C#特性(Attribute)
一、什么是特性
特性(Attribute)是用于在运行时传递程序中各种元素(比如类、方法、结构、枚举、组件等)的行为信息的声明性标签。您可以通过使用特性向程序添加声明性信息。一个声明性标签是通过放置在它所应用的元素前面的方括号([ ])来描述的。
特性(Attribute)用于添加元数据,如编译器指令和注释、描述、方法、类等其他信息。.Net 框架提供了两种类型的特性:预定义特性和自定义特性。
特性的语法如下:
[attribute(positional_parameters, name_parameter = value, ...)] element
特性(Attribute)的名称和值是在方括号内规定的,放置在它所应用的元素之前。positional_parameters 规定必需的信息,name_parameter 规定可选的信息。
二、预定义特性
Obsolete特性
这个预定义特性标记了不应被使用的程序实体。它可以让您通知编译器丢弃某个特定的目标元素。例如,当一个新方法被用在一个类中,但是您仍然想要保持类中的旧方法,您可以通过显示一个应该使用新方法,而不是旧方法的消息,来把它标记为 obsolete(过时的)。
语法如下:
[Obsolete( message )] [Obsolete( message, iserror )]
其中:
- 参数 message,是一个字符串,描述项目为什么过时的原因以及该替代使用什么。
- 参数 iserror,是一个布尔值。如果该值为 true,编译器应把该项目的使用当作一个错误。默认值是 false(编译器生成一个警告)。
请看下面的一个小例子:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute
{
[Obsolete("请不要使用该类了,该类已经过时了,请使用什么代替")]
public class Student
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Accont { get; set; }
public long QQ { get; set; }
public string Answer([Custom]string name)
{
return $"This is {name}";
}
}
}
上面的例子中,在Student类上面使用了Obsolete特性来标注该类已经过时了。编译代码结果:
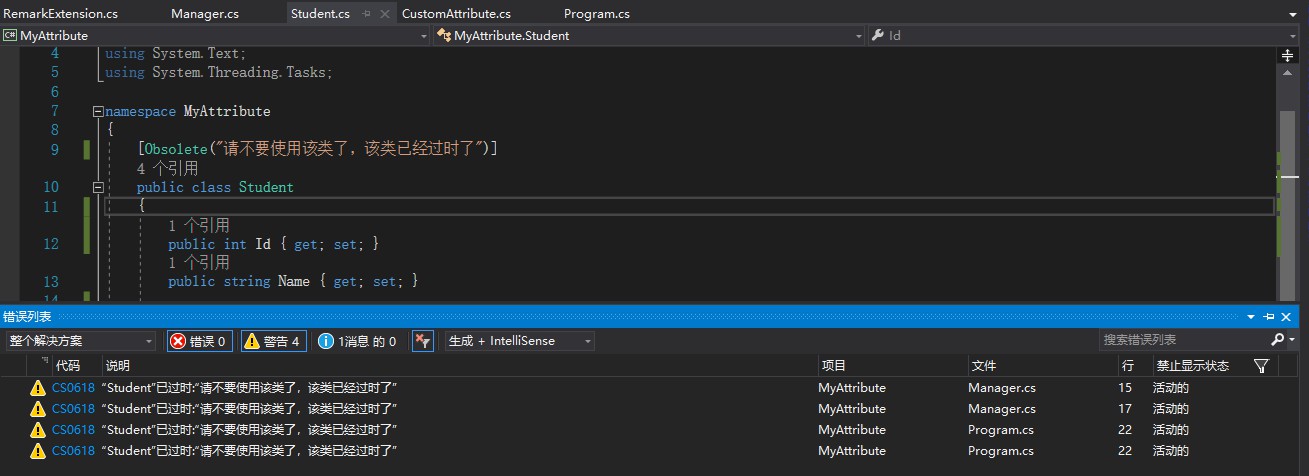
三、自定义特性
.Net 框架允许创建自定义特性,用于存储声明性的信息,且可在运行时被检索。该信息根据设计标准和应用程序需要,可与任何目标元素相关。
创建并使用自定义特性包含四个步骤:
- 声明自定义特性
- 构建自定义特性
- 在目标程序元素上应用自定义特性
- 通过反射访问特性
1、声明自定义特性
在上面的例子中,使用F12查看Obsolete的定义:
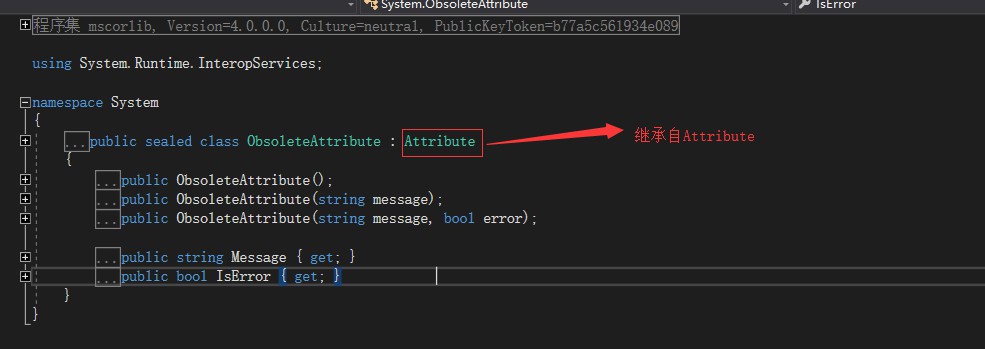
从上面的截图中可以看出,.NET框架中的预定义特性是继承自Attribute类,所以要自定义一个特性,只需要该类继承自Attribute即可,下面定义一个Custom自定义特性:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute
{
/// <summary>
/// 自定义Custom特性
/// </summary>
public class CustomAttribute :Attribute
{
}
}
注意:所有的特性默认以Attribute结尾,但声明的时候可以不以Attribute结尾。
2、构建自定义特性
每个特性必须至少有一个构造函数。必需的定位( positional)参数应通过构造函数传递。下面的代码演示了CustomAttribute类:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute
{
/// <summary>
/// 自定义Custom特性
/// </summary>
public class CustomAttribute :Attribute
{
/// <summary>
/// 无参构造函数
/// </summary>
public CustomAttribute()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// 有参构造函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="id"></param>
public CustomAttribute(string description)
{
this.Description = description;
}
/// <summary>
/// 属性
/// </summary>
public string Description { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 字段
/// </summary>
public string Remark = null;
public void Show()
{
Console.WriteLine("This Is CustomAttribute");
}
}
}
3、在目标程序元素上应用自定义特性
通过把特性放置在紧接着它的目标(类、方法、属性、字段等)上面,来应用该特性:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute
{
[Obsolete("请不要使用该类了,该类已经过时了")]
[Custom("这是Custom自定义特性")]
public class Student
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Accont { get; set; }
public long QQ { get; set; }
public string Answer([Custom]string name)
{
return $"This is {name}";
}
}
}
注意:
1、如果在声明自定义特性的时候使用了Attribute结尾,那么应用自定义特性的时候可以把Attribute省略掉;如果声明的时候没有以Attribute结尾,那么应用自定义特性的时候就不能把Attribute省略掉。
2、默认情况下相同的特性只能应用一次,如果想应用多次特性,那么需要给特性添加AttributeUsage特性,CustomAttribute特性修改如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute
{
/// <summary>
/// 自定义Custom特性
/// </summary>
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.All,AllowMultiple =true,Inherited =true)]
public class CustomAttribute :Attribute
{
/// <summary>
/// 无参构造函数
/// </summary>
