聊聊Spring Cloud Gateway过滤器精确控制异常返回问题
欢迎访问我的GitHub
这里分类和汇总了欣宸的全部原创(含配套源码):https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos
本篇概览在《Spring Cloud Gateway修改请求和响应body的内容》一文中,咱们通过filter成功修改请求body的内容,当时留下个问题:在filter中如果发生异常(例如请求参数不合法),抛出异常信息的时候,调用方收到的返回码和body都是Spring Cloud Gateway框架处理后的,调用方无法根据这些内容知道真正的错误原因,如下图:
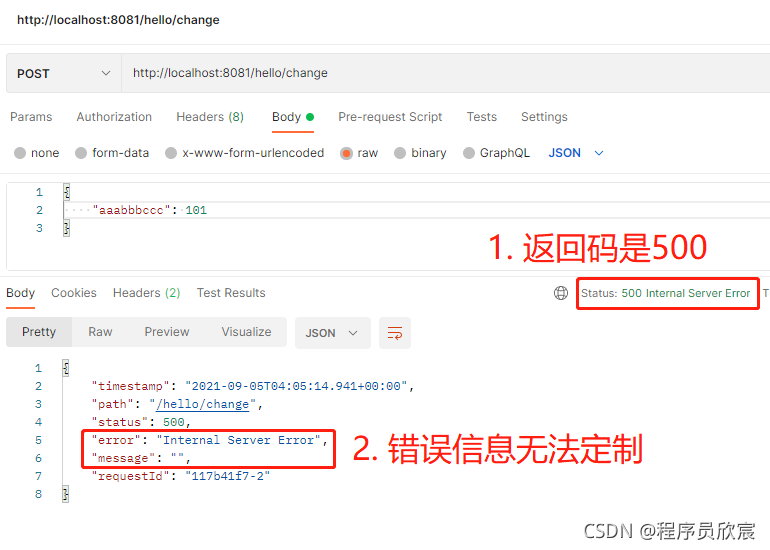
本篇任务就是分析上述现象的原因,通过阅读源码搞清楚返回码和响应body生成的具体逻辑
- 这里将分析结果提前小结出来,如果您很忙碌没太多时间却又想知道最终原因,直接关注以下小结即可:
- Spring Cloud Gateway应用中,有个ErrorAttributes类型的bean,它的getErrorAttributes方法返回了一个map
- 应用抛出异常时,返回码来自上述map的status的值,返回body是整个map序列化的结果
- 默认情况下ErrorAttributes的实现类是DefaultErrorAttributes
- 再看上述map的status值(也就是response的返回码),在DefaultErrorAttributes是如何生成的:
先看异常对象是不是ResponseStatusException类型
- 如果是ResponseStatusException类型,就调用异常对象的getStatus方法作为返回值
- 如果不是ResponseStatusException类型,再看异常类有没有ResponseStatus注解,
- 如果有,就取注解的code属性作为返回值
- 如果异常对象既不是ResponseStatusException类型,也没有ResponseStatus注解,就返回500
最后看map的message字段(也就是response body的message字段),在DefaultErrorAttributes是如何生成的:
- 异常对象是不是BindingResult类型
- 如果不是BindingResult类型,就看是不是ResponseStatusException类型
- 如果是,就用getReason作为返回值
- 如果也不是ResponseStatusException类型,就看异常类有没有ResponseStatus注解,如果有就取该注解的reason属性作为返回值
- 如果通过注解取得的reason也无效,就返回异常的getMessage字段
上述内容就是本篇精华,但是并未包含分析过程,如果您对Spring Cloud源码感兴趣,请允许欣宸陪伴您来一次短暂的源码阅读之旅
Spring Cloud Gateway错误处理源码
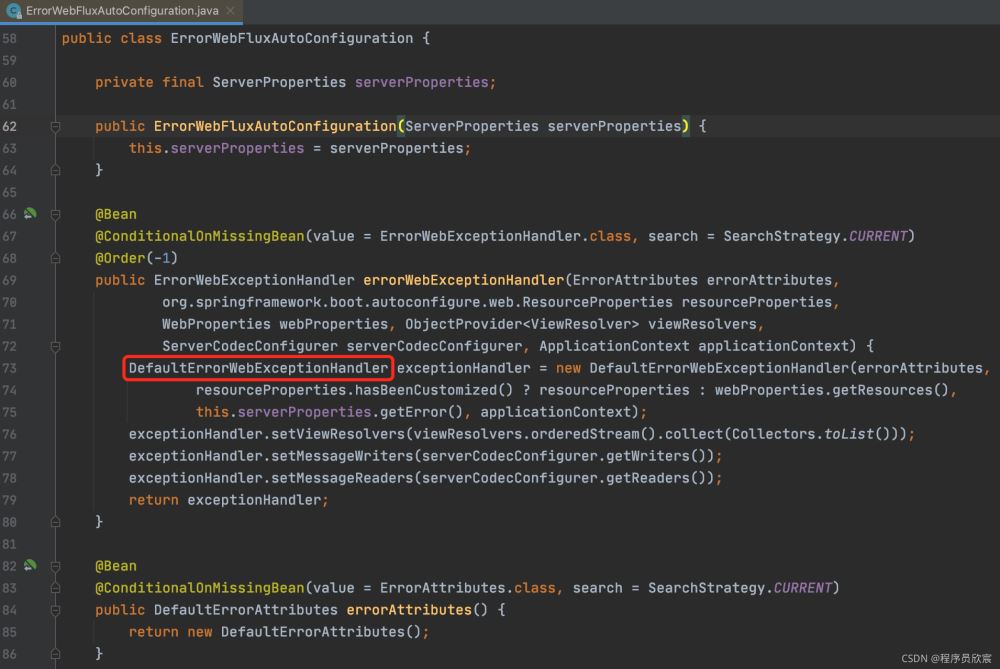
