world,子线程输出hello
*/
public static void showHello()
{
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Hello\t#{Thread.CurrentThread.Name}");
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Main Thread!";
var childThreadRef = new ThreadStart(showHello);
Console.WriteLine("This is Main process!!!");
var childThread = new Thread(childThreadRef);
childThread.Name = "Child Thread!";
childThread.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"World!\t#{Thread.CurrentThread.Name}");
}
}
}
}
实例1:窗体标签循环滚动

using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace RollMove
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
Thread th1 = null;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int _sx = 40;
int _ex = 280;
int _top = 70;
th1 = new Thread(() => {
while (true)
{
if (_sx <= _ex)
{
_ex = 280;
label1.Location = new Point(_sx, _top);
Thread.Sleep(20);
_sx += 5;
}
else
{
_ex = 40;
label1.Location = new Point(_sx, _top);
Thread.Sleep(20);
_sx -= 5;
}
}
});
th1.Start();
}
private void Form1_FormClosed(object sender, FormClosedEventArgs e)
{
if (th1!=null)
{
th1.Abort();
}
}
}
}
实例2:进度条
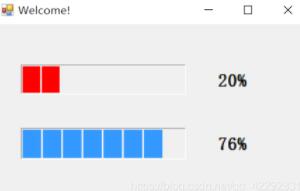
using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace month_9_10._1012
{
public partial class Form_3 : Form
{
public static Print.Print print = Console.WriteLine;
Thread th1, th2;
public Form_3()
{
InitializeComponent();
Text = "Welcome!";
CheckForIllegalCrossThreadCalls = false;
th1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(Pro1));
th1.Priority = ThreadPriority.Lowest;
th1.Start();
th2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(Pro2));
th2.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest;
//th2.Start();
print(th1.Priority);
print(th2.Priority);
}
void Pro1()
{
print("XXXXXXX");
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++)
{
progressBar1.Value = i;
label1.Text = $"{progressBar1.Value}%";
Thread.Sleep(200);
if (i == 20)
{
th2.Start();
th2.Join();
}
}
}
void Pro2()
{
print("YYYYYYYY");
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++)
{
progressBar2.Value = i;
label2.Text = $"{progressBar2.Value}%";
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
}
private void progressBar1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
print("This is Main threading!");
}
private void Form_3_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
private void Form_3_FormClosing_1(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
if (th1.ThreadState == ThreadState.Running)
th1.Abort();
if (th2.ThreadState == ThreadState.Running)
th2.Abort();
}
}
}
实例三:线程同步(售票模拟)
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace month_9_10._1012
{
class Run2
{
static Print.Print print = Console.WriteLine;
int _num = 10;
void Ticket()
{
while (true)
{
//上锁
//lock (this)
//{
// if (_num > 0)
// {
// Thread.Sleep(100);
// print(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + "--票数:" + _num--);
// }
//}
//放置监视器
Monitor.Enter(this);
if (_num > 0)
{
Thread.Sleep(100);
print(Thread.CurrentThread.Name + "--票数:" + _num--);
}
Monitor.Exit(this);
}
}
static void Main()
{
var a1 = new Run2();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(a1.Ticket));
t1.Name = "线程一";
Thread t2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(a1.Ticket));
t2.Name = "线程二";
Thread t3 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(a1.Ticket));
t3.Name = "线程三";
Thread t4 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(a1.Ticket));
t4.Name = "线程四";
t1.Start();
t2.Start();
t3.Start();
t4.Start();
}
}
}
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。
赞 (0)