public CustomAttribute()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// 有参构造函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="id"></param>
public CustomAttribute(string description)
{
this.Description = description;
}
/// <summary>
/// 属性
/// </summary>
public string Description { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 字段
/// </summary>
public string Remark = null;
public void Show()
{
Console.WriteLine("This Is CustomAttribute");
}
}
}
其中,AttributeTargets是枚举值,F12转到定义可以查看AttributeTargets的所有枚举值:
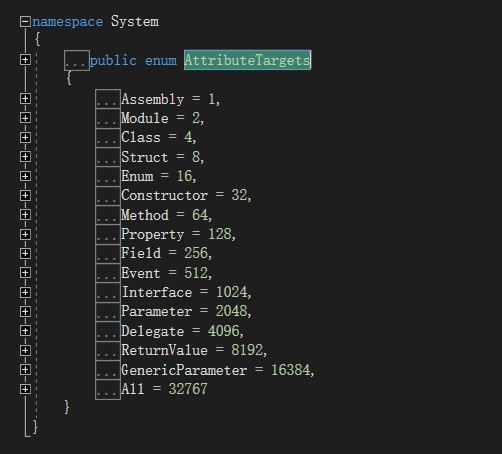
AttributeTargets的枚举值表示Custom特性可以应用在哪些目标上面。例如:AttributeTargets的枚举值是Class,则表示CustomAttribute只能应用在类上面。这里枚举值是All,表示可以在任何类型上面使用该特性。默认情况下枚举值是All。
AllowMultiple表示该特性是否可以在类型上面多次使用:

这里AllowMultiple的值为true,表示可以在类型上面多次使用该特性。如果为false,则表示只能使用一次。默认情况下是false。
Inherited表示该特性是否可以由子类继承:
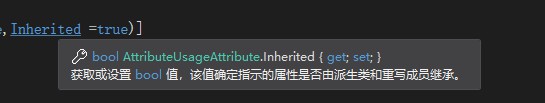
默认情况下Inherited为true。
这是在看Student类:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute
{
[Obsolete("请不要使用该类了,该类已经过时了")]
[Custom("这是Custom自定义特性")]//使用有参构造
[Custom()]//使用无参构造
public class Student
{
public int Id { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 在属性上面使用Custom特性
/// </summary>
[Custom("这是Name属性")]
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Accont { get; set; }
public long QQ { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 在方法和参数上面使用Custom特性
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[Custom("这是Answer方法")]
public string Answer([Custom("这是方法参数")]string name)
{
return $"This is {name}";
}
}
}
注意:如果一个类型上面多次使用了同一种特性,那么特性可以写在一起,中间用逗号隔开,例如上面的定义和下面的是同样的效果:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute
{
[Obsolete("请不要使用该类了,该类已经过时了")]
[Custom("这是Custom自定义特性"),Custom,Custom(),Custom(Remark ="备注")]
public class Student
{
public int Id { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 在属性上面使用Custom特性
/// </summary>
[Custom("这是Name属性")]
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Accont { get; set; }
public long QQ { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 在方法、方法参数、方法的返回值上面使用Custom特性
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[Custom("这是Answer方法")]//方法上面应用特性
[return:Custom()] //方法的返回值应用特性
public string Answer([Custom("这是方法参数")]string name)
{
return $"This is {name}";
}
}
}
注意:在Web API中FromBaby和FromUri就是给方法的参数应用特性。
4、通过反射访问特性
定义一个Manager类来管理特性:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute
{
/// <summary>
/// 管理特性
/// </summary>
public class Manager
{
public static void Show(Student student)
{
// 获取类型
Type type = typeof(Student); //或者使用student.GetType();
// 找到类型上面的特性 type.IsDefined表示找类型上面的特性
if (type.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))//检查有没有 性能高
{
//GetCustomAttribute 获取特性 type.GetCustomAttribute表示找到类型上面定义的特性,表示调用构造函数创建一个CustomAttribute类型的对象
CustomAttribute attribute = (CustomAttribute)type.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(CustomAttribute), true);
// attribute.Description表示特性类里面的属性 attribute.Remark表示特性类里面的字段
Console.WriteLine($"{attribute.Description}_{attribute.Remark}");
attribute.Show();
}
#region 获取ID属性上面定义的特性
// 获取Id属性
PropertyInfo property = type.GetProperty("Id");
//检查Id属性上面是否定义了CustomAttribute特性
if (property.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))
{
CustomAttribute attribute = (CustomAttribute)property.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(CustomAttribute), true);
