浅析ORB、SURF、SIFT特征点提取方法以及ICP匹配方法
目录
- main.cpp
- CMakeLists.txt
- 执行效果
- ICP
- CMakeLists.txt
- 执行效果
在进行编译视觉SLAM时,书中提到了ORB、SURF、SIFT提取方法,以及特征提取方法暴力匹配(Brute-Force Matcher)和快速近邻匹配(FLANN)。以及7.9讲述的3D-3D:迭代最近点(Iterative Closest Point,ICP)方法,ICP 的求解方式有两种:利用线性代数求解(主要是SVD),以及利用非线性优化方式求解。
完整代码代码如下:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1rlH9Jtg_aWtuYzmphqIJ3Q 提取码:8888
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include <opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <time.h>
#include <chrono>
#include <math.h>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d;
double picture1_size_change=1;
double picture2_size_change=1;
bool show_picture = true;
void extract_ORB2(string picture1, string picture2)
{
//-- 读取图像
Mat img_1 = imread(picture1, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
Mat img_2 = imread(picture2, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
assert(img_1.data != nullptr && img_2.data != nullptr);
resize(img_1, img_1, Size(), picture1_size_change, picture1_size_change);
resize(img_2, img_2, Size(), picture2_size_change, picture2_size_change);
//-- 初始化
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create(2000,(1.200000048F), 8, 100);
Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create(5000);
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming");
//-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
detector->detect(img_1, keypoints_1);
detector->detect(img_2, keypoints_2);
//-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子
descriptor->compute(img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1);
descriptor->compute(img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
// cout << "extract ORB cost = " << time_used.count() * 1000 << " ms " << endl;
cout << "detect " << keypoints_1.size() << " and " << keypoints_2.size() << " keypoints " << endl;
if (show_picture)
{
Mat outimg1;
drawKeypoints(img_1, keypoints_1, outimg1, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT);
imshow("ORB features", outimg1);
}
//-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离
vector<DMatch> matches;
// t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
matcher->match(descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches);
t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "extract and match ORB cost = " << time_used.count() * 1000 << " ms " << endl;
//-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选
// 计算最小距离和最大距离
auto min_max = minmax_element(matches.begin(), matches.end(),
[](const DMatch &m1, const DMatch &m2)
{ return m1.distance < m2.distance; });
double min_dist = min_max.first->distance;
double max_dist = min_max.second->distance;
// printf("-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist);
// printf("-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist);
//当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限.
std::vector<DMatch> good_matches;
for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++)
{
if (matches[i].distance <= max(2 * min_dist, 30.0))
{
good_matches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
}
cout << "match " << good_matches.size() << " keypoints " << endl;
//-- 第五步:绘制匹配结果
Mat img_match;
Mat img_goodmatch;
drawMatches(img_1, keypoints_1, img_2, keypoints_2, matches, img_match);
drawMatches(img_1, keypoints_1, img_2, keypoints_2, good_matches, img_goodmatch);
if (show_picture)
imshow("good matches", img_goodmatch);
if (show_picture)
waitKey(0);
}
void extract_SIFT(string picture1, string picture2)
{
// double t = (double)getTickCount();
Mat temp = imread(picture1, IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
Mat image_check_changed = imread(picture2, IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
if (!temp.data || !image_check_changed.data)
{
printf("could not load images...\n");
return;
}
resize(temp, temp, Size(), picture1_size_change, picture1_size_change);
resize(image_check_changed, image_check_changed, Size(), picture2_size_change, picture2_size_change);
//Mat image_check_changed = Change_image(image_check);
//("temp", temp);
if (show_picture)
imshow("image_check_changed", image_check_changed);
int minHessian = 500;
// Ptr<SURF> detector = SURF::create(minHessian); // surf
Ptr<SIFT> detector = SIFT::create(); // sift
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_obj;
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_scene;
Mat descriptor_obj, descriptor_scene;
clock_t startTime, endTime;
startTime = clock();
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
// cout << "extract ORB cost = " << time_used.count() * 1000 << " ms " << endl;
detector->detectAndCompute(temp, Mat(), keypoints_obj, descriptor_obj);
