Pytorch中torch.nn.Softmax的dim参数用法说明
Pytorch中torch.nn.Softmax的dim参数使用含义
涉及到多维tensor时,对softmax的参数dim总是很迷,下面用一个例子说明
import torch.nn as nn m = nn.Softmax(dim=0) n = nn.Softmax(dim=1) k = nn.Softmax(dim=2) input = torch.randn(2, 2, 3) print(input) print(m(input)) print(n(input)) print(k(input))
输出:
input
tensor([[[ 0.5450, -0.6264, 1.0446],
[ 0.6324, 1.9069, 0.7158]],[[ 1.0092, 0.2421, -0.8928],
[ 0.0344, 0.9723, 0.4328]]])
dim=0
tensor([[[0.3860, 0.2956, 0.8741],
[0.6452, 0.7180, 0.5703]],[[0.6140, 0.7044, 0.1259],
[0.3548, 0.2820, 0.4297]]])
dim=0时,在第0维上sum=1,即:
[0][0][0]+[1][0][0]=0.3860+0.6140=1
[0][0][1]+[1][0][1]=0.2956+0.7044=1
… …
dim=1
tensor([[[0.4782, 0.0736, 0.5815],
[0.5218, 0.9264, 0.4185]],[[0.7261, 0.3251, 0.2099],
[0.2739, 0.6749, 0.7901]]])
dim=1时,在第1维上sum=1,即:
[0][0][0]+[0][1][0]=0.4782+0.5218=1
[0][0][1]+[0][1][1]=0.0736+0.9264=1
… …
dim=2
tensor([[[0.3381, 0.1048, 0.5572],
[0.1766, 0.6315, 0.1919]],[[0.6197, 0.2878, 0.0925],
[0.1983, 0.5065, 0.2953]]])
dim=2时,在第2维上sum=1,即:
[0][0][0]+[0][0][1]+[0][0][2]=0.3381+0.1048+0.5572=1.0001(四舍五入问题)
[0][1][0]+[0][1][1]+[0][1][2]=0.1766+0.6315+0.1919=1
… …
用图表示223的张量如下:
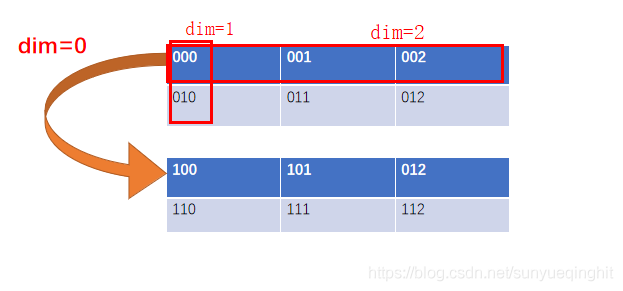
多分类问题torch.nn.Softmax的使用
为什么谈论这个问题呢?是因为我在工作的过程中遇到了语义分割预测输出特征图个数为16,也就是所谓的16分类问题。
因为每个通道的像素的值的大小代表了像素属于该通道的类的大小,为了在一张图上用不同的颜色显示出来,我不得不学习了torch.nn.Softmax的使用。
首先看一个简答的例子,倘若输出为(3, 4, 4),也就是3张4x4的特征图。
import torch img = torch.rand((3,4,4)) print(img)
输出为:
tensor([[[0.0413, 0.8728, 0.8926, 0.0693],
[0.4072, 0.0302, 0.9248, 0.6676],
[0.4699, 0.9197, 0.3333, 0.4809],
[0.3877, 0.7673, 0.6132, 0.5203]],[[0.4940, 0.7996, 0.5513, 0.8016],
[0.1157, 0.8323, 0.9944, 0.2127],
[0.3055, 0.4343, 0.8123, 0.3184],
[0.8246, 0.6731, 0.3229, 0.1730]],[[0.0661, 0.1905, 0.4490, 0.7484],
[0.4013, 0.1468, 0.2145, 0.8838],
[0.0083, 0.5029, 0.0141, 0.8998],
[0.8673, 0.2308, 0.8808, 0.0532]]])
我们可以看到共三张特征图,每张特征图上对应的值越大,说明属于该特征图对应类的概率越大。
import torch.nn as nn sogtmax = nn.Softmax(dim=0) img = sogtmax(img) print(img)
输出为:
tensor([[[0.2780, 0.4107, 0.4251, 0.1979],
[0.3648, 0.2297, 0.3901, 0.3477],
[0.4035, 0.4396, 0.2993, 0.2967],
[0.2402, 0.4008, 0.3273, 0.4285]],[[0.4371, 0.3817, 0.3022, 0.4117],
[0.2726, 0.5122, 0.4182, 0.2206],
[0.3423, 0.2706, 0.4832, 0.2522],
[0.3718, 0.3648, 0.2449, 0.3028]],[[0.2849, 0.2076, 0.2728, 0.3904],
[0.3627, 0.2581, 0.1917, 0.4317],
[0.2543, 0.2898, 0.2175, 0.4511],