Console.WriteLine($"{attribute.Description}_{attribute.Remark}");
attribute.Show();
}
#endregion
#region 获取Answer()方法上面定义的特性
// 获取Answer方法
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Answer");
if (method.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))
{
CustomAttribute attribute = (CustomAttribute)method.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(CustomAttribute), true);
Console.WriteLine($"{attribute.Description}_{attribute.Remark}");
attribute.Show();
}
#endregion
#region 获取参数定义的特性
ParameterInfo parameter = method.GetParameters()[0];
if (parameter.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))
{
CustomAttribute attribute = (CustomAttribute)parameter.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(CustomAttribute), true);
Console.WriteLine($"{attribute.Description}_{attribute.Remark}");
attribute.Show();
}
#endregion
#region 获取返回值定义的特性
ParameterInfo returnParameter = method.ReturnParameter;
if (returnParameter.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))
{
CustomAttribute attribute = (CustomAttribute)returnParameter.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(CustomAttribute), true);
Console.WriteLine($"{attribute.Description}_{attribute.Remark}");
attribute.Show();
}
#endregion
string result = student.Answer("Tom");
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
}
}
Main()方法里面调用:
using MyAttribute.Extension;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student();
student.Id = 123;
student.Name = "time";
// 使用Manager类管理Student
Manager.Show(student);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
结果:

四、应用特性
场景一:用户状态的枚举值,定义的是英文的字段,需要输出中文含义。枚举定义如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute.Extension
{
/// <summary>
/// 枚举类型 用户状态
/// </summary>
public enum UserState
{
/// <summary>
/// 正常
/// </summary>
Normal = 0,
/// <summary>
/// 冻结
/// </summary>
Frozen = 1,
/// <summary>
/// 删除
/// </summary>
Deleted = 2
}
}
普通做法:根据枚举值进行判断,然后输出中文含义:
UserState userState = UserState.Normal;
switch(userState)
{
case UserState.Normal:
Console.WriteLine("正常");
break;
case UserState.Frozen:
Console.WriteLine("冻结");
break;
case UserState.Deleted:
Console.WriteLine("删除");
break;
}
这种写法违反开不原则,不利于以后的扩展,下面使用特性实现。
先定义Remark特性:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Reflection;
namespace MyAttribute.Extension
{
/// <summary>
/// RemarkAttribute 特性
/// </summary>
public class RemarkAttribute :Attribute
{
private string _Remark = null;
/// <summary>
/// 有参构造
/// </summary>
/// <param name="remark"></param>
public RemarkAttribute(string remark)
{
this._Remark = remark;
}
public string GetRemark()
{
return _Remark;
}
}
}
UserState枚举修改如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute.Extension
{
/// <summary>
/// 枚举类型 用户状态
/// </summary>
public enum UserState
{
/// <summary>
/// 正常
/// </summary>
[Remark("正常")]
Normal = 0,
/// <summary>
/// 冻结
/// </summary>
[Remark("冻结")]
Frozen = 1,
/// <summary>
/// 删除
/// </summary>
[Remark("删除")]
Deleted = 2
}
}
对Enum类型进行扩展:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute.Extension
{
public static class EnumExtension
{
/// <summary>
/// Enum的扩展方法,静态类、静态方法 第一个参数前面添加this关键字
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static string GetRemark(this Enum value)
