浅析Spring配置文件
Spring的配置文件概述
简介
Spring的配置文件是用于指导Spring工厂进行Bean生成、依赖关系注入及Bean示例分发的”图纸”,他是一个或多个标砖的XML文档,J2EE程序员必须学会灵活应用这份”图纸”,准确的表达自己的”生成意图”。
Spring配置文件的示例
Spring配置文件的一般结构

Spring容器高层视图
Spring容器启动基本条件:
Spring的框架类包
Bean的配置信息
Bean的元数据信息
Bean的实现类
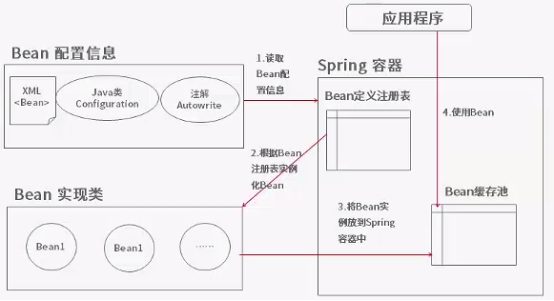
Bean的属性信息
例如:数据源的用户名、密码
Bean的依赖关系
Spring根据依赖关系配置完成Bean之间的装配
Bean的行为配置
例如:生命周期范围、生命周期各个过程的回调函数
Bean的创建方式
说明Bean是通过构造器还是工厂方法来创建的
Bean的实现类
基于XML的配置
Spring的配置文件是基于XML格式的,Spring1.0的配置采用DTD格式,Spring2.0以后使用Schema的格式,后者让不同类型的配置拥有了自己的命名空间,是配置文件更具有扩展性。
XML分析
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="saleProduct" class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" ></bean> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.sale.service.*.*(..))" id="mycut"/> </aop:config> </beans>
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans":表示默认命空间,用于Spring Bean定
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance":表示xsi标准命名空间,用于指定自定义命名空间的schema文件
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop":表示自定义命名空间,aop表示该命名空间的简称
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd">:用于为每个命名空间指定具体的schema文件
<bean id="saleProduct" class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" ></bean>:为默认命名空间中的配置
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.sale.service.*.*(..))" id="mycut"/>
</aop:config>:为aop命名空间的配置
Schema文件的用途
Spring3.0的配置Schema文件分部在各模块类包中,如果模块拥有对应的Schema文件,则可以在模块类包中找到一个config目录,Schema文件就为与该目录中,如下是对这些Schema文件的用途:
示例说明:spring-aop-3.0.xsd
命名空间:http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
Schema文件:http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd
1. Spring-beans.xsd :用于配置Bean
2. Spring-aop-3.0.xsd :AOP配置
3. Spring-tx-3.0.xsd:声明式事务配置的Schema
4. Spring-mvc-3.0.xsd:3.0新增的
5. Spring-utils-3.0.xsd:简化某些复杂的标准配置
6. Spring-jee-3.0.xsd:是为简化jee中ejb和jndi等功能的配置
7. Spring-jdbc-3.0.xsd:是3.0新增的,配置Spring内接数据库提供的Schema
8. Spring-jms-3.0.xsd:jms的配置
9. Spring-lang-3.0.xsd:添加了对动态语言的支持,集成动态语言定义的
10. Spring-oxm-3.0.xsd:配置对象xml映射到Schema
11. Spring-task-3.0.xsd:任务调度的Schema
12. Spring-tool-3.0.xsd:集成的Spring有用工具而定义的Schema
Spring Bean的命名
每个Bean可以有一个或多个id,我们把第一个id成为”标识符”,其余id叫做id别名,这些id在IoC容器中必须唯一。
Bean id的命名方式
配置全限定类名,唯一
<bean class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" ></bean>
指定id,唯一
<bean id="saleProduct"class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" ></bean>
指定name,唯一
<bean name="saleProduct" class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" ></bean>
指定id和name,唯一
<beanid="saleProduct"name="saleProduct"class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" ></bean>
指定多个name,唯一
<bean name="bean1;alias1;alias2" class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" ></bean>
指定多个id,唯一
<bean id="bean1;alias1;alias2" class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" ></bean>
指定别名,唯一
<bean id="saleProduct" class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" ></bean> <alias name="saleProduct" alias="alias1"/>
Bean id的命名约定
1、遵循xml命名规范
2、由字母,数字,下划线组成
3、驼峰式,第一个单词首字母小写,从第二个但是开始第首字母大写
Spring Bean的实例化
Spring IoC容器是如何实例化Bean呢?传统应用程序可以通过 new和反射方式进行实例化Bean。二Spring IoC容器则需要根据Bean定义的配置元数据使用反射机制来创建Bean。
Spring IoC容器创建Bean示例的方式
使用构造器实例化Bean
默认构造
<bean id="saleProduct" class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" ></bean>
必须存在无参数的构造
有参构造
<bean id="saleProduct" class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" > <constructor-arg name="prodName" value="哈哈" ></constructor-arg> </bean>
必须存有参数的构造
使用静态工厂实例化Bean
必须的class属性,factory-method属性指定实例化Bean的方法,而且使用静态工厂方法也允许指定方法参数,Spring IoC容器将调用此属性指定的方法来获取Bean
<bean factory-method="newInstance" id="saleProduct" class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" > <constructor-arg index="0" value="Hello" ></constructor-arg> </bean>
使用实例工厂方法实例化Bean
不能指定class属性,factory-bean来指定工厂Bean,factory-method指定实例化Bean的方法,而且使用实例工厂方法也允许指定参数
<!-- 定义实例工厂Bean --> <bean id="saleProduct1" class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" ></bean> <!-- 使用实例工厂Bean --> <bean id="saleProduct2" factory-bean="saleProduct1" > <constructor-arg index="0" value="Hello" ></constructor-arg> </bean>
Spring Bean的作用域
Spring Bean中所说的作用域,在配置文件中即是”scope”。早面向对象程序设计中一般指对象或变量之间的可见范围。而在Spring容器中是指其创建的Bean对象相对于其他Bean对象的请求范围。
Spring Bean的作用域类型
Singleton
Spring IoC容器中仅存在一个Bean的实例,Bean以单利方式存在,单实例模式是最重要的设置模式之一,在Spring中对此实现了超越,可以对那些非线程安全的对象采用单例模式(一般使用在DAO层)

