python实现A*寻路算法
A* 算法简介
A* 算法需要维护两个数据结构:OPEN 集和 CLOSED 集。OPEN 集包含所有已搜索到的待检测节点。初始状态,OPEN集仅包含一个元素:开始节点。CLOSED集包含已检测的节点。初始状态,CLOSED集为空。每个节点还包含一个指向父节点的指针,以确定追踪关系。
A* 算法会给每个搜索到的节点计算一个G+H 的和值F:
- F = G + H
- G:是从开始节点到当前节点的移动量。假设开始节点到相邻节点的移动量为1,该值会随着离开始点越来越远而增大。
- H:是从当前节点到目标节点的移动量估算值。
- 如果允许向4邻域的移动,使用曼哈顿距离。
- 如果允许向8邻域的移动,使用对角线距离。
算法有一个主循环,重复下面步骤直到到达目标节点:
1 每次从OPEN集中取一个最优节点n(即F值最小的节点)来检测。
2 将节点n从OPEN集中移除,然后添加到CLOSED集中。
3 如果n是目标节点,那么算法结束。
4 否则尝试添加节点n的所有邻节点n'。
- 邻节点在CLOSED集中,表示它已被检测过,则无需再添加。
- 邻节点在OPEN集中:
- 如果重新计算的G值比邻节点保存的G值更小,则需要更新这个邻节点的G值和F值,以及父节点;
- 否则不做操作
- 否则将该邻节点加入OPEN集,设置其父节点为n,并设置它的G值和F值。
有一点需要注意,如果开始节点到目标节点实际是不连通的,即无法从开始节点移动到目标节点,那算法在第1步判断获取到的节点n为空,就会退出
关键代码介绍
保存基本信息的地图类
地图类用于随机生成一个供寻路算法工作的基础地图信息
先创建一个map类, 初始化参数设置地图的长度和宽度,并设置保存地图信息的二维数据map的值为0, 值为0表示能移动到该节点。
class Map(): def __init__(self, width, height): self.width = width self.height = height self.map = [[0 for x in range(self.width)] for y in range(self.height)]
在map类中添加一个创建不能通过节点的函数,节点值为1表示不能移动到该节点。
def createBlock(self, block_num): for i in range(block_num): x, y = (randint(0, self.width-1), randint(0, self.height-1)) self.map[y][x] = 1
在map类中添加一个显示地图的函数,可以看到,这边只是简单的打印出所有节点的值,值为0或1的意思上面已经说明,在后面显示寻路算法结果时,会使用到值2,表示一条从开始节点到目标节点的路径。
def showMap(self):
print("+" * (3 * self.width + 2))
for row in self.map:
s = '+'
for entry in row:
s += ' ' + str(entry) + ' '
s += '+'
print(s)
print("+" * (3 * self.width + 2))
添加一个随机获取可移动节点的函数
def generatePos(self, rangeX, rangeY): x, y = (randint(rangeX[0], rangeX[1]), randint(rangeY[0], rangeY[1])) while self.map[y][x] == 1: x, y = (randint(rangeX[0], rangeX[1]), randint(rangeY[0], rangeY[1])) return (x , y)
搜索到的节点类
每一个搜索到将到添加到OPEN集的节点,都会创建一个下面的节点类,保存有entry的位置信息(x,y),计算得到的G值和F值,和该节点的父节点(pre_entry)。
class SearchEntry(): def __init__(self, x, y, g_cost, f_cost=0, pre_entry=None): self.x = x self.y = y # cost move form start entry to this entry self.g_cost = g_cost self.f_cost = f_cost self.pre_entry = pre_entry def getPos(self): return (self.x, self.y)
算法主函数介绍
下面就是上面算法主循环介绍的代码实现,OPEN集和CLOSED集的数据结构使用了字典,在一般情况下,查找,添加和删除节点的时间复杂度为O(1), 遍历的时间复杂度为O(n), n为字典中对象数目。
def AStarSearch(map, source, dest):
...