{
// 获取类型
Type type = value.GetType();
// 获取字段
FieldInfo field = type.GetField(value.ToString());
// 判断字段上面是否定义了RemarkAttribute特性
if (field.IsDefined(typeof(RemarkAttribute)))
{
// 创建实例
RemarkAttribute attribute = (RemarkAttribute)field.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(RemarkAttribute));
// 返回RemarkAttribute特性里面的GetRemark()方法
return attribute.GetRemark();
}
else
{
return value.ToString();
}
}
}
}
Main()方法里面调用:
using MyAttribute.Extension;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student student = new Student();
student.Id = 123;
student.Name = "time";
// 使用Manager类管理Student
//Manager.Show(student);
UserState userState = UserState.Normal;
//switch(userState)
//{
// case UserState.Normal:
// Console.WriteLine("正常");
// break;
// case UserState.Frozen:
// Console.WriteLine("冻结");
// break;
// case UserState.Deleted:
// Console.WriteLine("删除");
// break;
//}
Console.WriteLine(userState.GetRemark());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
结果:

场景二、做数据校验
Student中有QQ这个属性,范围是10000-999999999999,校验QQ属性的值在这个范围区间内。
1、定义一个RangeAttribute特性,用来验证属性范围
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute.Extension
{
/// <summary>
/// 定义LongAttribute特性,并且特性只能应用在字段和属性上面
/// </summary>
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Field|AttributeTargets.Property)]
public class RangeAttribute :Attribute
{
/// <summary>
/// 最小范围
/// </summary>
private long _MinRange = 0;
/// <summary>
/// 最大范围
/// </summary>
private long _MaxRange = 0;
public RangeAttribute(long min,long max)
{
this._MinRange = min;
this._MaxRange = max;
}
/// <summary>
/// 检查属性范围
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool Check(object value)
{
if(value!=null && !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(value.ToString()))
{
if(long.TryParse(value.ToString(),out long IResult))
{
if(IResult>this._MinRange && IResult<this._MaxRange)
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
}
2、在Student类的QQ属性上面应用特性
[Range(10001,999999999999)]
public long QQ { get; set; }
3、对Object类型进行扩展
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute.Extension
{
/// <summary>
/// object类型的验证扩展
/// </summary>
public static class ObjectExtension
{
/// <summary>
/// 对object类型扩展一个Validate的方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="obj"></param>
/// <param name="msg">输出参数,输出验证信息。如果验证通过,输出空字符串;如果验证不通过,输出具体信息</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static bool Validate(this object obj,out string msg)
{
// 获取类型
Type type = obj.GetType();
// 获取属性
PropertyInfo[] propertyInfos= type.GetProperties();
foreach(PropertyInfo prop in propertyInfos)
{
if(prop.IsDefined(typeof(LongAttribute)))
{
LongAttribute attribute = (LongAttribute)prop.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(LongAttribute));
if(!attribute.Check(prop.GetValue(obj)))
{
msg = prop.Name + "检查失败";
return false;
}
}
}
msg = "";
return true;
}
}
}
4、在Manager类里面使用Validate扩展方法
// 验证
string msg = string.Empty;
bool tfResult= student.Validate(out msg);
if(!tfResult)
{
Console.WriteLine(msg);
}
5、在Main()方法里面调用
Student student = new Student(); student.Id = 123; student.Name = "time"; student.QQ = 9999; // 使用Manager类管理Student Manager.Show(student);
结果:

