Javascript数据结构之栈和队列详解
目录
- 前言
- 栈(stack)
- 栈实现
- 解决实际问题
- 栈的另外应用
- 简单队列(Queue)
- 队列实现
- 队列应用 - 树的广度优先搜索(breadth-first search,BFS)
- 优先队列
- 优先队列实现
- 线性数据结构实现优先队列
- Heap(堆)数据结构实现优先队列
- 代码实现一个二叉堆
- 小顶堆在 React Scheduler 事务调度的包应用
- 最后
前言
我们实际开发中,比较熟悉的数据结构是数组。一般情况下够用了。但如果遇到复杂的问题,数组就捉襟见肘了。在解决一个复杂的实际问题的时候,选择一个更为合适的数据结构,是顺利完成这些任务的前提基础。所以好好了解学习数据结构,对我们高效的解决问题非常重要。
下面我总结了两种我们在实际开发过程中比较常用到的数据结构,简单整理说明一下,希望对大家有帮助。
栈(stack)
栈是一种具有 「后入先出」(Last-in-First-Out,LIFO) 特点的抽象数据结构。
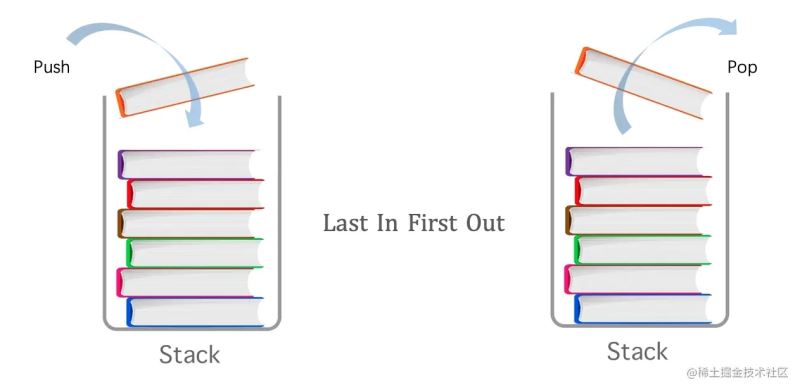
了解栈的样子,最常见的例子如:一摞盘子、一个压入子弹的弹夹。还有比如我们上网使用的浏览器,都有『后退』、『前进』按钮。后退操作,就是把当前正在浏览的页面(栈顶)地址出栈,倒退回之前的地址。我们使用的编辑类的软件,比如 IDE,Word,PhotoShop,他们的撤销(undo)操作,也是用栈来实现的,软件的具体实现代码可能会有比较大的差异,但原理是一样的。
由于栈后入先出的特点,每次只能操作栈顶的元素,任何不在栈顶的元素,都无法访问。要访问下面的元素,先得拿掉上面的元素。所以它是一种高效的数据结构。
用 Javascript 实现一个栈,通常我们用数组就可以。可以做一个简单的封装。
栈实现
栈通常需要实现下面常用功能:
- push(插入新元素,并让新元素成为栈顶元素)
- pop(栈顶元素出栈,并返回栈顶元素)
- peek(想知道栈最后添加的是哪个,用这个方法。返回栈顶元素,不出栈。是个辅助方法)
- clear(清空栈)
- isEmpty(若栈为空,返回 true,否则返回 false)
- size(返回栈元素个数)
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
push(item) {
this.items.push(item);
}
pop() {
return this.items.pop();
}
peek() {
return this.items[this.items.length - 1];
}
clear() {
this.items = [];
}
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
size() {
return this.items.length;
}
}
const stack = new Stack();
stack.push('c++');
stack.push('swift');
stack.push('python');
stack.push('javascript');
console.log(stack.isEmpty()); // false