detector->detectAndCompute(image_check_changed, Mat(), keypoints_scene, descriptor_scene);
cout << "detect " << keypoints_obj.size() << " and " << keypoints_scene.size() << " keypoints " << endl;
// matching
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
vector<DMatch> matches;
matcher.match(descriptor_obj, descriptor_scene, matches);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "extract and match cost = " << time_used.count() * 1000 << " ms " << endl;
//求最小最大距离
double minDist = 1000;
double maxDist = 0;
//row--行 col--列
for (int i = 0; i < descriptor_obj.rows; i++)
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if (dist > maxDist)
{
maxDist = dist;
}
if (dist < minDist)
{
minDist = dist;
}
}
// printf("max distance : %f\n", maxDist);
// printf("min distance : %f\n", minDist);
// find good matched points
vector<DMatch> goodMatches;
for (int i = 0; i < descriptor_obj.rows; i++)
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if (dist < max(5 * minDist, 1.0))
{
goodMatches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
}
//rectangle(temp, Point(1, 1), Point(177, 157), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 8, 0);
cout << "match " << goodMatches.size() << " keypoints " << endl;
endTime = clock();
// cout << "took time : " << (double)(endTime - startTime) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000 << " ms" << endl;
Mat matchesImg;
drawMatches(temp, keypoints_obj, image_check_changed, keypoints_scene, goodMatches, matchesImg, Scalar::all(-1),
Scalar::all(-1), vector<char>(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS);
if (show_picture)
imshow("Flann Matching Result01", matchesImg);
// imwrite("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/matchesImg04.jpg", matchesImg);
//求h
std::vector<Point2f> points1, points2;
//保存对应点
for (size_t i = 0; i < goodMatches.size(); i++)
{
//queryIdx是对齐图像的描述子和特征点的下标。
points1.push_back(keypoints_obj[goodMatches[i].queryIdx].pt);
//queryIdx是是样本图像的描述子和特征点的下标。
points2.push_back(keypoints_scene[goodMatches[i].trainIdx].pt);
}
// Find homography 计算Homography,RANSAC随机抽样一致性算法
Mat H = findHomography(points1, points2, RANSAC);
//imwrite("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/C-train/C-train/result/sift/Image4_SURF_MinHessian1000_ minDist1000_a0.9b70.jpg", matchesImg);
vector<Point2f> obj_corners(4);
vector<Point2f> scene_corners(4);
obj_corners[0] = Point(0, 0);
obj_corners[1] = Point(temp.cols, 0);
obj_corners[2] = Point(temp.cols, temp.rows);
obj_corners[3] = Point(0, temp.rows);
//透视变换(把斜的图片扶正)
perspectiveTransform(obj_corners, scene_corners, H);
//Mat dst;
cvtColor(image_check_changed, image_check_changed, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
line(image_check_changed, scene_corners[0], scene_corners[1], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, 0);
line(image_check_changed, scene_corners[1], scene_corners[2], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, 0);
line(image_check_changed, scene_corners[2], scene_corners[3], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, 0);
line(image_check_changed, scene_corners[3], scene_corners[0], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, 0);
if (show_picture)
{
Mat outimg1;
Mat temp_color = imread(picture1, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
drawKeypoints(temp_color, keypoints_obj, outimg1, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT);
imshow("SIFT features", outimg1);
}
if (show_picture)
imshow("Draw object", image_check_changed);
// imwrite("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/image04.jpg", image_check_changed);
// t = ((double)getTickCount() - t) / getTickFrequency();
// printf("averagetime:%f\n", t);
if (show_picture)
waitKey(0);
}
void extract_SURF(string picture1, string picture2)
{
// double t = (double)getTickCount();
Mat temp = imread(picture1, IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
Mat image_check_changed = imread(picture2, IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
if (!temp.data || !image_check_changed.data)
{
printf("could not load images...\n");
return;
}
resize(temp, temp, Size(), picture1_size_change, picture1_size_change);
resize(image_check_changed, image_check_changed, Size(), picture2_size_change, picture2_size_change);
//Mat image_check_changed = Change_image(image_check);
//("temp", temp);
if (show_picture)
imshow("image_check_changed", image_check_changed);
int minHessian = 500;
Ptr<SURF> detector = SURF::create(minHessian); // surf
// Ptr<SIFT> detector = SIFT::create(minHessian); // sift
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_obj;
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_scene;