openlist = {}
closedlist = {}
location = SearchEntry(source[0], source[1], 0.0)
dest = SearchEntry(dest[0], dest[1], 0.0)
openlist[source] = location
while True:
location = getFastPosition(openlist)
if location is None:
# not found valid path
print("can't find valid path")
break;
if location.x == dest.x and location.y == dest.y:
break
closedlist[location.getPos()] = location
openlist.pop(location.getPos())
addAdjacentPositions(map, location, dest, openlist, closedlist)
#mark the found path at the map
while location is not None:
map.map[location.y][location.x] = 2
location = location.pre_entry
我们按照算法主循环的实现来一个个讲解用到的函数。
下面函数就是从OPEN集中获取一个F值最小的节点,如果OPEN集会空,则返回None。
# find a least cost position in openlist, return None if openlist is empty def getFastPosition(openlist): fast = None for entry in openlist.values(): if fast is None: fast = entry elif fast.f_cost > entry.f_cost: fast = entry return fast
addAdjacentPositions 函数对应算法主函数循环介绍中的尝试添加节点n的所有邻节点n'。
# add available adjacent positions def addAdjacentPositions(map, location, dest, openlist, closedlist): poslist = getPositions(map, location) for pos in poslist: # if position is already in closedlist, do nothing if isInList(closedlist, pos) is None: findEntry = isInList(openlist, pos) h_cost = calHeuristic(pos, dest) g_cost = location.g_cost + getMoveCost(location, pos) if findEntry is None : # if position is not in openlist, add it to openlist openlist[pos] = SearchEntry(pos[0], pos[1], g_cost, g_cost+h_cost, location) elif findEntry.g_cost > g_cost: # if position is in openlist and cost is larger than current one, # then update cost and previous position findEntry.g_cost = g_cost findEntry.f_cost = g_cost + h_cost findEntry.pre_entry = location
getPositions 函数获取到所有能够移动的节点,这里提供了2种移动的方式:
- 允许上,下,左,右 4邻域的移动
- 允许上,下,左,右,左上,右上,左下,右下 8邻域的移动
def getNewPosition(map, locatioin, offset): x,y = (location.x + offset[0], location.y + offset[1]) if x < 0 or x >= map.width or y < 0 or y >= map.height or map.map[y][x] == 1: return None return (x, y) def getPositions(map, location): # use four ways or eight ways to move offsets = [(-1,0), (0, -1), (1, 0), (0, 1)] #offsets = [(-1,0), (0, -1), (1, 0), (0, 1), (-1,-1), (1, -1), (-1, 1), (1, 1)] poslist = [] for offset in offsets: pos = getNewPosition(map, location, offset) if pos is not None: poslist.append(pos) return poslist
isInList 函数判断节点是否在OPEN集 或CLOSED集中
# check if the position is in list def isInList(list, pos): if pos in list: return list[pos] return None
calHeuristic 函数简单得使用了曼哈顿距离,这个后续可以进行优化。
getMoveCost 函数根据是否是斜向移动来计算消耗(斜向就是2的开根号,约等于1.4)
# imporve the heuristic distance more precisely in future def calHeuristic(pos, dest): return abs(dest.x - pos[0]) + abs(dest.y - pos[1]) def getMoveCost(location, pos): if location.x != pos[0] and location.y != pos[1]: return 1.4 else: return 1
代码的初始化
可以调整地图的长度,宽度和不可移动节点的数目。
可以调整开始节点和目标节点的取值范围。
WIDTH = 10
HEIGHT = 10
BLOCK_NUM = 15
map = Map(WIDTH, HEIGHT)
map.createBlock(BLOCK_NUM)
map.showMap()
source = map.generatePos((0,WIDTH//3),(0,HEIGHT//3))
dest = map.generatePos((WIDTH//2,WIDTH-1),(HEIGHT//2,HEIGHT-1))
print("source:", source)
print("dest:", dest)
AStarSearch(map, source, dest)
map.showMap()
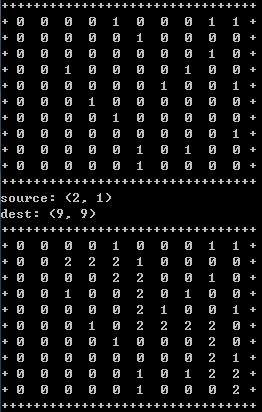
执行的效果图如下,第一个表示随机生成的地图,值为1的节点表示不能移动到该节点。
第二个图中值为2的节点表示找到的路径。
完整代码
使用python3.7编译
from random import randint
class SearchEntry():
def __init__(self, x, y, g_cost, f_cost=0, pre_entry=None):
self.x = x
self.y = y
# cost move form start entry to this entry
self.g_cost = g_cost
self.f_cost = f_cost
self.pre_entry = pre_entry
def getPos(self):
return (self.x, self.y)
class Map():
def __init__(self, width, height):