[0.3880, 0.2344, 0.4278, 0.2686]]])
可以看到,上面的代码对每张特征图对应位置的像素值进行Softmax函数处理, 图中标红位置加和=1,同理,标蓝位置加和=1。
我们看到Softmax函数会对原特征图每个像素的值在对应维度(这里dim=0,也就是第一维)上进行计算,将其处理到0~1之间,并且大小固定不变。
print(torch.max(img,0))
输出为:
torch.return_types.max(
values=tensor([[0.4371, 0.4107, 0.4251, 0.4117],
[0.3648, 0.5122, 0.4182, 0.4317],
[0.4035, 0.4396, 0.4832, 0.4511],
[0.3880, 0.4008, 0.4278, 0.4285]]),
indices=tensor([[1, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 2],
[0, 0, 1, 2],
[2, 0, 2, 0]]))
可以看到这里3x4x4变成了1x4x4,而且对应位置上的值为像素对应每个通道上的最大值,并且indices是对应的分类。
清楚理解了上面的流程,那么我们就容易处理了。
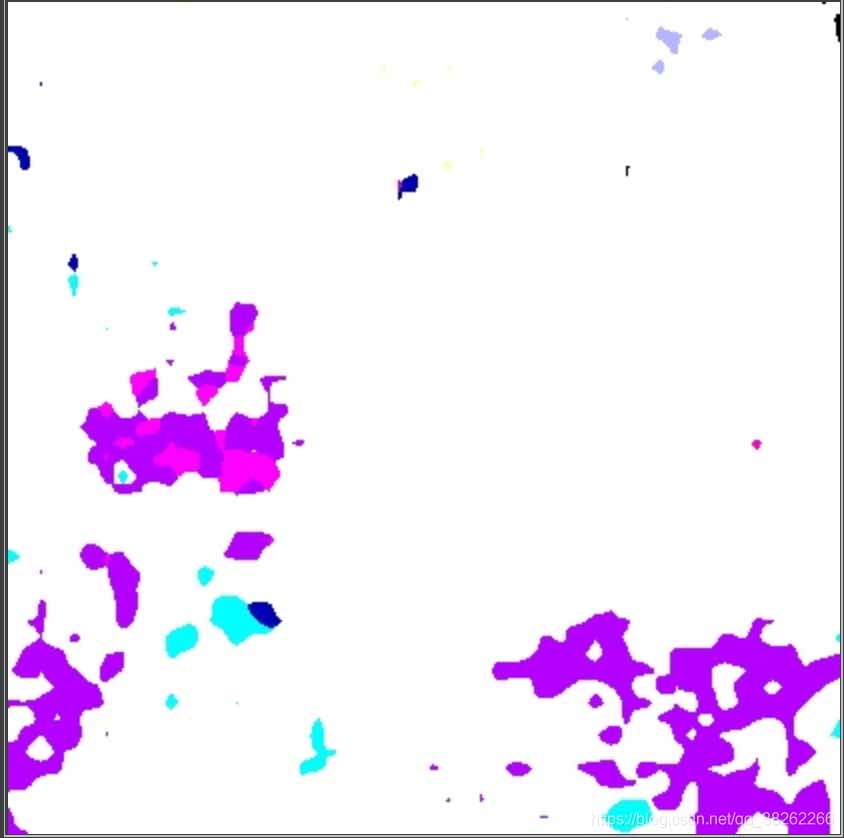
看具体案例,这里输出output的大小为:16x416x416.
output = torch.tensor(output)
sm = nn.Softmax(dim=0)
output = sm(output)
mask = torch.max(output,0).indices.numpy()
# 因为要转化为RGB彩色图,所以增加一维
rgb_img = np.zeros((output.shape[1], output.shape[2], 3))
for i in range(len(mask)):
for j in range(len(mask[0])):
if mask[i][j] == 0:
rgb_img[i][j][0] = 255
rgb_img[i][j][1] = 255
rgb_img[i][j][2] = 255
if mask[i][j] == 1:
rgb_img[i][j][0] = 255
rgb_img[i][j][1] = 180
rgb_img[i][j][2] = 0
if mask[i][j] == 2:
rgb_img[i][j][0] = 255
rgb_img[i][j][1] = 180
rgb_img[i][j][2] = 180
if mask[i][j] == 3:
rgb_img[i][j][0] = 255
rgb_img[i][j][1] = 180
rgb_img[i][j][2] = 255
if mask[i][j] == 4:
rgb_img[i][j][0] = 255
rgb_img[i][j][1] = 255
rgb_img[i][j][2] = 180
if mask[i][j] == 5:
rgb_img[i][j][0] = 255
rgb_img[i][j][1] = 255
rgb_img[i][j][2] = 0
if mask[i][j] == 6:
rgb_img[i][j][0] = 255
rgb_img[i][j][1] = 0
rgb_img[i][j][2] = 180
if mask[i][j] == 7:
rgb_img[i][j][0] = 255
rgb_img[i][j][1] = 0
rgb_img[i][j][2] = 255
if mask[i][j] == 8:
rgb_img[i][j][0] = 255
rgb_img[i][j][1] = 0
rgb_img[i][j][2] = 0
if mask[i][j] == 9:
rgb_img[i][j][0] = 180
rgb_img[i][j][1] = 0
rgb_img[i][j][2] = 0
if mask[i][j] == 10:
rgb_img[i][j][0] = 180
rgb_img[i][j][1] = 255
rgb_img[i][j][2] = 255
if mask[i][j] == 11:
rgb_img[i][j][0] = 180
rgb_img[i][j][1] = 0
rgb_img[i][j][2] = 180
if mask[i][j] == 12:
rgb_img[i][j][0] = 180
rgb_img[i][j][1] = 0
rgb_img[i][j][2] = 255
if mask[i][j] == 13:
rgb_img[i][j][0] = 180
rgb_img[i][j][1] = 255
rgb_img[i][j][2] = 180
if mask[i][j] == 14:
rgb_img[i][j][0] = 0
rgb_img[i][j][1] = 180
rgb_img[i][j][2] = 255
if mask[i][j] == 15:
rgb_img[i][j][0] = 0
rgb_img[i][j][1] = 0
rgb_img[i][j][2] = 0
cv2.imwrite('output.jpg', rgb_img)
最后保存得到的图为:

以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

