springboot如何读取自定义properties并注入到bean中
目录
- 读取自定义properties注入到bean
- springboot启动日志如下
- springboot bean实例化和属性注入过程
- springboot版本(2.0.4 RELEASE)
- Bean的实例化
- Bean的属性注入
读取自定义properties注入到bean
在使用springboot项目时,可使用@value的方式直接读取application.properties中的文件,但有时我们需要配置自定义的properties,下面方法将在springboot启动时利用fileinputstream读取properties文件中的内容,并注入到bean中,@Configuration注解会在springboot启动时执行一次,代码如下:
package com.shanqis.parking.properties;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* 读取resource下的.properties文件,将文件中的内容封装到map中,注入到bean中方便依赖注入
*
* @author Administrator
*/
@Configuration
public class PropertiesClassLoader {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PropertiesClassLoader.class);
private Map<String, Object> versionProperties = new HashMap<>(16);
private void init(String name) {
try {
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream in = PropertiesClassLoader.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(name + ".properties");
properties.load(in);
logger.info("加载{}.properties参数", name);
for (String keyName : properties.stringPropertyNames()) {
String value = properties.getProperty(keyName);
if ("version".equals(name)) {
versionProperties.put(keyName, value);
}
logger.info("{}.properties---------key:{},value:{}", name, keyName, value);
}
logger.info("{}.properties参数加载完毕", name);
} catch (IOException ignored) {
}
}
@Bean(name = "versionProperties")
public Map<String, Object> commonMap() {
init("version");
return versionProperties;
}
}
springboot启动日志如下

