详解Java中IO字节流基本操作(复制文件)并测试性能
此次案例将以复制文件的形式来演示IO字节流的基本操作,复制一个mp3文件,文件信息如下图:

main方法测试
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//源文件
String srcFile = "src/a.mp3";
//目的文件
String destFile = "src/b.mp3";
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
...
复制文件方法
...
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("共耗时"+(end-start)+"毫秒");
}
一、一次读取一个字节
//一次读取一个字节
public static void copy1(String srcFile,String destFile) throws Exception {
//封装文件
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
//复制文件
int b = 0;
while ((b = in.read()) != -1) {
out.write(b);
}
//释放资源
in.close();
out.close();
}
运行截图:
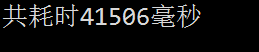
二、一次读取一个字节数组
// 一次读取一个字节数组
public static void copy2(String srcFile, String destFile) throws Exception {
// 封装文件
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
// 复制文件
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = in.read(buff)) != -1) {
out.write(buff, 0, len);
}
// 释放资源
in.close();
out.close();
}
运行截图:
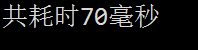
三、使用高效缓冲区一次读取一个字节
/ 使用高效缓冲区一次读取一个字节
public static void copy3(String srcFile, String destFile) throws Exception {
// 封装文件
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFile));
// 复制文件
int b = 0;
while ((b = bis.read()) != -1) {
bos.write(b);
}
// 释放资源
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
运行截图:
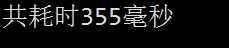
四、使用高效缓冲区一次读取一个字节数组
// 使用高效缓冲区一次读取一个字节数组
public static void copy4(String srcFile, String destFile) throws Exception {
// 封装文件
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFile));
// 复制文件
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = bis.read(buf)) != -1) {
bos.write(buf, 0, len);
}
// 释放资源
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
运行截图:
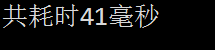
注:每台测试的速度结果不一样
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的Java中IO字节流基本操作(复制文件)并测试性能,详解整合,希望对大家有所帮助,如果大家有任何疑问请给我留言,小编会及时回复大家的。在此也非常感谢大家对我们网站的支持!
赞 (0)

