Java按时间梯度实现异步回调接口的方法
1. 背景
在业务处理完之后,需要调用其他系统的接口,将相应的处理结果通知给对方,若是同步请求,假如调用的系统出现异常或是宕机等事件,会导致自身业务受到影响,事务会一直阻塞,数据库连接不够用等异常现象,可以通过异步回调来防止阻塞,但异步的情况还存在一个问题,若调用一次不成功的话接下来怎么处理?这个地方就需要按时间梯度回调,比如前期按10s间隔回调,回调3次,若不成功按30s回调,回调2次,再不成功按分钟回调,依次类推……相当于给了对方系统恢复的时间,不可能一直处于异常或宕机等异常状态,若是再不成功可以再通过人工干预的手段去处理了,具体业务具体实现。
2. 技术实现
大体实现思路如下图,此过程用到两个队列,当前队列和Next队列,当前队列用来存放第一次需要回调的数据对象,如果调用不成功则放入Next队列,按照制定的时间策略再继续回调,直到成功或最终持久化后人工接入处理。
用到的技术如下:
•http请求库,retrofit2
•队列,LinkedBlockingQueue
•调度线程池,ScheduledExecutorService
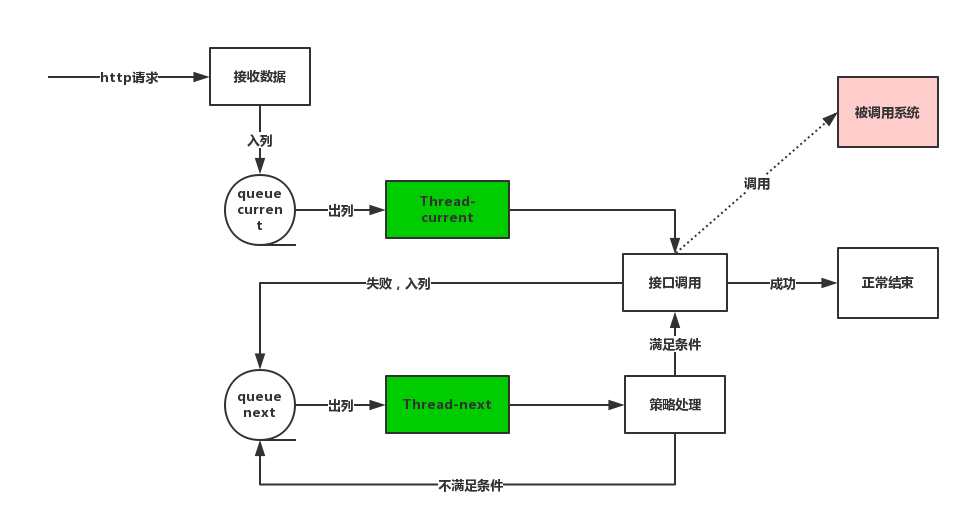
3. 主要代码说明
3.1 回调时间梯度的策略设计
采用枚举来对策略规则进行处理,便于代码上的维护,该枚举设计三个参数,级别、回调间隔、回调次数;
/**
* 回调策略
*/
public enum CallbackType {
//等级1,10s执行3次
SECONDS_10(1, 10, 3),
//等级2,30s执行2次
SECONDS_30(2, 30, 2),
//等级3,60s执行2次
MINUTE_1(3, 60, 2),
//等级4,5min执行1次
MINUTE_5(4, 300, 1),
//等级5,30min执行1次
MINUTE_30(5, 30*60, 1),
//等级6,1h执行2次
HOUR_1(6, 60*60, 1),
//等级7,3h执行2次
HOUR_3(7, 60*60*3, 1),
//等级8,6h执行2次
HOUR_6(8, 60*60*6, 1);
//级别
private int level;
//回调间隔时间 秒
private int intervalTime;
//回调次数
private int count;
}
3.2 数据传输对象设计
声明抽象父类,便于其他对象调用传输继承。
/**
* 消息对象父类
*/
public abstract class MessageInfo {
//开始时间
private long startTime;
//更新时间
private long updateTime;
//是否回调成功
private boolean isSuccess=false;
//回调次数
private int count=0;
//回调策略
private CallbackType callbackType;
}
要传输的对象,继承消息父类;
/**
* 工单回调信息
*/
public class WorkOrderMessage extends MessageInfo {
//车架号
private String vin;
//工单号
private String workorderno;
//工单状态
private Integer status;
//工单原因
private String reason;
//操作用户
private Integer userid;
}
3.3 调度线程池的使用
//声明线程池,大小为16
private ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(16);
...略
while (true){
//从队列获取数据,交给定时器执行
try {
WorkOrderMessage message = MessageQueue.getMessageFromNext();
long excueTime = message.getUpdateTime()+message.getCallbackType().getIntervalTime()* 1000;
long t = excueTime - System.currentTimeMillis();
if (t/1000 < 5) {//5s之内将要执行的数据提交给调度线程池
System.out.println("MessageHandleNext-满足定时器执行条件"+JSONObject.toJSONString(message));
pool.schedule(new Callable<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean call() throws Exception {
remoteCallback(message);
return true;
}
}, t, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}else {
MessageQueue.putMessageToNext(message);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
3.4 retrofit2的使用,方便好用。
具体可查看官网相关文档进行了解,用起来还是比较方便的。http://square.github.io/retrofit/
retrofit初始化:
import retrofit2.Retrofit;
import retrofit2.converter.gson.GsonConverterFactory;
public class RetrofitHelper {
private static final String HTTP_URL = "http://baidu.com/";
private static Retrofit retrofit;
public static Retrofit instance(){
if (retrofit == null){
retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl(HTTP_URL)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.build();
}
return retrofit;
}
}
如果需要修改超时时间,连接时间等可以这样初始话,Retrofit采用OkHttpClient
import okhttp3.OkHttpClient;
import retrofit2.Retrofit;
import retrofit2.converter.gson.GsonConverterFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class RetrofitHelper {
