python目标检测非极大抑制NMS与Soft-NMS
目录
睿智的目标检测31——非极大抑制NMS与Soft-NMS 注意事项学习前言什么是非极大抑制NMS1、非极大抑制NMS的实现过程2、柔性非极大抑制Soft-NMS的实现过程
注意事项
Soft-NMS对于大多数数据集而言,作用比较小,提升效果非常不明显,它起作用的地方是大量密集的同类重叠场景,大量密集的不同类重叠场景其实也没什么作用,同学们可以借助Soft-NMS理解非极大抑制的含义,但是实现的必要性确实不强,在提升网络性能上,不建议死磕Soft-NMS。
已对该博文中的代码进行了重置,视频中实现的代码是numpy形式,而且库比较久远。这里改成pytorch的形式,且适应当前的库。
学习前言
非极大抑制是目标检测中非常非常非常非常非常重要的一部分,了解一下原理,撕一下代码是必要的!
什么是非极大抑制NMS
非极大抑制的概念只需要看这两幅图就知道了:
下图是经过非极大抑制的。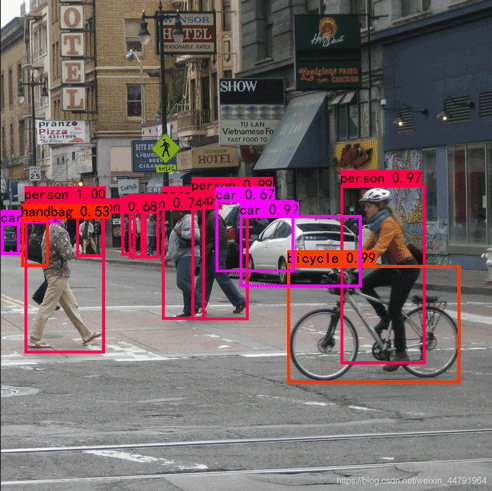
下图是未经过非极大抑制的。
可以很明显的看出来,未经过非极大抑制的图片有许多重复的框,这些框都指向了同一个物体!
可以用一句话概括非极大抑制的功能就是:
筛选出一定区域内属于同一种类得分最大的框。
1、非极大抑制NMS的实现过程
本博文实现的是多分类的非极大抑制,该非极大抑制使用在我的pytorch-yolov3例子中:
输入shape为[ batch_size, all_anchors, 5+num_classes ]
第一个维度是图片的数量。
第二个维度是所有的预测框。
第三个维度是所有的预测框的预测结果。
非极大抑制的执行过程如下所示:
1、对所有图片进行循环。
2、找出该图片中得分大于门限函数的框。在进行重合框筛选前就进行得分的筛选可以大幅度减少框的数量。
3、判断第2步中获得的框的种类与得分。取出预测结果中框的位置与之进行堆叠。此时最后一维度里面的内容由5+num_classes变成了4+1+2,四个参数代表框的位置,一个参数代表预测框是否包含物体,两个参数分别代表种类的置信度与种类。
4、对种类进行循环,非极大抑制的作用是筛选出一定区域内属于同一种类得分最大的框,对种类进行循环可以帮助我们对每一个类分别进行非极大抑制。
5、根据得分对该种类进行从大到小排序。
6、每次取出得分最大的框,计算其与其它所有预测框的重合程度,重合程度过大的则剔除。
视频中实现的代码是numpy形式,而且库比较久远。这里改成pytorch的形式,且适应当前的库。
实现代码如下:
def bbox_iou(self, box1, box2, x1y1x2y2=True): """ 计算IOU """ if not x1y1x2y2: b1_x1, b1_x2 = box1[:, 0] - box1[:, 2] / 2, box1[:, 0] + box1[:, 2] / 2 b1_y1, b1_y2 = box1[:, 1] - box1[:, 3] / 2, box1[:, 1] + box1[:, 3] / 2 b2_x1, b2_x2 = box2[:, 0] - box2[:, 2] / 2, box2[:, 0] + box2[:, 2] / 2 b2_y1, b2_y2 = box2[:, 1] - box2[:, 3] / 2, box2[:, 1] + box2[:, 3] / 2 else: b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[:, 0], box1[:, 1], box1[:, 2], box1[:, 3] b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[:, 0], box2[:, 1], box2[:, 2], box2[:, 3] inter_rect_x1 = torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1) inter_rect_y1 = torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1) inter_rect_x2 = torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2) inter_rect_y2 = torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2) inter_area = torch.clamp(inter_rect_x2 - inter_rect_x1, min=0) * \ torch.clamp(inter_rect_y2 - inter_rect_y1, min=0) b1_area = (b1_x2 - b1_x1) * (b1_y2 - b1_y1) b2_area = (b2_x2 - b2_x1) * (b2_y2 - b2_y1) iou = inter_area / torch.clamp(b1_area + b2_area - inter_area, min = 1e-6) return ioudef non_max_suppression(self, prediction, num_classes, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image, conf_thres=0.5, nms_thres=0.4): #----------------------------------------------------------# # 将预测结果的格式转换成左上角右下角的格式。 # prediction [batch_size, num_anchors, 85] #----------------------------------------------------------# box_corner = prediction.new(prediction.shape) box_corner[:, :, 0] = prediction[:, :, 0] - prediction[:, :, 2] / 2 box_corner[:, :, 1] = prediction[:, :, 1] - prediction[:, :, 3] / 2 box_corner[:, :, 2] = prediction[:, :, 0] + prediction[:, :, 2] / 2 box_corner[:, :, 3] = prediction[:, :, 1] + prediction[:, :, 3] / 2 prediction[:, :, :4] = box_corner[:, :, :4] output = [None for _ in range(len(prediction))] for i, image_pred in enumerate(prediction): #----------------------------------------------------------# # 对种类预测部分取max。 # class_conf [num_anchors, 1] 种类置信度 # class_pred [num_anchors, 1] 种类 #----------------------------------------------------------# class_conf, class_pred = torch.max(image_pred[:, 5:5 + num_classes], 1, keepdim=True) #----------------------------------------------------------# # 利用置信度进行第一轮筛选 #----------------------------------------------------------# conf_mask = (image_pred[:, 4] * class_conf[:, 0] >= conf_thres).squeeze() #----------------------------------------------------------# # 根据置信度进行预测结果的筛选 #----------------------------------------------------------# image_pred = image_pred[conf_mask] class_conf = class_conf[conf_mask] class_pred = class_pred[conf_mask] if not image_pred.size(0): continue #-------------------------------------------------------------------------# # detections [num_anchors, 7] # 7的内容为:x1, y1, x2, y2, obj_conf, class_conf, class_pred #-------------------------------------------------------------------------# detections = torch.cat((image_pred[:, :5], class_conf.float(), class_pred.float()), 1) #------------------------------------------# # 获得预测结果中包含的所有种类 #------------------------------------------# unique_labels = detections[:, -1].cpu().unique() if prediction.is_cuda: unique_labels = unique_labels.cuda() detections = detections.cuda() for c in unique_labels: #------------------------------------------# # 获得某一类得分筛选后全部的预测结果 #------------------------------------------# detections_class = detections[detections[:, -1] == c] # #------------------------------------------# # # 使用官方自带的非极大抑制会速度更快一些! # #------------------------------------------# # keep = nms( # detections_class[:, :4], # detections_class[:, 4] * detections_class[:, 5], # nms_thres # ) # max_detections = detections_class[keep] # 按照存在物体的置信度排序 _, conf_sort_index = torch.sort(detections_class[:, 4]*detections_class[:, 5], descending=True) detections_class = detections_class[conf_sort_index] # 进行非极大抑制 max_detections = [] while detections_class.size(0): # 取出这一类置信度最高的,一步一步往下判断,判断重合程度是否大于nms_thres,如果是则去除掉 max_detections.append(detections_class[0].unsqueeze(0)) if len(detections_class) == 1: break ious = self.bbox_iou(max_detections[-1], detections_class[1:]) detections_class = detections_class[1:][ious < nms_thres] # 堆叠 max_detections = torch.cat(max_detections).data # Add max detections to outputs output[i] = max_detections if output[i] is None else torch.cat((output[i], max_detections)) if output[i] is not None: output[i] = output[i].cpu().numpy() box_xy, box_wh = (output[i][:, 0:2] + output[i][:, 2:4])/2, output[i][:, 2:4] - output[i][:, 0:2] output[i][:, :4] = self.yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image) return output2、柔性非极大抑制Soft-NMS的实现过程
柔性非极大抑制和普通的非极大抑制相差不大,只差了几行代码。
柔性非极大抑制认为不应该直接只通过重合程度进行筛选,如图所示,很明显图片中存在两匹马,但是此时两匹马的重合程度较高,此时我们如果使用普通nms,后面那匹得分比较低的马会直接被剔除。
Soft-NMS认为在进行非极大抑制的时候要同时考虑得分和重合程度。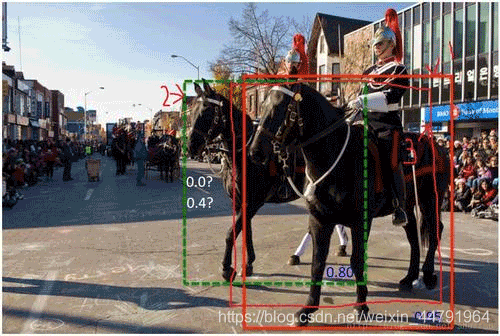
我们直接看NMS和Soft-NMS的代码差别:
视频中实现的代码是numpy形式,而且库比较久远。这里改成pytorch的形式,且适应当前的库。