self.width = width
self.height = height
self.map = [[0 for x in range(self.width)] for y in range(self.height)]
def createBlock(self, block_num):
for i in range(block_num):
x, y = (randint(0, self.width-1), randint(0, self.height-1))
self.map[y][x] = 1
def generatePos(self, rangeX, rangeY):
x, y = (randint(rangeX[0], rangeX[1]), randint(rangeY[0], rangeY[1]))
while self.map[y][x] == 1:
x, y = (randint(rangeX[0], rangeX[1]), randint(rangeY[0], rangeY[1]))
return (x , y)
def showMap(self):
print("+" * (3 * self.width + 2))
for row in self.map:
s = '+'
for entry in row:
s += ' ' + str(entry) + ' '
s += '+'
print(s)
print("+" * (3 * self.width + 2))
def AStarSearch(map, source, dest):
def getNewPosition(map, locatioin, offset):
x,y = (location.x + offset[0], location.y + offset[1])
if x < 0 or x >= map.width or y < 0 or y >= map.height or map.map[y][x] == 1:
return None
return (x, y)
def getPositions(map, location):
# use four ways or eight ways to move
offsets = [(-1,0), (0, -1), (1, 0), (0, 1)]
#offsets = [(-1,0), (0, -1), (1, 0), (0, 1), (-1,-1), (1, -1), (-1, 1), (1, 1)]
poslist = []
for offset in offsets:
pos = getNewPosition(map, location, offset)
if pos is not None:
poslist.append(pos)
return poslist
# imporve the heuristic distance more precisely in future
def calHeuristic(pos, dest):
return abs(dest.x - pos[0]) + abs(dest.y - pos[1])
def getMoveCost(location, pos):
if location.x != pos[0] and location.y != pos[1]:
return 1.4
else:
return 1
# check if the position is in list
def isInList(list, pos):
if pos in list:
return list[pos]
return None
# add available adjacent positions
def addAdjacentPositions(map, location, dest, openlist, closedlist):
poslist = getPositions(map, location)
for pos in poslist:
# if position is already in closedlist, do nothing
if isInList(closedlist, pos) is None:
findEntry = isInList(openlist, pos)
h_cost = calHeuristic(pos, dest)
g_cost = location.g_cost + getMoveCost(location, pos)
if findEntry is None :
# if position is not in openlist, add it to openlist
openlist[pos] = SearchEntry(pos[0], pos[1], g_cost, g_cost+h_cost, location)
elif findEntry.g_cost > g_cost:
# if position is in openlist and cost is larger than current one,
# then update cost and previous position
findEntry.g_cost = g_cost
findEntry.f_cost = g_cost + h_cost
findEntry.pre_entry = location
# find a least cost position in openlist, return None if openlist is empty
def getFastPosition(openlist):
fast = None
for entry in openlist.values():
if fast is None:
fast = entry
elif fast.f_cost > entry.f_cost:
fast = entry
return fast
openlist = {}
closedlist = {}
location = SearchEntry(source[0], source[1], 0.0)
dest = SearchEntry(dest[0], dest[1], 0.0)
openlist[source] = location
while True:
location = getFastPosition(openlist)
if location is None:
# not found valid path
print("can't find valid path")
break;
if location.x == dest.x and location.y == dest.y:
break
closedlist[location.getPos()] = location
openlist.pop(location.getPos())
addAdjacentPositions(map, location, dest, openlist, closedlist)
#mark the found path at the map
while location is not None:
map.map[location.y][location.x] = 2
location = location.pre_entry
WIDTH = 10
HEIGHT = 10
BLOCK_NUM = 15
map = Map(WIDTH, HEIGHT)
map.createBlock(BLOCK_NUM)
map.showMap()
source = map.generatePos((0,WIDTH//3),(0,HEIGHT//3))
dest = map.generatePos((WIDTH//2,WIDTH-1),(HEIGHT//2,HEIGHT-1))
print("source:", source)
print("dest:", dest)
AStarSearch(map, source, dest)
map.showMap()
到此这篇关于python实现A*寻路算法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python A*寻路算法内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