Mat descriptor_obj, descriptor_scene;
clock_t startTime, endTime;
startTime = clock();
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
// cout << "extract ORB cost = " << time_used.count() * 1000 << " ms " << endl;
detector->detectAndCompute(temp, Mat(), keypoints_obj, descriptor_obj);
detector->detectAndCompute(image_check_changed, Mat(), keypoints_scene, descriptor_scene);
cout << "detect " << keypoints_obj.size() << " and " << keypoints_scene.size() << " keypoints " << endl;
// matching
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
vector<DMatch> matches;
matcher.match(descriptor_obj, descriptor_scene, matches);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "extract and match cost = " << time_used.count() * 1000 << " ms " << endl;
//求最小最大距离
double minDist = 1000;
double maxDist = 0;
//row--行 col--列
for (int i = 0; i < descriptor_obj.rows; i++)
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if (dist > maxDist)
{
maxDist = dist;
}
if (dist < minDist)
{
minDist = dist;
}
}
// printf("max distance : %f\n", maxDist);
// printf("min distance : %f\n", minDist);
// find good matched points
vector<DMatch> goodMatches;
for (int i = 0; i < descriptor_obj.rows; i++)
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if (dist < max(2 * minDist, 0.15))
{
goodMatches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
}
//rectangle(temp, Point(1, 1), Point(177, 157), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 8, 0);
cout << "match " << goodMatches.size() << " keypoints " << endl;
endTime = clock();
// cout << "took time : " << (double)(endTime - startTime) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000 << " ms" << endl;
Mat matchesImg;
drawMatches(temp, keypoints_obj, image_check_changed, keypoints_scene, goodMatches, matchesImg, Scalar::all(-1),
Scalar::all(-1), vector<char>(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS);
if (show_picture)
imshow("Flann Matching Result01", matchesImg);
// imwrite("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/matchesImg04.jpg", matchesImg);
//求h
std::vector<Point2f> points1, points2;
//保存对应点
for (size_t i = 0; i < goodMatches.size(); i++)
{
//queryIdx是对齐图像的描述子和特征点的下标。
points1.push_back(keypoints_obj[goodMatches[i].queryIdx].pt);
//queryIdx是是样本图像的描述子和特征点的下标。
points2.push_back(keypoints_scene[goodMatches[i].trainIdx].pt);
}
// Find homography 计算Homography,RANSAC随机抽样一致性算法
Mat H = findHomography(points1, points2, RANSAC);
//imwrite("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/C-train/C-train/result/sift/Image4_SURF_MinHessian1000_ minDist1000_a0.9b70.jpg", matchesImg);
vector<Point2f> obj_corners(4);
vector<Point2f> scene_corners(4);
obj_corners[0] = Point(0, 0);
obj_corners[1] = Point(temp.cols, 0);
obj_corners[2] = Point(temp.cols, temp.rows);
obj_corners[3] = Point(0, temp.rows);
//透视变换(把斜的图片扶正)
perspectiveTransform(obj_corners, scene_corners, H);
//Mat dst;
cvtColor(image_check_changed, image_check_changed, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
line(image_check_changed, scene_corners[0], scene_corners[1], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, 0);
line(image_check_changed, scene_corners[1], scene_corners[2], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, 0);
line(image_check_changed, scene_corners[2], scene_corners[3], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, 0);
line(image_check_changed, scene_corners[3], scene_corners[0], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, 0);
if (show_picture)
{
Mat outimg1;
Mat temp_color = imread(picture1, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
drawKeypoints(temp_color, keypoints_obj, outimg1, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT);
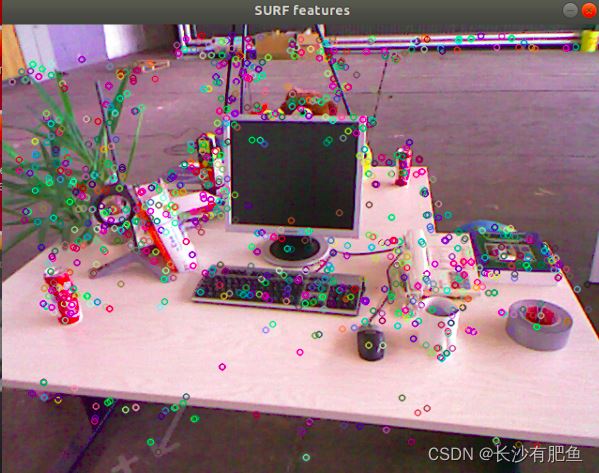
imshow("SURF features", outimg1);
}
if (show_picture)
imshow("Draw object", image_check_changed);
// imwrite("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/image04.jpg", image_check_changed);
// t = ((double)getTickCount() - t) / getTickFrequency();
// printf("averagetime:%f\n", t);
if (show_picture)
waitKey(0);
}
void extract_AKAZE(string picture1,string picture2)
{
//读取图片
Mat temp = imread(picture1,IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
Mat image_check_changed = imread(picture2,IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
//如果不能读到其中任何一张图片,则打印不能下载图片
if(!temp.data || !image_check_changed.data)
{
printf("could not load iamges...\n");
return;
}
resize(temp,temp,Size(),picture1_size_change,picture1_size_change);
resize(image_check_changed,image_check_changed,Size(),picture2_size_change,picture2_size_change);
//Mat image_check_changed = Change_image(image_check);