console.log(stack.size()); // 4
console.log(stack.peek()); // javascript
const removedItem = stack.pop();
console.log(removedItem); // javascript
console.log(stack.peek()); // python
stack.clear();
console.log(stack.isEmpty()); // true
console.log(stack.size()); // 0
解决实际问题
那么栈如何应用解决实际问题,下面是一个例子。
一个十进制转换为二进制的例子:
function transitionToBin(decNumber) {
const stack = new Stack();
do {
// 每次循环计算出的低位值,依次入栈
stack.push(decNumber % 2);
decNumber = Math.floor(decNumber / 2);
} while(decNumber > 0);
let result = '';
// 此时,stack 中存放的是转换后二进制值,栈顶是高位,依次向下。
while (stack.size() > 0) {
// 从栈顶的高位依次出栈,拼接到显示结果中
result += stack.pop();
}
return result;
}
const binNumber = transitionToBin(321);
console.log('binNumber: ', binNumber);
栈的另外应用
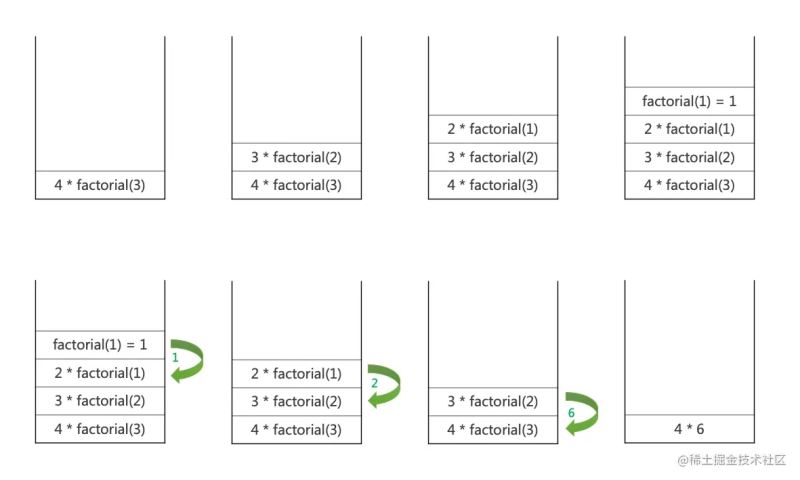
栈也被用于内存保存变量和方法调用。函数调用的时候压栈,return 结果的时候,出栈。比如我们经常用的递归 (recursion) ,就是栈应用的例子。
比如下面一个计算阶乘的例子:
function factorial(n) {
return n > 1 ? n * factorial(n - 1) : n;
}
console.log(factorial(4));
简单队列(Queue)
除了栈,队列也是一种常用的数据结构。队列是由顺序元素组成的线性数据结构,又不同于栈 (Last-in-First-Out,LIFO) ,他遵循的是先进先出(First-In-First-Out,FIFO) 。
队列在队尾添加新元素,在顶部移除元素。
现实中,最常见的队列例子就是排队。
计算机中,队列应用也相当广泛。例如计算机 CPU 作业调度(Job Scheduling)、外围设备联机并发(spooling)、树和图的广度优先搜索(BFS)

队列实现
一个队列数据结构,主要是要实现两个操作:
- enqueue 把一个新元素推入队列
- dequeue 从队列中移除一个已有元素
我们创建一个类来封装一个队列。我们可以使用 javascript 原生的数组来存储里面的数据内容,和 javascript 自带的函数来实现队列的操作。
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
// 推入
enqueue(item) {
