Spring-Boot框架初步搭建
一、简介
SpringMVC是非常伟大的框架,开源,发展迅速。优秀的设计必然会划分、解耦。所以,spring有很多子项目,比如core、context、bean、mvc等。这对知根底的人来说很简单明了,然而springmvc就是为了傻瓜式的操作而发明的。对于初学springmvc的人来说,想要入手就开发需要拷贝一连串的dependency而不知道这个是干嘛,不知道是不是少了依赖。像我刚接触springmvc的时候到处百度教程而发现各有不同,于是复制了一个又一个代码却不能自己设置,根本原因是不了解各个依赖的包。
Spring-Boot 正是为了解决繁复的代码配置而产生的。Spring-Boot 也是基于java-base 开发的代码,及不用xml文件配置,所有代码都由java来完成。还可以加入Groovy的动态语言执行。
二、搭建一个基本的web-mvc 项目
2.1 Configure environment
- java 1.8+
- maven 3.3+
- spring-boot 1.3.5
- idea 15
- Thymeleaf 3
2.2 Start
在idea中,选择new-》maven创建一个空的maven项目,比如名字springboot-test。
2.2.1pom.xml
设定java版本:
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
添加依赖版本管理dependencyManagement
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<!-- Import dependency management from Spring Boot -->
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>1.3.5.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
添加spring-web项目依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
添加build-plugin
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<fork>true</fork>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
如此,一个简单的restful的webservice的项目就搭建好了。如果想要支持视图渲染,即jsp、freeMark、velocity等,添加对应的依赖即可。比如,我使用Thymeleaf模板:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.2.2 创建java代码
如果新建项目的名字是:springboot-test. 则创建包springboot-test/src/main/java/com/test.
com
+- example
+- myproject
+- Application.java
|
+- domain
| +- Customer.java
| +- CustomerRepository.java
|
+- service
| +- CustomerService.java
|
+- web
+- CustomerController.java
com.test是我们的基本包名。下面创建配置类com.test.AppConfig。
package com.test;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* Created by miaorf on 2016/6/19.
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class AppConfig {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AppConfig.class);
}
}
@SpringBootApplication 标注启动配置入口,可以发现通过一个main方法启动。使用这个注解的类必须放置于最外层包中,因为默认扫描这个类以下的包。否则需要自己配置@ComponentScan。
这样,配置基本完成了。下面开发控制层controller:
创建com.test.controller.HelloController。
package com.test.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Created by miaorf on 2016/6/19.
*/
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(Model model){
model.addAttribute("name","Ryan");
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/json")
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> json(){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("name","Ryan");
map.put("age","18");
map.put("sex","man");
return map;
}
}
创建视图代码:
视图默认放在springboot-test\src\main\resources\templates**.
所以创建springboot-test\src\main\resources\templates\index.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Getting Started: Serving Web Content</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="'Hello, ' + ${name} + '!'" />
</body>
</html>
D:\workspace\springboot\springboot-test\src\main\webapp\hello.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <title>Getting Started: Serving Web Content</title> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" /> </head> <body> hello, This is static page. not resolve by server, just the html. </body> </html>
2.2.3 run
启动方式多种,可以启动main方法,也可以通过命令行启动:
D:\temp\springboot-test>mvn spring-boot:run [INFO] Scanning for projects... [WARNING] [WARNING] Some problems were encountered while building the effective model for com.test:springboot-test:jar:1.0-SNAPSHOT [WARNING] 'build.plugins.plugin.version' for org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-maven-plugin is missing. @ line 49, column 21 [WARNING] [WARNING] It is highly recommended to fix these problems because they threaten the stability of your build. [WARNING] [WARNING] For this reason, future Maven versions might no longer support building such malformed projects. [WARNING] [INFO] [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] Building springboot-test 1.0-SNAPSHOT [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] [INFO] >>> spring-boot-maven-plugin:1.3.5.RELEASE:run (default-cli) > test-compile @ springboot-test >>> [INFO] [INFO] --- maven-resources-plugin:2.6:resources (default-resources) @ springboot-test --- [WARNING] Using platform encoding (GBK actually) to copy filtered resources, i.e. build is platform dependent! [INFO] Copying 2 resources [INFO] [INFO] --- maven-compiler-plugin:3.1:compile (default-compile) @ springboot-test --- [INFO] Nothing to compile - all classes are up to date [INFO] [INFO] --- maven-resources-plugin:2.6:testResources (default-testResources) @ springboot-test --- [WARNING] Using platform encoding (GBK actually) to copy filtered resources, i.e. build is platform dependent! [INFO] skip non existing resourceDirectory D:\temp\springboot-test\src\test\resources [INFO] [INFO] --- maven-compiler-plugin:3.1:testCompile (default-testCompile) @ springboot-test --- [INFO] No sources to compile [INFO] [INFO] <<< spring-boot-maven-plugin:1.3.5.RELEASE:run (default-cli) < test-compile @ springboot-test <<< [INFO] [INFO] --- spring-boot-maven-plugin:1.3.5.RELEASE:run (default-cli) @ springboot-test --- [INFO] Attaching agents: [] . ____ _ __ _ _ /\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \ ( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \ \\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) ) ' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / / =========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/ :: Spring Boot :: (v1.3.5.RELEASE)
浏览器访问:localhost:8080/index

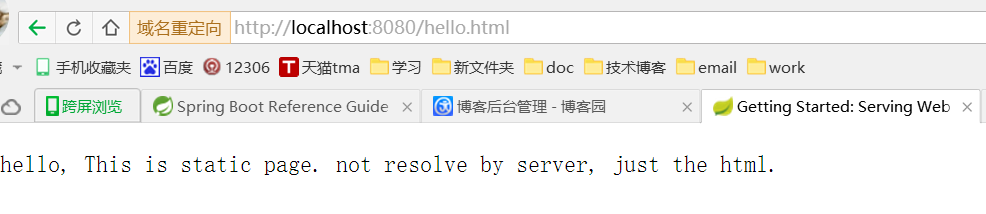
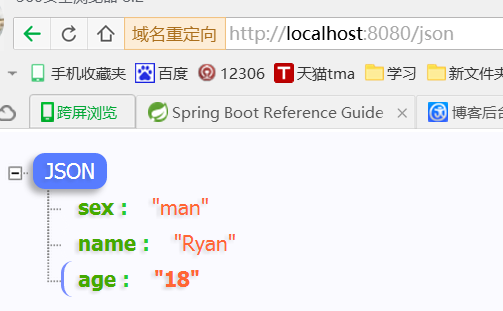
demo下载路径:springboot_jb51.rar
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。