//("temp", temp);
if(show_picture)
{
imshow("image_checked_changed",image_check_changed);
}
int minHessian=500;
Ptr<AKAZE> detector=AKAZE::create();//AKAZE
vector<keypoint> keypoints_obj;
vector<keypoint> keypoints_scene;
Mat descriptor_obj,descriptor_scene;
clock_t startTime,endTime;
startTime=clock();
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1=chrono::steady_clock::now();
detector->detectAndCompute(temp,Mat(),keypoints_obj,descriptor_obj);
detector->detectAndCompute(image_check_changed,Mat(),keypoints_scene,descriptor_scene);
cout<<" detect "<<keypoints_obj.size()<<" and "<<keypoints_scene.size<<" keypoints "<<endl;
//matching
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
vector<DMatch> matches;
matcher.match(descriptor_obj,descriptor_scene,matches);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2-t1);
cout << "extract and match cost = " << time_used.count()*1000<<" ms "<<endl;
//求最小最大距离
double minDist = 1000;
double max_dist = 0;
//row--行 col--列
for(int i=0;i<descriptor_obj.rows;i++)
{
double dist = match[i].distance;
if(dist > maxDist)
{
maxDist = dist;
}
if(dist<minDist)
{
minDist = dist;
}
}
// printf("max distance : %f\n", maxDist);
// printf("min distance : %f\n", minDist);
// find good matched points
vector<DMatch> goodMatches;
for(imt i=0;i<descriptor_obj.rows;i++)
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if(dist < max(5 * minDist,1.0))
{
goodMatches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
}
//rectangle(temp, Point(1, 1), Point(177, 157), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 8, 0);
cout<<" match "<<goodMatches.size()<<" keypoints "<<endl;
endTime = clock();
// cout << "took time : " << (double)(endTime - startTime) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000 << " ms" << endl;
Mat matchesImg;
drawMatches(temp,keypoints_obj,image_check_changed,keypoints_scene,goodMatches,
matchesImg,Scalar::all(-1),
Scalar::all(-1),vector<char>(),DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS);
if(show_picture)
imshow("Flann Matching Result01",matchesImg);
// imwrite("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/matchesImg04.jpg", matchesImg);
//求h
std::vector<Point2f> points1,points2;
//保存对应点
for(size_t i = 0;i < goodMatches.size();i++)
{
//queryIdx是对齐图像的描述子和特征点的下标。
points1.push_back(keypoints_obj[goodMatches[i].queryIdx].pt);
//queryIdx是是样本图像的描述子和特征点的下标。
points2.push_back(keypoints_scene[goodMatches[i].trainIdx].pt);
}
// Find homography 计算Homography,RANSAC随机抽样一致性算法
Mat H = findHomography(points1,points2,RANSAC);
//imwrite("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/C-train/C-train/result/sift/Image4_SURF_MinHessian1000_ minDist1000_a0.9b70.jpg", matchesImg);
vector<Point2f> obj_corners(4);
vector<Point2f> scene_corners(4);
obj_corners[0] = Point(0,0);
obj_corners[0] = Point(temp.count,0);
obj_corners[0] = Point(temp.cols,temp.rows);
obj_corners[0] = Point(0,temp.rows);
//透视变换(把斜的图片扶正)
perspectiveTransform(obj_corners,scene_corners,H);
//Mat dst
cvtColor(image_check_changed,image_check_changed,COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
line(image_check_changed,scene_corners[0],scene_corners[1],Scalar(0,0,255),2,8,0);
line(image_check_changed,scene_corners[1],scene_corners[2],Scalar(0,0,255),2,8,0);
line(image_check_changed,scene_corners[2],scene_corners[3],Scalar(0,0,255),2,8,0);
line(image_check_changed,scene_corners[3],scene_corners[0],Scalar(0,0,255),2,8,0);
if(show_picture)
{
Mat outimg1;
Mat temp_color = imread(picture1,CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
drawKeypoints(temp_color,keypoints_obj,outimg1,Scalar::all(-1),DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT);
imshow("AKAZE features",outimg1);
}
if(show_picture)
waitKey(0);
}
void extract_ORB(string picture1, string picture2)
{
Mat img_1 = imread(picture1);
Mat img_2 = imread(picture2);
resize(img_1, img_1, Size(), picture1_size_change, picture1_size_change);
resize(img_2, img_2, Size(), picture2_size_change, picture2_size_change);
if (!img_1.data || !img_2.data)
{
cout << "error reading images " << endl;
return ;
}
vector<Point2f> recognized;
vector<Point2f> scene;
recognized.resize(1000);
scene.resize(1000);
Mat d_srcL, d_srcR;
Mat img_matches, des_L, des_R;
//ORB算法的目标必须是灰度图像
cvtColor(img_1, d_srcL, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);//CPU版的ORB算法源码中自带对输入图像灰度化,此步可省略
cvtColor(img_2, d_srcR, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
Ptr<ORB> d_orb = ORB::create(1500);
Mat d_descriptorsL, d_descriptorsR, d_descriptorsL_32F, d_descriptorsR_32F;
vector<KeyPoint> keyPoints_1, keyPoints_2;
//设置关键点间的匹配方式为NORM_L2,更建议使用 FLANNBASED = 1, BRUTEFORCE = 2, BRUTEFORCE_L1 = 3, BRUTEFORCE_HAMMING = 4, BRUTEFORCE_HAMMINGLUT = 5, BRUTEFORCE_SL2 = 6