this.items.push(item);
}
// 移除
dequeue() {
return this.items.shift();
}
// 队列头元素
peek() {
return this.items[0];
}
// 为空判断
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
size() {
return this.items.length;
}
}
队列应用 - 树的广度优先搜索(breadth-first search,BFS)
我们在遍历一颗树的时候,可以使用栈思路进行深度优先遍历,也可以采用队列的思路,广度优先遍历。假设我们有下面这样一个树形的数据结构,我们查找它所有的节点值。
const treeData = {
node: {
value: 12,
children: [{
value: 30,
children: [{
value: 22,
children: null
}, {
value: 10,
children: [{
value: 5,
children: null
}, {
value: 4,
children: null
}]
}]
}, {
value: 6,
children: [{
value: 8,
children: null
}, {
value: 70,
children: null
}]
}]
}
};
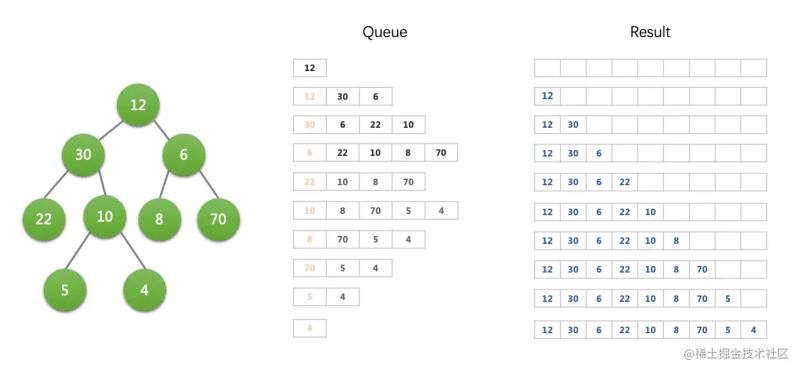
我们用队列进行广度优先的思路来遍历。代码和示意图如下:
function bfs(tree) {
// 准备一个空的队列
const queue = new Queue();
queue.enqueue(tree);
// 一个用于显示结果的数组
const result = [];
do {
// 出队列
let node = queue.dequeue();
result.push(node.value);
if (node.children && node.children.length > 0) {
node.children.forEach(sub => {
queue.enqueue(sub);
});
}
} while (queue.size() > 0);
// 显示遍历结果
console.log('result:', result.join(', '));
}
bfs(treeData.node);
// result: 12, 30, 6, 22, 10, 8, 70, 5, 4
优先队列
在实际情况中,有的队列需要一些特殊的处理方式,出队列规则的不一定是简单粗暴的最早进入队列最先出。 比如:
- 医院对病人的分诊,重症的优先给予治疗
- 我们销售某件商品时,可以按照该商品入库的进货价作为条件,进货价高的优先拿出销售。
于是,就有了优先队列。优先队列是普通队列的一种扩展,它和普通队列不同的在于,队列中的元素具有指定的优先级别(或者叫权重)。 让优先级高的排在队列前面,优先出队。优先队列具有队列的所有特性,包括基本操作,只是在这基础上添加了内部的一个排序。
优先队列实现
因为设置了一些规则,我们可以用顺序存储的方式来存储队列,而不是链式存储。换句话说,所有的节点都可以存储到数组中。