如果这时候Student里面增加了Name属性,并且要验证Name属性的长度,这时需要增加一个验证属性长度的特性:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute.Extension
{
/// <summary>
/// 验证长度的特性,只能应用于字段和属性上面
/// </summary>
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Field|AttributeTargets.Property)]
public class LengthAttribute:Attribute
{
/// <summary>
/// 最小长度
/// </summary>
private int _MinLength = 0;
/// <summary>
/// 最大长度
/// </summary>
private int _MaxLength = 0;
public LengthAttribute(int min, int max)
{
this._MinLength = min;
this._MaxLength = max;
}
/// <summary>
/// 检查属性长度
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool Check(object value)
{
if (value != null && !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(value.ToString()))
{
if (long.TryParse(value.ToString(), out long IResult))
{
if (IResult > this._MinLength && IResult < this._MaxLength)
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
}
在Student类的Name属性上面应用LengthAttribute特性:
[Length(5,10)]
public string Name { get; set; }
在ObjectExtension里面增加长度的验证:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute.Extension
{
/// <summary>
/// object类型的验证扩展
/// </summary>
public static class ObjectExtension
{
/// <summary>
/// 对object类型扩展一个Validate的方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="obj"></param>
/// <param name="msg">输出参数,输出验证信息。如果验证通过,输出空字符串;如果验证不通过,输出具体信息</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static bool Validate(this object obj,out string msg)
{
// 获取类型
Type type = obj.GetType();
// 获取属性
PropertyInfo[] propertyInfos= type.GetProperties();
foreach(PropertyInfo prop in propertyInfos)
{
// 检查属性上面是否定义了RangeAttribute特性
if (prop.IsDefined(typeof(RangeAttribute)))
{
RangeAttribute attribute = (RangeAttribute)prop.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(RangeAttribute));
if(!attribute.Check(prop.GetValue(obj)))
{
msg = string.Format($"属性{ prop.Name}范围检查失败");
return false;
}
}
// 检查属性上面是否定义了LengthAttribute特性
if (prop.IsDefined(typeof(LengthAttribute)))
{
LengthAttribute attribute = (LengthAttribute)prop.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(LengthAttribute));
if (!attribute.Check(prop.GetValue(obj)))
{
msg = string.Format($"属性{ prop.Name}长度检查失败");
return false;
}
}
}
msg = "";
return true;
}
}
}
最后在Main()方法里面调用:
Student student = new Student(); student.Id = 123; student.Name = "time"; // 使用Manager类管理Student Manager.Show(student);
结果:

仔细查看ObjectExtension扩展类:每增加一个特性,扩展方法里面就要增加一段相同的代码(只是特性的类型不同),那么能不能做到增加特性,而这里不需要修改呢?请看下面的修改:
1、定义一个抽象类继承自Attribute,里面有一个抽象的Check()方法,定义如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute.Extension
{
/// <summary>
/// 抽象基类,继承自Attribute
/// </summary>
public abstract class AbstractValidateAttribute:Attribute
{
public abstract bool Check(object value);
}
}
2、修改RangeAttribute和LengthAttribute两个特性类,都继承自AbstractValidateAttribute基类
RangeAttribute类:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute.Extension
{
/// <summary>
/// 定义LongAttribute特性,并且特性只能应用在字段和属性上面
/// </summary>
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Field|AttributeTargets.Property)]
public class RangeAttribute : AbstractValidateAttribute
{
/// <summary>
/// 最小范围
/// </summary>
private long _MinRange = 0;
/// <summary>
/// 最大范围
/// </summary>
private long _MaxRange = 0;