然后在controller层或者service层等可以这样使用
/**
* 读取common.properties文件
*/
@Autowired @Qualifier("commonMap")
protected Map<String, String> commonMap;
springboot bean实例化和属性注入过程
springboot版本(2.0.4 RELEASE)
大致描述springboot中bean的实例化和属性注入过程流程
1) 在某一时刻Spring调用了Bean工厂的getBean(beanName)方法。beanName可能是simpleController,或者simpleService,simpleDao,顺序没关系(因为后面会有依赖关系的处理)。我们假设simpleController吧
2)getBean方法首先会调用Bean工厂中定义的getSingleton(beanName)方法,来判断是否存在该名字的bean单例,如果存在则返回,方法调用结束(spring默认是单例,这样可以提高效率)
3) 否则,Spring会检查是否存在父工厂,如果有则返回,方法调用结束
4) 否则,Spring会检查bean定义(BeanDefinition实例,用来描述Bean结果,component-scan扫描后,就是将beanDefinition实例放入Bean工厂,此时还没有被实例化)是否有依赖关系,如果有,执行1)步,获取依赖的bean实例
5) 否则,Spring会尝试创建这个bean实例,创建实例前,Spring会检查调用的构造器,并实例化该Bean,(通过Constructor.newInstance(args)进行实例化)
6) 实例化完成后,Spring会调用Bean工厂的populateBean方法来填充bean实例的属性,也就是自动装配。populateBean方法便是调用了BeanPostProcessor实例来完成属性元素的自动装配工作
7)在元素装配过程中,Spring会检查被装配的属性是否存在自动装配的其他属性,然后递归调用getBean方法,知道所有@Autowired的元素都被装配完成。如在装配simpleController中的simpleService属性时,发现SimpleServiceImpl实例中存在@Autowired属性simpleDao,然后调用getBean(simpleDao)方法,同样会执行1)----7)整个过程。所有可以看成一个递归过程。
8)装配完成后,Bean工厂会将所有的bean实例都添加到工厂中来。
Bean的实例化
1. 进入SpringApplication类中refreshContext()方法
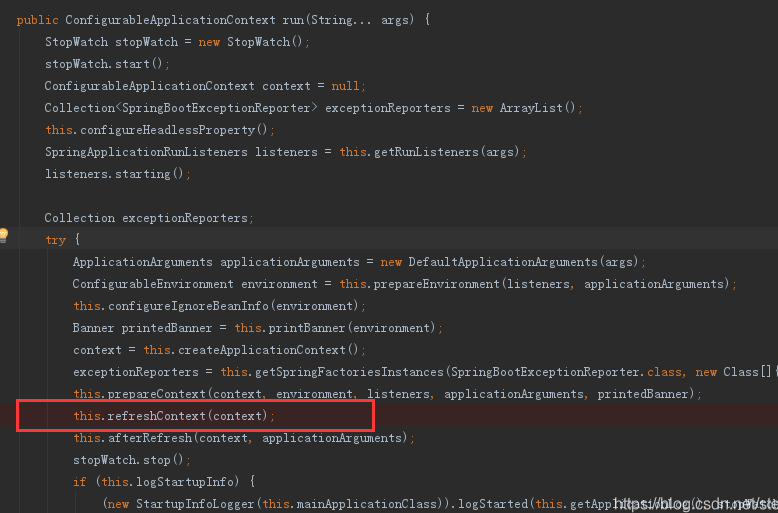
2. 进入AbstractApplicationContext类中refresh()方法,找到this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization()方法,这个方法就是完成beanFactory的实例化
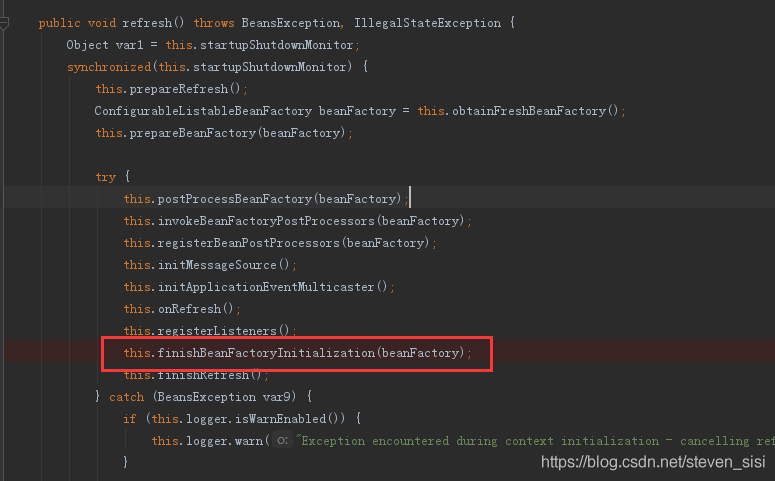
3. 进入AbstractApplicationContext类中finishBeanFactoryInitialization()方法,找到preInstantiateSingletons()
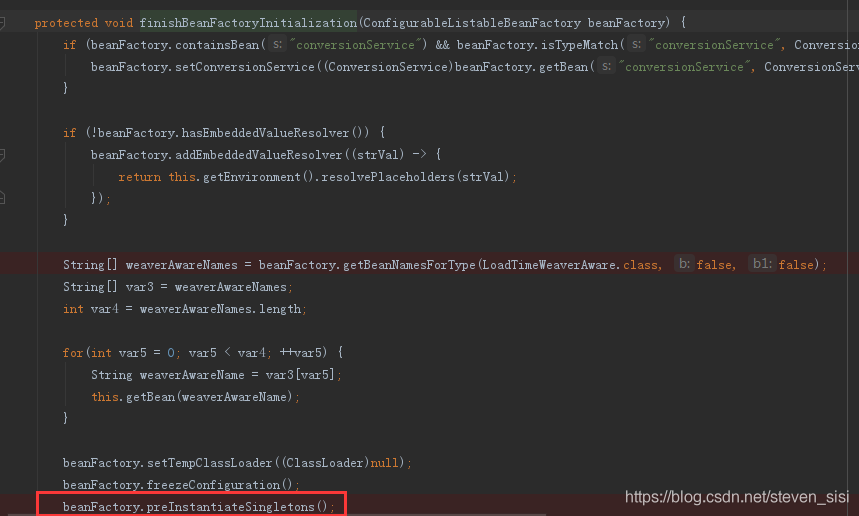
4. 进入DefaultListableBeanFactory类中preInstantiateSingletons()方法,找到getBean()方法