满足上面条件,我们可以利用线性数据结构的方式实现,但时间复杂度较高,并不是最理想方式
线性数据结构实现优先队列
我们要实现优先队列,就会有两种方法。
- 第一种,就是插入的时候,不考虑其他,就在队列末尾插入。而移除的时候,则要根据优先级找出队列中合适的元素移除。
- 第二种是,插入元素的时候,根据优先级找到合适的放置位置,而移除的时候,直接从队列前面移除。
下面以第二种情况为例,实现一个优先队列:
class QItem {
constructor(item, priority) {
this.item = item;
this.priority = priority;
}
toString() {
return `${this.item} - ${this.priority}`;
}
}
class PriorityQueue {
constructor() {
this.queues = [];
}
// 推入
enqueue(item, priority) {
const q = new QItem(item, priority);
let contain = false;
// 这个队列本身总是按照优先级,从大到小的
// 所以找到第一个比要插入值小的那个位置
for (let i = 0; i < this.queues.length; i++) {
if (this.queues[i].priority < q.priority) {
this.queues.splice(i, 0, q);
contain = true;
break;
}
}
// 都比它大,放最后
if (!contain) {
this.queues.push(q);
}
}
// 移除
dequeue() {
return this.queues.shift();
}
// 队列头元素
peek() {
return this.queues[0];
}
isEmpty() {
return this.queues.length === 0;
}
size() {
return this.queues.length;
}
}
const queue = new PriorityQueue();
queue.enqueue('K40', 3100);
queue.enqueue('K50', 5000);
queue.enqueue('K10', 6100);
queue.enqueue('K10', 6000);
queue.enqueue('K10', 5600);
queue.enqueue('K50', 4600);
queue.enqueue('K40', 5900);
console.log(queue.dequeue());
console.log(queue.dequeue());
console.log(queue.dequeue());
console.log(queue.dequeue());
console.log(queue.dequeue());
console.log(queue.dequeue());
console.log(queue.dequeue());
/*
QItem { item: 'K10', priority: 6100 }