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> d_matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create(NORM_L2);
std::vector<DMatch> matches;//普通匹配
std::vector<DMatch> good_matches;//通过keyPoint之间距离筛选匹配度高的匹配结果
clock_t startTime, endTime;
startTime = clock();
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
d_orb -> detectAndCompute(d_srcL, Mat(), keyPoints_1, d_descriptorsL);
d_orb -> detectAndCompute(d_srcR, Mat(), keyPoints_2, d_descriptorsR);
cout << "detect " << keyPoints_1.size() << " and " << keyPoints_2.size() << " keypoints " << endl;
// endTime = clock();
// cout << "took time : " << (double)(endTime - startTime) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000 << " ms" << endl;
d_matcher -> match(d_descriptorsL, d_descriptorsR, matches);//L、R表示左右两幅图像进行匹配
//计算匹配所需时间
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "extract and match cost = " << time_used.count() * 1000 << " ms " << endl;
int sz = matches.size();
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if (dist < min_dist) min_dist = dist;
if (dist > max_dist) max_dist = dist;
}
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
if (matches[i].distance < 0.6*max_dist)
{
good_matches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
}
cout << "match " << good_matches.size() << " keypoints " << endl;
// endTime = clock();
// cout << "took time : " << (double)(endTime - startTime) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000 << " ms" << endl;
//提取良好匹配结果中在待测图片上的点集,确定匹配的大概位置
for (size_t i = 0; i < good_matches.size(); ++i)
{
scene.push_back(keyPoints_2[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt);
}
for(unsigned int j = 0; j < scene.size(); j++)
cv::circle(img_2, scene[j], 2, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
//画出普通匹配结果
Mat ShowMatches;
drawMatches(img_1,keyPoints_1,img_2,keyPoints_2,matches,ShowMatches);
if (show_picture)
imshow("matches", ShowMatches);
// imwrite("matches.png", ShowMatches);
//画出良好匹配结果
Mat ShowGoodMatches;
drawMatches(img_1,keyPoints_1,img_2,keyPoints_2,good_matches,ShowGoodMatches);
if (show_picture)
imshow("good_matches", ShowGoodMatches);
// imwrite("good_matches.png", ShowGoodMatches);
//画出良好匹配结果中在待测图片上的点集
if (show_picture)
imshow("MatchPoints_in_img_2", img_2);
// imwrite("MatchPoints_in_img_2.png", img_2);
if (show_picture)
waitKey(0);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
string picture1=string(argv[1]);
string picture2=string(argv[2]);
// string picture1 = "data/picture1/6.jpg";
// string picture2 = "data/picture2/16.PNG";
cout << "\nextract_ORB::" << endl;
extract_ORB(picture1, picture2);
cout << "\nextract_ORB::" << endl;
extract_ORB2(picture1, picture2);
cout << "\nextract_SURF::" << endl;
extract_SURF(picture1, picture2);
cout << "\nextract_AKAZE::" << endl;
extract_AKAZE(picture1, picture2);
cout << "\nextract_SIFT::" << endl;
extract_SIFT(picture1, picture2);
cout << "success!!" << endl;
}
CMakeLists.txt
CMAKE_MINIMUM_REQUIRED(VERSION 2.8.3) # 设定版本
PROJECT(DescriptorCompare) # 设定工程名
SET(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER "g++") # 设定编译器
add_compile_options(-std=c++14) #编译选项,选择c++版本
# 设定可执行二进制文件的目录(最后生成的可执行文件放置的目录)
SET(EXECUTABLE_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR})
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -Wall -fpermissive -g -O3 -Wno-unused-function -Wno-return-type")
find_package(OpenCV 3.0 REQUIRED)
message(STATUS "Using opencv version ${OpenCV_VERSION}")
find_package(Eigen3 3.3.8 REQUIRED)
find_package(Pangolin REQUIRED)
# 设定链接目录
LINK_DIRECTORIES(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/lib)
# 设定头文件目录
INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES(
${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include
${EIGEN3_INCLUDE_DIR}
${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIR}
${Pangolin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
add_library(${PROJECT_NAME}
test.cc
)
target_link_libraries( ${PROJECT_NAME}
${OpenCV_LIBS}
${EIGEN3_LIBS}
${Pangolin_LIBRARIES}
)
add_executable(main main.cpp )
target_link_libraries(main ${PROJECT_NAME} )
add_executable(icp icp.cpp )
target_link_libraries(icp ${PROJECT_NAME} )
执行效果
./main 1.png 2.png
extract_ORB:: detect 1500 and 1500 keypoints extract and match cost = 21.5506 ms match 903 keypoints extract_ORB:: detect 1304 and 1301 keypoints extract and match ORB cost = 25.4976 ms match 313 keypoints extract_SURF:: detect 915 and 940 keypoints extract and match cost = 53.8371 ms match 255 keypoints extract_SIFT:: detect 1536 and 1433 keypoints extract and match cost = 97.9322 ms match 213 keypoints success!!