5. 进入AbstractBeanFactory类中getBean()方法,找到doGetBean()方法

6. 在AbstractBeanFactory类中doGetBean方法中,找到createBean()方法

7. 进入AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类中createBean方法中,找到doCreateBean()方法
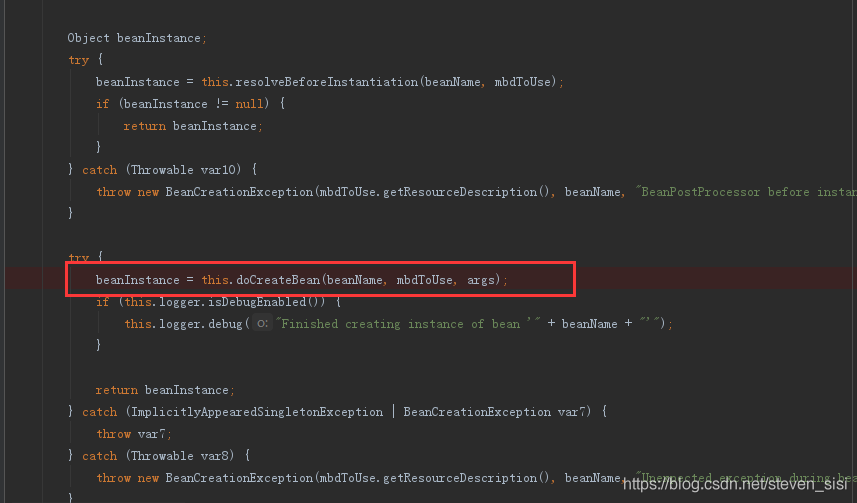
8. 在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类中doCreateBean()方法中,找到createBeanInstance()方法,看名字就知道是实例化bean的
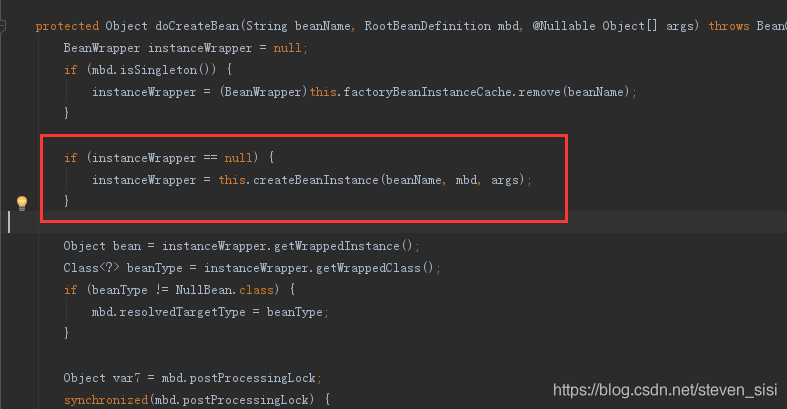
9. 在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类createBeanInstance()方法中,找到instantiateBean()方法

10. 在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类instantiateBean()方法中,找到instantiate()方法

11. 在SimpleInstantiationStrategy类instantiate()方法中,找到instantiateClass()方法

12. 在BeanUtils类instantiateClass()方法中,可知bean的实例化是通过Constructor.newInstance()进行实例化

Bean的属性注入
1. 在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类doCreateBean()方法中,找到populateBean()方法,从名字可知是用来填充bean的

2. 在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类中populateBean()方法,找到postProcessPropertyValues()方法

3. 进入AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类中postProcessPropertyValues()方法中,找到findAutowiringMetadata()方法,在这个方法中,如果属性中含有@Autowired注解则会递归getBean()。没有然后进入inject()方法中

4. 进入AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类inject方法中,找到resolveDependency()方法,通过这个方法获取对应字段的值

5. 进入AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类inject方法中,找到field.set(bean, value)方法,通过反射将值设置到属性中

以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