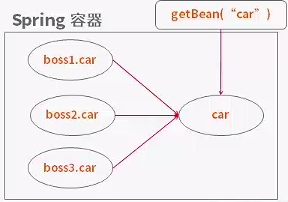
<bean scope="singleton" id="saleProduct" class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" ></bean>
prototype
每次从容器中调用Bean时,都会返回一个全新的实例,即每次调用getBea()时,相当于执行new Bean()的操作。在默认情况下,Spring容器在启动时不实例化propotype的Bean。

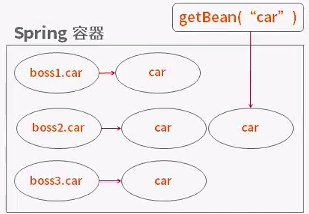
<bean scope="prototype" id="saleProduct" class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" ></bean>
当用于使用Spring的WebApplicationConext时,还可以使用另外三种Bean的作用域,即request,session和globleSession。在使用Web应用环境相关的Bean作用域时,必须在Web容器中进行一些额外的配置
低版本web容器配置:
<filter> <filter-name>requestContextFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.RequestConextFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>requestContextFilter</filter-name> <servlet-name>/*</servlet-name> </filter-mapping>
高版本的Web容器配置:
<listener> <listener-class> org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestConextLinstener </listener-class> </listener>
request
发起一次http请求的时候Spring会创建一个全新实例
<bean scope="request" id="saleProduct" class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" ></bean>
Session
当前会话
<bean scope="Session" id="saleProduct" class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" ></bean>
Global session
httpSession会话
<bean scope="Global session" id="saleProduct" class="com.sale.entity.SaleProduct" ></bean>
自定义作用域
在spring 2.0中,Spring的Bean作用域机制是可以扩展的,这意味着,不仅可以使用Spring提供的预定义Bean作用域,还可以定义自己的作用域,甚至重启定义现有的作用域(不提倡这么做,而且不能覆盖内置的sinleton和prototype作用域)
实现自定义Scope类:
Org.springframework.bean.factory.config.scope
注册自定义Scope类:
ConfigurableBeanFactory.registerScope(String scopeName,Scope scope)
使用自定义的Scope:
Scope customScope = new ThreadScope(); beanFactory.registerScope(“thread”,customScope); <bean id=”***” class=”***” scope=”scopeName”>
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作能带来一定的帮助,同时也希望多多支持我们!