ICP
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
#include <Eigen/SVD>
#include <pangolin/pangolin.h>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int picture_h=480;
int picture_w=640;
bool show_picture = true;
void find_feature_matches(
const Mat &img_1, const Mat &img_2,
std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,
std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,
std::vector<DMatch> &matches);
// 像素坐标转相机归一化坐标
Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K);
void pose_estimation_3d3d(
const vector<Point3f> &pts1,
const vector<Point3f> &pts2,
Mat &R, Mat &t
);
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 5) {
cout << "usage: pose_estimation_3d3d img1 img2 depth1 depth2" << endl;
return 1;
}
//-- 读取图像
Mat img_1 = imread(argv[1], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
Mat img_2 = imread(argv[2], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
vector<DMatch> matches;
find_feature_matches(img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches);
cout << "picture1 keypoints: " << keypoints_1.size() << " \npicture2 keypoints: " << keypoints_2.size() << endl;
cout << "一共找到了 " << matches.size() << " 组匹配点" << endl;
// 建立3D点
Mat depth1 = imread(argv[3], CV_8UC1); // 深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像
Mat depth2 = imread(argv[4], CV_8UC1); // 深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像
Mat K = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 595.2, 0, 328.9, 0, 599.0, 253.9, 0, 0, 1);
vector<Point3f> pts1, pts2;
for (DMatch m:matches) {
int d1 = 255-(int)depth1.ptr<uchar>(int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.y))[int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.x)];
int d2 = 255-(int)depth2.ptr<uchar>(int(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt.y))[int(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt.x)];
if (d1 == 0 || d2 == 0) // bad depth
continue;
Point2d p1 = pixel2cam(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K);
Point2d p2 = pixel2cam(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt, K);
float dd1 = int(d1) / 1000.0;
float dd2 = int(d2) / 1000.0;
pts1.push_back(Point3f(p1.x * dd1, p1.y * dd1, dd1));
pts2.push_back(Point3f(p2.x * dd2, p2.y * dd2, dd2));
}
cout << "3d-3d pairs: " << pts1.size() << endl;
Mat R, t;
pose_estimation_3d3d(pts1, pts2, R, t);
//DZQ ADD
cv::Mat Pose = (Mat_<double>(4, 4) << R.at<double>(0, 0), R.at<double>(0, 1), R.at<double>(0, 2), t.at<double>(0),
R.at<double>(1, 0), R.at<double>(1, 1), R.at<double>(1, 2), t.at<double>(1),
R.at<double>(2, 0), R.at<double>(2, 1), R.at<double>(2, 2), t.at<double>(2),
0, 0, 0, 1);
cout << "[delete outliers] Matched objects distance: ";
vector<double> vDistance;
double allDistance = 0; //存储总距离,用来求平均匹配距离,用平均的误差距离来剔除外点
for (int i = 0; i < pts1.size(); i++)
{
Mat point = Pose * (Mat_<double>(4, 1) << pts2[i].x, pts2[i].y, pts2[i].z, 1);
double distance = pow(pow(pts1[i].x - point.at<double>(0), 2) + pow(pts1[i].y - point.at<double>(1), 2) + pow(pts1[i].z - point.at<double>(2), 2), 0.5);
vDistance.push_back(distance);
allDistance += distance;
// cout << distance << " ";
}
// cout << endl;
double avgDistance = allDistance / pts1.size(); //求一个平均距离
int N_outliers = 0;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < pts1.size(); i++, j++) //i用来记录剔除后vector遍历的位置,j用来记录原位置
{
if (vDistance[i] > 1.5 * avgDistance) //匹配物体超过平均距离的N倍就会被剔除 [delete outliers] DZQ FIXED_PARAM
{
N_outliers++;
}
}
cout << "N_outliers:: " << N_outliers << endl;
// show points
{
//创建一个窗口
pangolin::CreateWindowAndBind("show points", 640, 480);