private static final String HTTP_URL = "http://baidu.com/";
private static Retrofit retrofit;
public static Retrofit instance(){
if (retrofit == null){
retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl(HTTP_URL)
.client(new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.connectTimeout(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS)//连接时间
.readTimeout(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS)//读时间
.writeTimeout(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS)//写时间
.build())
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.build();
}
return retrofit;
}
}
Retrofit使用通过接口调用,要先声明一个接口;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.woasis.callbackdemo.bean.WorkOrderMessage;
import retrofit2.Call;
import retrofit2.http.Body;
import retrofit2.http.POST;
public interface WorkOrderMessageInterface {
@POST("/api")
Call<JSONObject> updateBatteryInfo(@Body WorkOrderMessage message);
}
接口和实例对象准备好了,接下来就是调用;
private void remoteCallback(WorkOrderMessage message){
//实例接口对象
WorkOrderMessageInterface workOrderMessageInterface = RetrofitHelper.instance().create(WorkOrderMessageInterface.class);
//调用接口方法
Call<JSONObject> objectCall = workOrderMessageInterface.updateBatteryInfo(message);
System.out.println("远程调用执行:"+new Date());
//异步调用执行
objectCall.enqueue(new Callback<JSONObject>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(Call<JSONObject> call, Response<JSONObject> response) {
System.out.println("MessageHandleNext****调用成功"+Thread.currentThread().getId());
message.setSuccess(true);
System.out.println("MessageHandleNext-回调成功"+JSONObject.toJSONString(message));
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Call<JSONObject> call, Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("MessageHandleNext++++调用失败"+Thread.currentThread().getId());
//失败后再将数据放入队列
try {
//对回调策略初始化
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
message.setUpdateTime(currentTime);
message.setSuccess(false);
CallbackType callbackType = message.getCallbackType();
//获取等级
int level = CallbackType.getLevel(callbackType);
//获取次数
int count = CallbackType.getCount(callbackType);
//如果等级已经最高,则不再回调
if (CallbackType.HOUR_6.getLevel() == callbackType.getLevel() && count == message.getCount()){
System.out.println("MessageHandleNext-等级最高,不再回调, 线下处理:"+JSONObject.toJSONString(message));
}else {
//看count是否最大,count次数最大则增加level
if (message.getCount()<callbackType.getCount()){
message.setCount(message.getCount()+1);
}else {//如果不小,则增加level
message.setCount(1);
level += 1;
message.setCallbackType(CallbackType.getTypeByLevel(level));
}
MessageQueue.putMessageToNext(message);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("MessageHandleNext-放入队列数据失败");
}
}
});
}
3.5结果实现

4.总结
本次实现了按照时间梯度去相应其他系统的接口,不再导致本身业务因其他系统的异常而阻塞。
源码:https://github.com/liuzwei/callback-demo
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的Java按时间梯度实现异步回调接口,希望对大家有所帮助,如果大家有任何疑问请给我留言,小编会及时回复大家的。在此也非常感谢大家对我们网站的支持!

