matplotlib quiver箭图绘制案例
quiver绘制表示梯度变化非常有用,下面是学习过程中给出的两个例子,可以很好理解quiver的用法
from pylab import * close() ## example 1 x = linspace(0,10,40) y = x**2*exp(-x) u = array([x[i+1]-x[i] for i in range(len(x)-1)]) v = array([y[i+1]-y[i] for i in range(len(x)-1)]) x = x[:len(u)] # 使得维数和u,v一致 y = y[:len(v)] c = randn(len(u)) # arrow颜色 figure() quiver(x,y,u,v,c, angles='xy', scale_units='xy', scale=1) # 注意参数的赋值 ## example 2 x = linspace(0,20,30) y = sin(x) u = array([x[i+1]-x[i] for i in range(len(x)-1)]) v = array([y[i+1]-y[i] for i in range(len(x)-1)]) x = x[:len(u)] # 使得维数和u,v一致 y = y[:len(v)] c = randn(len(u)) # arrow颜色 figure() quiver(x,y,u,v,c, angles='xy', scale_units='xy', scale=1) # 注意参数的赋值 show()
结果如下:

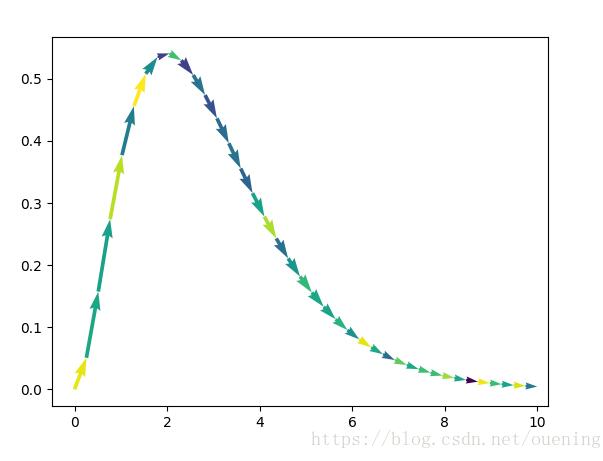
补充知识:Matlab矢量图图例函数quiverkey
Matlab自带函数中不包含构造 quiver 函数注释过程,本文参照 matplotlib 中 quiverkey 函数,构造类似函数为 Matlab 中 quiver 矢量场进行标注。
quiverkey函数
首先看 matplotlib 中 quiverkey 如何定义的
quiverkey(*args, **kw) Add a key to a quiver plot. Call signature:: quiverkey(Q, X, Y, U, label, **kw) Arguments: *Q*: The Quiver instance returned by a call to quiver. *X*, *Y*: The location of the key; additional explanation follows. *U*: The length of the key *label*: A string with the length and units of the key Keyword arguments: *coordinates* = [ 'axes' | 'figure' | 'data' | 'inches' ] Coordinate system and units for *X*, *Y*: 'axes' and 'figure' are normalized coordinate systems with 0,0 in the lower left and 1,1 in the upper right; 'data' are the axes data coordinates (used for the locations of the vectors in the quiver plot itself); 'inches' is position in the figure in inches, with 0,0 at the lower left corner. *color*: overrides face and edge colors from *Q*. *labelpos* = [ 'N' | 'S' | 'E' | 'W' ] Position the label above, below, to the right, to the left of the arrow, respectively. *labelsep*: Distance in inches between the arrow and the label. Default is 0.1 *labelcolor*: defaults to default :class:`~matplotlib.text.Text` color. *fontproperties*: A dictionary with keyword arguments accepted by the :class:`~matplotlib.font_manager.FontProperties` initializer: *family*, *style*, *variant*, *size*, *weight* Any additional keyword arguments are used to override vector properties taken from *Q*. The positioning of the key depends on *X*, *Y*, *coordinates*, and *labelpos*. If *labelpos* is 'N' or 'S', *X*, *Y* give the position of the middle of the key arrow. If *labelpos* is 'E', *X*, *Y* positions the head, and if *labelpos* is 'W', *X*, *Y* positions the tail; in either of these two cases, *X*, *Y* is somewhere in the middle of the arrow+label key object. Additional kwargs: hold = [True|False] overrides default hold state
可以看到主要参数有这么些个
quiver绘图指针
图例位置 X, Y
标注大小 U
标注单位字符
其他参数
1). 输入坐标 X, Y 单位
2). (文字)标注在图例哪个位置
3). 标注与图例相对距离
4). 标注字体颜色
使用方法:
对应Matlab函数也应该使用这么个流程
使用quiver绘图
将quiver返回指针与图例位置坐标和大小等作为参数传入
示例
[x,y] = meshgrid(0:0.2:2,0:0.2:2); u = cos(x).*y; v = sin(x).*y; figure; Qh = quiver(x,y,u,v); quiverkey(Qh, 0.5, 2.5, 1, 'm/s', 'Color', 'r', 'Coordinates', 'data')
最终效果图
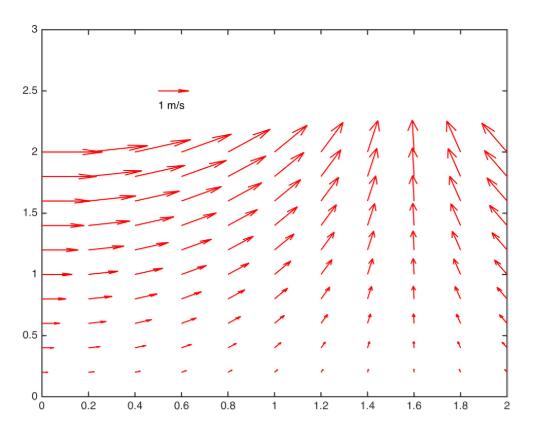
代码
function Q = quiverkey(Q, X, Y, U, label, varargin)
%QUIVERKEY legend for quiver
%
% QUIVERKEY(Q, X, Y, U, label)
%
% Arguments:
% Q : The quiver handle returned by a call to quiver
% X,Y : The location of the legend
% U : The unit length. If U<0, the arrow will be reversed
% label : The string with the length and units of the key
%
% Addition arguments:
% Coordinates = [ 'axes' | 'data'(default) ]
%
% 'axes' & 'figure' : 'axes' and 'figure' are normalized
% coordinate systems with 0,0 in the lower left
% and 1,1 in the upper right;
% 'data' : use the axes data coordinates
%
% LabelDistance : Distance in 'coordinates' between the arrow and the
% label. Deauft is 0.1 (units 'axes').