//启动深度测试
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
// Define Projection and initial ModelView matrix
pangolin::OpenGlRenderState s_cam(
pangolin::ProjectionMatrix(640, 480, 420, 420, 320, 240, 0.05, 500),
//对应的是gluLookAt,摄像机位置,参考点位置,up vector(上向量)
pangolin::ModelViewLookAt(0, -5, 0.1, 0, 0, 0, pangolin::AxisY));
// Create Interactive View in window
pangolin::Handler3D handler(s_cam);
//setBounds 跟opengl的viewport 有关
//看SimpleDisplay中边界的设置就知道
pangolin::View &d_cam = pangolin::CreateDisplay()
.SetBounds(0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, -640.0f / 480.0f)
.SetHandler(&handler);
while (!pangolin::ShouldQuit())
{
// Clear screen and activate view to render into
glClearColor(0.97,0.97,1.0, 1); //背景色
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
d_cam.Activate(s_cam);
glBegin(GL_POINTS); //绘制匹配点
glLineWidth(5);
for (int i = 0; i < pts1.size(); i++)
{
glColor3f(1, 0, 0);
glVertex3d(pts1[i].x,pts1[i].y,pts1[i].z);
Mat point = Pose * (Mat_<double>(4, 1) << pts2[i].x, pts2[i].y, pts2[i].z, 1);
glColor3f(0, 1, 0);
glVertex3d(point.at<double>(0),point.at<double>(1),point.at<double>(2));
}
glEnd();
glBegin(GL_LINES); //绘制匹配线
glLineWidth(1);
for (int i = 0; i < pts1.size(); i++)
{
glColor3f(0, 0, 1);
glVertex3d(pts1[i].x,pts1[i].y,pts1[i].z);
Mat point = Pose * (Mat_<double>(4, 1) << pts2[i].x, pts2[i].y, pts2[i].z, 1);
glVertex3d(point.at<double>(0),point.at<double>(1),point.at<double>(2));
}
glEnd();
glBegin(GL_POINTS); //绘制所有点
glLineWidth(5);
glColor3f(1, 0.5, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < picture_h; i+=2)
{
for (int j = 0; j < picture_w; j+=2)
{
int d1 = 255-(int)depth1.ptr<uchar>(i)[j];
if (d1 == 0) // bad depth
continue;
Point2d temp_p;
temp_p.y=i; //这里的x和y应该和i j相反
temp_p.x=j;
Point2d p1 = pixel2cam(temp_p, K);
float dd1 = int(d1) / 1000.0;
glVertex3d(p1.x * dd1, p1.y * dd1, dd1);
// glVertex3d(j/1000.0, i/1000.0, d1/200.0);
}
}
glEnd();
// Swap frames and Process Events
pangolin::FinishFrame();
}
}
}
void find_feature_matches(const Mat &img_1, const Mat &img_2,
std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,
std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,
std::vector<DMatch> &matches) {
//-- 初始化
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
// used in OpenCV3
Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create(2000,(1.200000048F), 8, 100);
Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create(5000);
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming");
//-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置
detector->detect(img_1, keypoints_1);
detector->detect(img_2, keypoints_2);
//-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子
descriptor->compute(img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1);
descriptor->compute(img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2);
//-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离
vector<DMatch> match;
// BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING );
matcher->match(descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match);
//-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选
double min_dist = 10000, max_dist = 0;
//找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离
for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {
double dist = match[i].distance;
if (dist < min_dist) min_dist = dist;
if (dist > max_dist) max_dist = dist;
}
printf("-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist);
printf("-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist);
//当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限.