首先要看的是配置类ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration.java,这里面向spring注册了两个实例,每个都非常重要,咱们先关注第一个,也就是说ErrorWebExceptionHandler的实现类是DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler:
处理异常时,会通过FluxOnErrorResume调用到这个ErrorWebExceptionHandler的handle方法处理,该方法在其父类AbstractErrorWebExceptionHandler.java中,如下图,红框位置的代码是关键,异常返回内容就是在这里决定的:
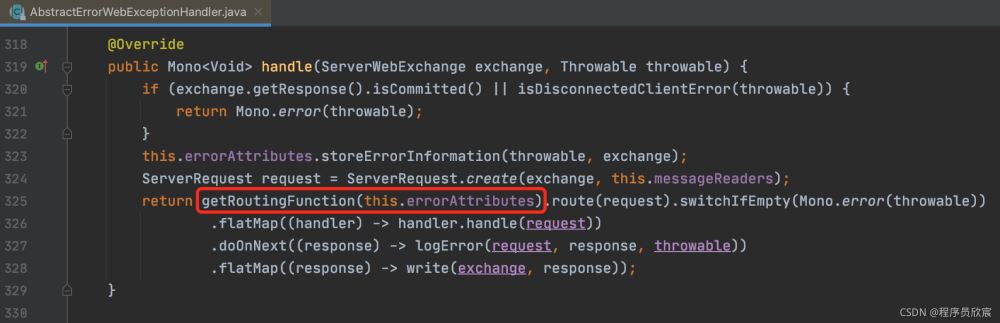
展开这个getRoutingFunction方法,可见会调用renderErrorResponse来处理响应:
@Override
protected RouterFunction<ServerResponse> getRoutingFunction(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) {
return route(acceptsTextHtml(), this::renderErrorView).andRoute(all(), this::renderErrorResponse);
}
打开renderErrorResponse方法,如下所示,真相大白了!
protected Mono<ServerResponse> renderErrorResponse(ServerRequest request) {
// 取出所有错误信息
Map<String, Object> error = getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL));
// 构造返回的所有信息
return ServerResponse
// 控制返回码
.status(getHttpStatus(error))
// 控制返回ContentType
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
// 控制返回内容
.body(BodyInserters.fromValue(error));
}
通过上述代码,咱们得到两个重要结论:
- 返回给调用方的状态码,取决于getHttpStatus方法的返回值
- 返回给调用方的body,取决于error的内容
都已经读到了这里,自然要看看getHttpStatus的内部,如下所示,status来自入参:
protected int getHttpStatus(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes) {
return (int) errorAttributes.get("status");
}
- 至此,咱们可以得出一个结论:getErrorAttributes方法的返回值是决定返回码和返回body的关键!