如下为NMS:
while detections_class.size(0): # 取出这一类置信度最高的,一步一步往下判断,判断重合程度是否大于nms_thres,如果是则去除掉 max_detections.append(detections_class[0].unsqueeze(0)) if len(detections_class) == 1: break ious = self.bbox_iou(max_detections[-1], detections_class[1:]) detections_class = detections_class[1:][ious < nms_thres]如下为Soft-NMS:
while detections_class.size(0): # 取出这一类置信度最高的,一步一步往下判断,判断重合程度是否大于nms_thres,如果是则去除掉 max_detections.append(detections_class[0].unsqueeze(0)) if len(detections_class) == 1: break ious = self.bbox_iou(max_detections[-1], detections_class[1:]) detections_class[1:, 4] = torch.exp(-(ious * ious) / sigma) * detections_class[1:, 4] detections_class = detections_class[1:] detections_class = detections_class[detections_class[:, 4] >= conf_thres] arg_sort = torch.argsort(detections_class[:, 4], descending = True) detections_class = detections_class[arg_sort]我们可以看到,对于NMS而言,其直接将 与得分最大的框 重合程度较高的其它预测剔除。而Soft-NMS则以一个权重的形式,将获得的IOU取高斯指数后乘上原得分,之后重新排序。继续循环。
视频中实现的代码是numpy形式,而且库比较久远。这里改成pytorch的形式,且适应当前的库。
实现代码如下:
def bbox_iou(self, box1, box2, x1y1x2y2=True): """ 计算IOU """ if not x1y1x2y2: b1_x1, b1_x2 = box1[:, 0] - box1[:, 2] / 2, box1[:, 0] + box1[:, 2] / 2 b1_y1, b1_y2 = box1[:, 1] - box1[:, 3] / 2, box1[:, 1] + box1[:, 3] / 2 b2_x1, b2_x2 = box2[:, 0] - box2[:, 2] / 2, box2[:, 0] + box2[:, 2] / 2 b2_y1, b2_y2 = box2[:, 1] - box2[:, 3] / 2, box2[:, 1] + box2[:, 3] / 2 else: b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[:, 0], box1[:, 1], box1[:, 2], box1[:, 3] b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[:, 0], box2[:, 1], box2[:, 2], box2[:, 3] inter_rect_x1 = torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1) inter_rect_y1 = torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1) inter_rect_x2 = torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2) inter_rect_y2 = torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2) inter_area = torch.clamp(inter_rect_x2 - inter_rect_x1, min=0) * \ torch.clamp(inter_rect_y2 - inter_rect_y1, min=0) b1_area = (b1_x2 - b1_x1) * (b1_y2 - b1_y1) b2_area = (b2_x2 - b2_x1) * (b2_y2 - b2_y1) iou = inter_area / torch.clamp(b1_area + b2_area - inter_area, min = 1e-6) return ioudef non_max_suppression(self, prediction, num_classes, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image, conf_thres=0.5, nms_thres=0.4, sigma=0.5): #----------------------------------------------------------# # 将预测结果的格式转换成左上角右下角的格式。 # prediction [batch_size, num_anchors, 85] #----------------------------------------------------------# box_corner = prediction.new(prediction.shape) box_corner[:, :, 0] = prediction[:, :, 0] - prediction[:, :, 2] / 2 box_corner[:, :, 1] = prediction[:, :, 1] - prediction[:, :, 3] / 2 box_corner[:, :, 2] = prediction[:, :, 0] + prediction[:, :, 2] / 2 box_corner[:, :, 3] = prediction[:, :, 1] + prediction[:, :, 3] / 2 prediction[:, :, :4] = box_corner[:, :, :4] output = [None for _ in range(len(prediction))] for i, image_pred in enumerate(prediction): #----------------------------------------------------------# # 对种类预测部分取max。 # class_conf [num_anchors, 1] 种类置信度 # class_pred [num_anchors, 1] 种类 #----------------------------------------------------------# class_conf, class_pred = torch.max(image_pred[:, 5:5 + num_classes], 1, keepdim=True) #----------------------------------------------------------# # 利用置信度进行第一轮筛选 #----------------------------------------------------------# conf_mask = (image_pred[:, 4] * class_conf[:, 0] >= conf_thres).squeeze() #----------------------------------------------------------# # 根据置信度进行预测结果的筛选 #----------------------------------------------------------# image_pred = image_pred[conf_mask] class_conf = class_conf[conf_mask] class_pred = class_pred[conf_mask] if not image_pred.size(0): continue #-------------------------------------------------------------------------# # detections [num_anchors, 7] # 7的内容为:x1, y1, x2, y2, obj_conf, class_conf, class_pred #-------------------------------------------------------------------------# detections = torch.cat((image_pred[:, :5], class_conf.float(), class_pred.float()), 1) #------------------------------------------# # 获得预测结果中包含的所有种类 #------------------------------------------# unique_labels = detections[:, -1].cpu().unique() if prediction.is_cuda: unique_labels = unique_labels.cuda() detections = detections.cuda() for c in unique_labels: #------------------------------------------# # 获得某一类得分筛选后全部的预测结果 #------------------------------------------# detections_class = detections[detections[:, -1] == c] # #------------------------------------------# # # 使用官方自带的非极大抑制会速度更快一些! # #------------------------------------------# # keep = nms( # detections_class[:, :4], # detections_class[:, 4] * detections_class[:, 5], # nms_thres # ) # max_detections = detections_class[keep] # 按照存在物体的置信度排序 _, conf_sort_index = torch.sort(detections_class[:, 4]*detections_class[:, 5], descending=True) detections_class = detections_class[conf_sort_index] # 进行非极大抑制 max_detections = [] while detections_class.size(0): # 取出这一类置信度最高的,一步一步往下判断,判断重合程度是否大于nms_thres,如果是则去除掉 max_detections.append(detections_class[0].unsqueeze(0)) if len(detections_class) == 1: break ious = self.bbox_iou(max_detections[-1], detections_class[1:]) detections_class[1:, 4] = torch.exp(-(ious * ious) / sigma) * detections_class[1:, 4] detections_class = detections_class[1:] detections_class = detections_class[detections_class[:, 4] >= conf_thres] arg_sort = torch.argsort(detections_class[:, 4], descending = True) detections_class = detections_class[arg_sort] # 堆叠 max_detections = torch.cat(max_detections).data # Add max detections to outputs output[i] = max_detections if output[i] is None else torch.cat((output[i], max_detections)) if output[i] is not None: output[i] = output[i].cpu().numpy() box_xy, box_wh = (output[i][:, 0:2] + output[i][:, 2:4])/2, output[i][:, 2:4] - output[i][:, 0:2] output[i][:, :4] = self.yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image) return output以上就是python目标检测非极大抑制NMS与Soft-NMS的详细内容,更多关于非极大抑制NMS Soft-NMS的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!