public RangeAttribute(long min,long max)
{
this._MinRange = min;
this._MaxRange = max;
}
/// <summary>
/// 重写基类方法 检查属性范围
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public override bool Check(object value)
{
if(value!=null && !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(value.ToString()))
{
if(long.TryParse(value.ToString(),out long IResult))
{
if(IResult>this._MinRange && IResult<this._MaxRange)
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
}
LengthAttribute类:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute.Extension
{
/// <summary>
/// 验证长度的特性,只能应用于字段和属性上面
/// </summary>
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Field|AttributeTargets.Property)]
public class LengthAttribute: AbstractValidateAttribute
{
/// <summary>
/// 最小长度
/// </summary>
private int _MinLength = 0;
/// <summary>
/// 最大长度
/// </summary>
private int _MaxLength = 0;
public LengthAttribute(int min, int max)
{
this._MinLength = min;
this._MaxLength = max;
}
/// <summary>
/// 重写基类方法 检查属性长度
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public override bool Check(object value)
{
if (value != null && !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(value.ToString()))
{
if (long.TryParse(value.ToString(), out long IResult))
{
if (IResult > this._MinLength && IResult < this._MaxLength)
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
}
3、修改ObjectExtension扩展类
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyAttribute.Extension
{
/// <summary>
/// object类型的验证扩展
/// </summary>
public static class ObjectExtension
{
/// <summary>
/// 对object类型扩展一个Validate的方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="obj"></param>
/// <param name="msg">输出参数,输出验证信息。如果验证通过,输出空字符串;如果验证不通过,输出具体信息</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static bool Validate(this object obj,out string msg)
{
// 获取类型
Type type = obj.GetType();
// 获取属性
PropertyInfo[] propertyInfos= type.GetProperties();
foreach(PropertyInfo prop in propertyInfos)
{
// 判断属性上面是否定义了AbstractValidateAttribute特性
if (prop.IsDefined(typeof(AbstractValidateAttribute),true))
{
// 属性上面可能会定义多个特性,所以这里使用数组
object[] attributeArray = prop.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(AbstractValidateAttribute), true);
foreach(AbstractValidateAttribute attribute in attributeArray)
{
if (!attribute.Check(prop.GetValue(obj)))
{
msg = string.Format($"属性{ prop.Name}检查失败");
return false;
}
}
}
//// 检查属性上面是否定义了RangeAttribute特性
//if (prop.IsDefined(typeof(RangeAttribute)))
//{
// RangeAttribute attribute = (RangeAttribute)prop.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(RangeAttribute));
// if(!attribute.Check(prop.GetValue(obj)))
// {
// msg = string.Format($"属性{ prop.Name}范围检查失败");
// return false;
// }
//}
//// 检查属性上面是否定义了LengthAttribute特性
//if (prop.IsDefined(typeof(LengthAttribute)))
//{
// LengthAttribute attribute = (LengthAttribute)prop.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(LengthAttribute));
// if (!attribute.Check(prop.GetValue(obj)))
// {
// msg = string.Format($"属性{ prop.Name}长度检查失败");
// return false;
// }
//}
}
msg = "";
return true;
}
}
}
4、运行结果:

经过上面的修改以后,如果以后要新增一个特性,那么该特性只需要在本类中重写基类的Check()方法即可,而不需要在修改ObjectExtension扩展类。
到此这篇关于C#特性的文章就介绍到这了。希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。