%
% Color : overrides face and edge colors from Q.
%
% LabelPosition = [ 'N' | 'S'(default) | 'E' | 'W' ]
%
% Position the label above, below, to the right,
% to the left of the arrow, respectively.
%
% LabelColor : defaults to black
%
% Examples:
%
% [x,y] = meshgrid(0:0.2:2,0:0.2:2);
% u = cos(x).*y;
% v = sin(x).*y;
% figure; Qh = quiver(x,y,u,v);
% quiverkey(Qh, 0.5, 2.5, 1, 'm/s', 'Color', 'r', 'Coordinates', 'data')
%
% Author:
% li12242 - Department of Civil Engineering in Tianjin University
% Email:
% li12242@tju.edu.cn
%
%% get input argument
if nargin < 5
error('Input arguments" Number incorrect!')
end
if isempty(varargin) && mod(length(varargin), 2) ~= 0
error('Input arguments donot pairs!')
else
[CoorUnit, LabelDist, Color, LabelPosition, LabelColor] = getInput(varargin);
end
%% add legend arrow
% get original data
xData = get(Q, 'XData'); yData = get(Q, 'YData');
uData = get(Q, 'UData'); vData = get(Q, 'VData');
% get axes properties
haxes = get(Q, 'Parent');
xLim = get(haxes, 'XLim'); yLim = get(haxes, 'YLim');
NextPlot = get(haxes, 'NextPlot');
% set axes properties
set(haxes, 'NextPlot', 'add')
if strcmp(CoorUnit, 'axes')
% position of legend arrow
xa = xLim(1) + X*(xLim(2) - xLim(1));
ya = yLim(1) + Y*(yLim(2) - yLim(1));
else
xa = X; ya = Y;
end
% add legend arrow into data vector
xData = [xData(:); xa]; yData = [yData(:); ya];
uData = [uData(:); U]; vData = [vData(:); 0];
% reset data
set(Q, 'XData', xData, 'YData', yData, 'UData', uData, 'VData', vData);
set(Q, 'Color', Color)
%% add text
dx = LabelDist*(xLim(2) - xLim(1));
dy = LabelDist*(yLim(2) - yLim(1));
% set position of label
switch LabelPosition
case 'N'
xl = xa; yl = ya + dy;
case 'S'
xl = xa; yl = ya - dy;
case 'E'
xl = xa + dx; yl = ya;
case 'W'
xl = xa - dx; yl = ya;
end% switch
th = text(xl, yl, [num2str(U), ' ', label]);
set(th, 'Color', LabelColor);
% turn axes properties to original
set(haxes, 'NextPlot', NextPlot)
end% func
%% sub function
function [CoorUnit, LabelDist, Color, LabelPosition, LabelColor] = getInput(varcell)
% Input:
% varcell - cell variable
% Output:
%
nargin = numel(varcell);
%% set default arguments
CoorUnit = 'data';
LabelDist = 0.05; % units 'axes'
Color = 'k';
LabelPosition = 'S';
LabelColor = 'k';
%% get input arguments
contour = 1;
while contour < nargin
switch varcell{contour}
case 'Coordinates'
CoorUnit = varcell{contour+ 1};
case 'LabelDistance'
LabelDist = varcell{contour+ 1};
case 'Color'
Color = varcell{contour+ 1};
case 'LabelPosition'
LabelPosition = varcell{contour+ 1};
case 'LabelColor'
LabelColor = varcell{contour+ 1};
otherwise
error('Unknown input argument.')
end% switch
contour = contour + 2;
end% while
end% fun
以上这篇matplotlib quiver箭图绘制案例就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。
赞 (0)

