Spring5学习之基础知识总结
1.概述
1、Spring 是轻量级的开源的 JavaEE 框架
2、 Spring 可以解决企业应用开发的复杂性
3、Spring 有两个核心部分:IOC 和 Aop
IOC:控制反转,把创建对象过程交给 Spring 进行管理Aop:面向切面,不修改源代码进行功能增强
4、Spring 特点
方便解耦,简化开发Aop 编程支持方便程序测试方便和其他框架进行整合方便进行事务操作降低 API 开发难度
2.入门Demo
1.jar包引入
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>cn.zj.springDemo</groupId>
<artifactId>springDemo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<description>spring的入门demo</description>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>5.3.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>5.3.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
2.bean
package cn.zj.demo.bean;
public class User {
public void add() {
System.out.println("add....");
}
}
3.spring的xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--1 配置User对象创建-->
<bean id="user" class="cn.zj.demo.bean.User"></bean>
</beans>
4.测试代码
package cn.zj.demo.test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import cn.zj.demo.bean.User;
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void testAdd() {
// 1 加载 spring 配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
// 2 获取配置创建的对象
User user = context.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println(user);
user.add();
}
}
5.输出
cn.zj.demo.bean.User@24111ef1 add....
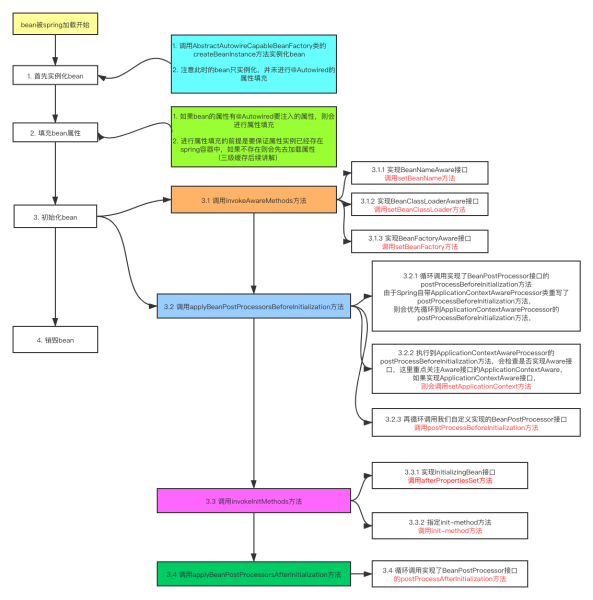
3.源码
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
//容器刷新前的准备,设置上下文状态,获取属性,验证必要的属性等
prepareRefresh();
//获取新的beanFactory,销毁原有beanFactory、为每个bean生成BeanDefinition等
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
//配置标准的beanFactory,设置ClassLoader,设置SpEL表达式解析器,添加忽略注入的接口,添加bean,添加bean后置处理器等
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 实例化并调用所有注册的beanFactory后置处理器(实现接口BeanFactoryPostProcessor的bean,在beanFactory标准初始化之后执行)。
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//实例化和注册beanFactory中扩展了BeanPostProcessor的bean。
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
//初始化国际化工具类MessageSource
initMessageSource();
//初始化事件广播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//模板方法,在容器刷新的时候可以自定义逻辑,不同的Spring容器做不同的事情。
onRefresh();
//注册监听器,广播early application events
registerListeners();
//实例化所有剩余的(非懒加载)单例
//实例化的过程各种BeanPostProcessor开始起作用。
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//refresh做完之后需要做的其他事情。
//清除上下文资源缓存(如扫描中的ASM元数据)
//初始化上下文的生命周期处理器,并刷新(找出Spring容器中实现了Lifecycle接口的bean并执行start()方法)。
//发布ContextRefreshedEvent事件告知对应的ApplicationListener进行响应的操作
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
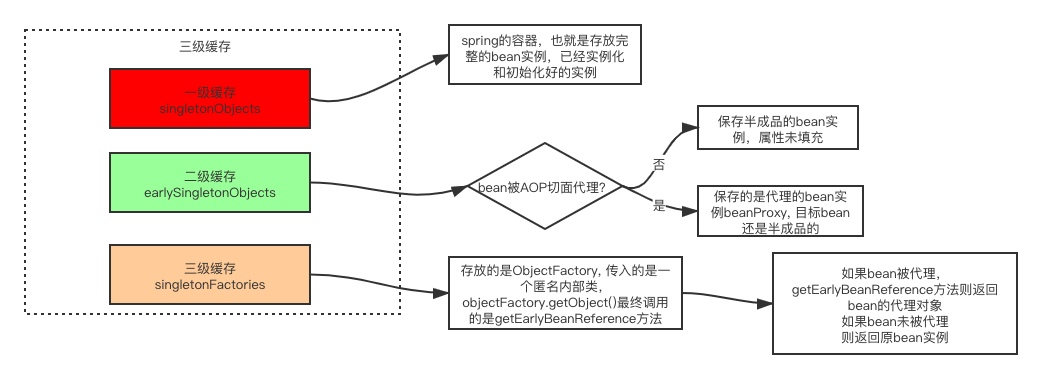
三级缓存
到此这篇关于Spring5学习之基础知识总结的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring5知识总结内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!
赞 (0)