- 来看看这个getErrorAttributes方法的庐山真面吧,在DefaultErrorAttributes.java中(回忆刚才看ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration.java的时候,前面曾提到里面的东西都很重要,也包括errorAttributes方法):
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(ServerRequest request, ErrorAttributeOptions options) {
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = this.getErrorAttributes(request, options.isIncluded(Include.STACK_TRACE));
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(this.includeException)) {
options = options.including(new Include[]{Include.EXCEPTION});
}
if (!options.isIncluded(Include.EXCEPTION)) {
errorAttributes.remove("exception");
}
if (!options.isIncluded(Include.STACK_TRACE)) {
errorAttributes.remove("trace");
}
if (!options.isIncluded(Include.MESSAGE) && errorAttributes.get("message") != null) {
errorAttributes.put("message", "");
}
if (!options.isIncluded(Include.BINDING_ERRORS)) {
errorAttributes.remove("errors");
}
return errorAttributes;
}
篇幅所限,就不再展开上述代码了,直接上结果吧:
- 返回码来自determineHttpStatus的返回
- message字段来自determineMessage的返回打开determineHttpStatus方法,终极答案揭晓,请关注中文注释:
private HttpStatus determineHttpStatus(Throwable error, MergedAnnotation<ResponseStatus> responseStatusAnnotation) {
// 异常对象是不是ResponseStatusException类型
return error instanceof ResponseStatusException
// 如果是ResponseStatusException类型,就调用异常对象的getStatus方法作为返回值
? ((ResponseStatusException)error).getStatus()
// 如果不是ResponseStatusException类型,再看异常类有没有ResponseStatus注解,
// 如果有,就取注解的code属性作为返回值
: (HttpStatus)responseStatusAnnotation.getValue("code", HttpStatus.class)
// 如果异常对象既不是ResponseStatusException类型,也没有ResponseStatus注解,就返回500
.orElse(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
另外,message字段的内容也确定了:
private String determineMessage(Throwable error, MergedAnnotation<ResponseStatus> responseStatusAnnotation) {
// 异常对象是不是BindingResult类型
if (error instanceof BindingResult) {
// 如果是,就用getMessage作为返回值
return error.getMessage();
}
// 如果不是BindingResult类型,就看是不是ResponseStatusException类型
else if (error instanceof ResponseStatusException) {
// 如果是,就用getReason作为返回值
return ((ResponseStatusException)error).getReason();
} else {
// 如果也不是ResponseStatusException类型,
// 就看异常类有没有ResponseStatus注解,如果有就取该注解的reason属性作为返回值
String reason = (String)responseStatusAnnotation.getValue("reason", String.class).orElse("");
if (StringUtils.hasText(reason)) {
return reason;
} else {
// 如果通过注解取得的reason也无效,就返回异常的getMessage字段
return error.getMessage() != null ? error.getMessage() : "";
}
}
}
- 至此,源码分析已完成,最终的返回码和返回内容究竟如何控制,相信聪明的您心里应该有数了,下一篇《实战篇》咱们趁热打铁,写代码试试精确控制返回码和返回内容
- 提前剧透,接下来的《实战篇》会有以下内容呈现:
- 直接了当,控制返回码和body中的error字段
- 小小拦路虎,见招拆招
- 简单易用,通过注解控制返回信息
- 终极方案,完全定制返回内容
到此这篇关于Spring Cloud Gateway过滤器精确控制异常返回(分析篇)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring Cloud Gateway过滤器内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