for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {
if (match[i].distance <= max(2 * min_dist, 30.0)) {
matches.push_back(match[i]);
}
}
//-- 第五步:绘制匹配结果
if(show_picture)
{
Mat img_match;
Mat img_goodmatch;
drawMatches(img_1, keypoints_1, img_2, keypoints_2, matches, img_match);
imshow("all matches", img_match);
waitKey(0);
}
}
Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K) {
return Point2d(
(p.x - K.at<double>(0, 2)) / K.at<double>(0, 0),
(p.y - K.at<double>(1, 2)) / K.at<double>(1, 1)
);
}
void pose_estimation_3d3d(const vector<Point3f> &pts1,
const vector<Point3f> &pts2,
Mat &R, Mat &t) {
Point3f p1, p2; // center of mass
int N = pts1.size();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
p1 += pts1[i];
p2 += pts2[i];
}
p1 = Point3f(Vec3f(p1) / N);
p2 = Point3f(Vec3f(p2) / N);
vector<Point3f> q1(N), q2(N); // remove the center
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
q1[i] = pts1[i] - p1;
q2[i] = pts2[i] - p2;
}
// compute q1*q2^T
Eigen::Matrix3d W = Eigen::Matrix3d::Zero();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
W += Eigen::Vector3d(q1[i].x, q1[i].y, q1[i].z) * Eigen::Vector3d(q2[i].x, q2[i].y, q2[i].z).transpose();
}
// cout << "W=" << W << endl;
// SVD on W
Eigen::JacobiSVD<Eigen::Matrix3d> svd(W, Eigen::ComputeFullU | Eigen::ComputeFullV);
Eigen::Matrix3d U = svd.matrixU();
Eigen::Matrix3d V = svd.matrixV();
Eigen::Matrix3d R_ = U * (V.transpose());
if (R_.determinant() < 0) {
R_ = -R_;
}
Eigen::Vector3d t_ = Eigen::Vector3d(p1.x, p1.y, p1.z) - R_ * Eigen::Vector3d(p2.x, p2.y, p2.z);
// convert to cv::Mat
R = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) <<
R_(0, 0), R_(0, 1), R_(0, 2),
R_(1, 0), R_(1, 1), R_(1, 2),
R_(2, 0), R_(2, 1), R_(2, 2)
);
t = (Mat_<double>(3, 1) << t_(0, 0), t_(1, 0), t_(2, 0));
}
void convertRGB2Gray(string picture)
{
double min;
double max;
Mat depth_new_1 = imread(picture); // 深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像
Mat test=Mat(20,256,CV_8UC3);
int s;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
std::cout<<i<<" ";
Vec3b* p = test.ptr<Vec3b>(i);
for (s = 0; s < 32; s++) {
p[s][0] = 128 + 4 * s;
p[s][1] = 0;
p[s][2] = 0;
}
p[32][0] = 255;
p[32][1] = 0;
p[32][2] = 0;
for (s = 0; s < 63; s++) {
p[33+s][0] = 255;
p[33+s][1] = 4+4*s;
p[33+s][2] = 0;
}
p[96][0] = 254;
p[96][1] = 255;
p[96][2] = 2;
for (s = 0; s < 62; s++) {
p[97 + s][0] = 250 - 4 * s;
p[97 + s][1] = 255;
p[97 + s][2] = 6+4*s;
}
p[159][0] = 1;
p[159][1] = 255;
p[159][2] = 254;
for (s = 0; s < 64; s++) {
p[160 + s][0] = 0;
p[160 + s][1] = 252 - (s * 4);
p[160 + s][2] = 255;
}
for (s = 0; s < 32; s++) {
p[224 + s][0] = 0;
p[224 + s][1] = 0;
p[224 + s][2] = 252-4*s;
}
}
cout<<"depth_new_1 :: "<<depth_new_1.cols<<" "<<depth_new_1.rows<<" "<<endl;
Mat img_g=Mat(picture_h,picture_w,CV_8UC1);
for(int i=0;i<picture_h;i++)
{
Vec3b *p = test.ptr<Vec3b>(0);
Vec3b *q = depth_new_1.ptr<Vec3b>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < picture_w; j++)
{
for(int k=0;k<256;k++)
{
if ( (((int)p[k][0] - (int)q[j][0] < 4) && ((int)q[j][0] - (int)p[k][0] < 4))&&
(((int)p[k][1] - (int)q[j][1] < 4) && ((int)q[j][1] - (int)p[k][1] < 4))&&
(((int)p[k][2] - (int)q[j][2] < 4) && ((int)q[j][2] - (int)p[k][2] < 4)))
{
img_g.at<uchar>(i,j)=k;
}
}
}
}
imwrite("14_Depth_3.png", img_g);
waitKey();
}
CMakeLists.txt
和上面一样。
./icp 1.png 2.png 1_depth.png 2_depth.png
-- Max dist : 87.000000 -- Min dist : 4.000000 picture1 keypoints: 1304 picture2 keypoints: 1301 一共找到了 313 组匹配点 3d-3d pairs: 313 [delete outliers] Matched objects distance: N_outliers:: 23
执行效果


以上就是浅析ORB、SURF、SIFT特征点提取方法以及ICP匹配方法的详细内容,更多关于特征点提取方法 ICP匹配方法的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!
赞 (0)