QItem { item: 'K10', priority: 6000 }
QItem { item: 'K40', priority: 5900 }
QItem { item: 'K10', priority: 5600 }
QItem { item: 'K50', priority: 5000 }
QItem { item: 'K50', priority: 4600 }
QItem { item: 'K40', priority: 3100 }
*/
Heap(堆)数据结构实现优先队列
上面是简单的使用一个线性数据结构,实现了一个优先队列。我们也可以用实现。这种堆数据存储的时候也是一个线性的,只是这些数据的存放位置有一定规则。
堆可以理解为可以迅速找到一堆数中的最大或者最小值的数据结构
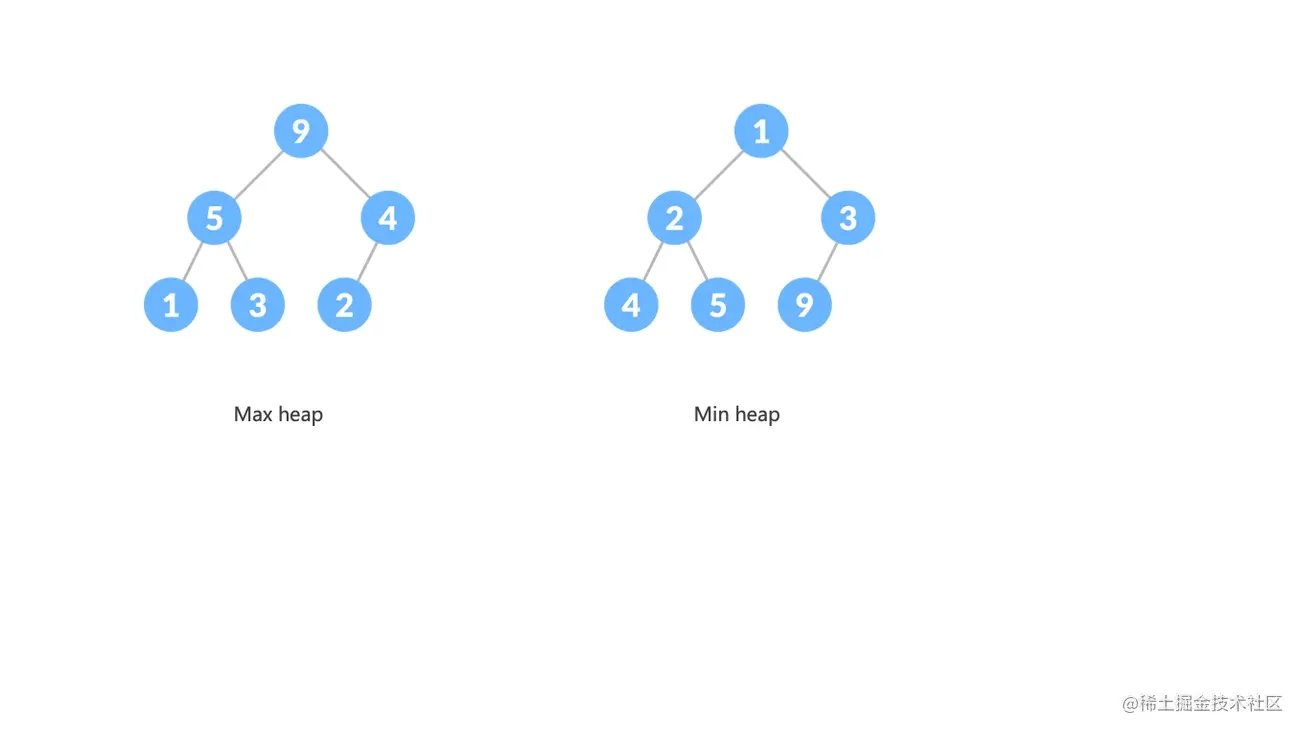
堆是具有特殊特征的完全二叉树(也叫二叉堆)。
二叉堆特点:
- 它是一个完全二叉树(complete binary tree) 的数据结构。所谓完全二叉树(complete binary tree),就是整个二叉树,除了底层的叶子节点,其他的层都是填满的,而且底层的叶子节点,从左到右不能有空的。(这样一个完全二叉树就能使用 Array 这种线性结构来存储)
- 大顶堆(Max heap) :父节点的值大于或者等于子节点的值,堆顶是这个堆的最大元素
- 小顶堆(Min heap) :父节点的值小于或者等于子节点的值,堆顶是这个堆的最小元素
因为完全二叉树的特性,我们可以用一个数组来存储二叉堆
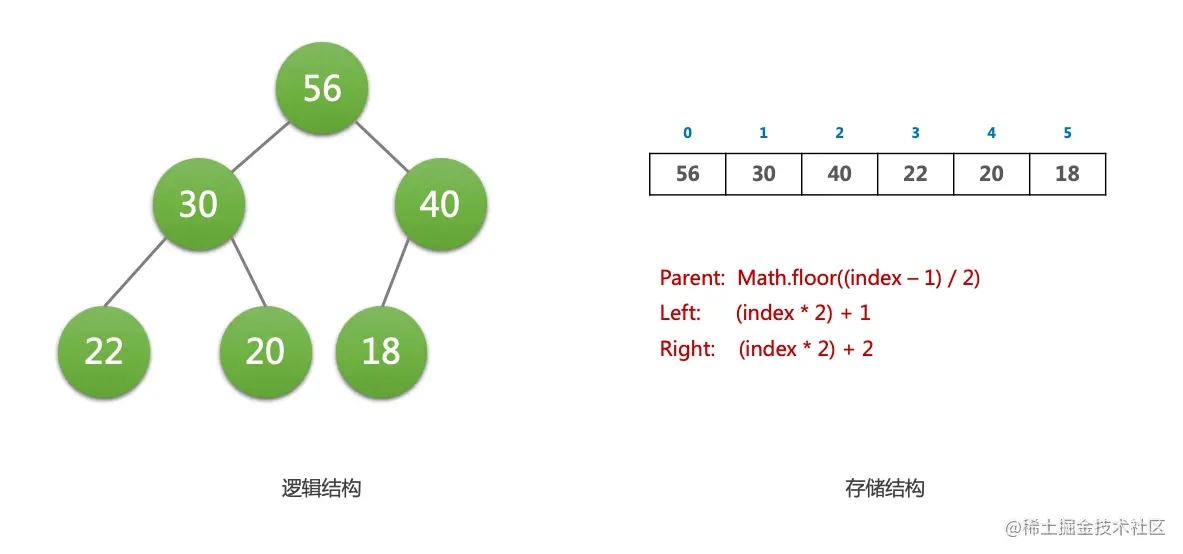
二叉堆是实现堆排序和优先队列的基础。二叉堆常用的应用场景就是优先队列,它处理最大、最小值效率很高。同时堆排序算法也用到了二叉堆。
代码实现一个二叉堆
二叉堆的插入和删除操作比较复杂,我们用 max-heap 举例说明。
插入(enqueue)操作
- 新元素一律先插入到堆的尾部
- 依次向上调整整个堆的结构(一直到根即可)
HeapifyUp

删除(dequeue)操作
- 取出顶部元素(因为它永远是最大那个)
- 将尾元素替换到顶部(先不用管它的大小)
- 依次从根部向下调整整个堆的结构(一直到堆尾即可)
HeapifyDown
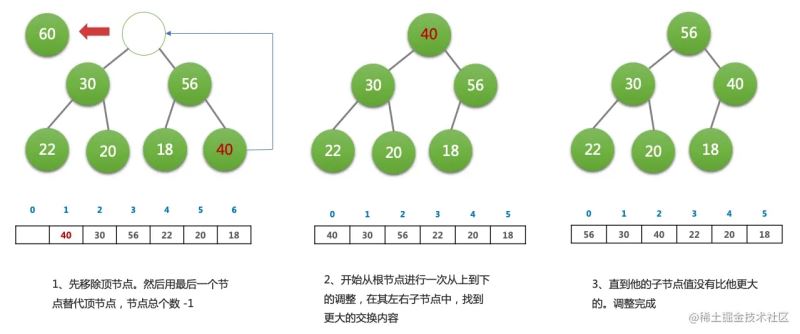
下面是一个 max-heap 的实现。comparator 函数里面修改一下,就可以变成一个 min-heap
class Heap {
constructor(comparator = (a, b) => a - b) {
this.arr = [];
this.comparator = (iSource, iTarget) => {
const value = comparator(this.arr[iSource], this.arr[iTarget]);
if (Number.isNaN(value)) {
throw new Error(`Comparator should evaluate to a number. Got ${value}!`);
}
return value;
}
}
enqueue(val) {
// 插入到末尾
this.arr.push(val);
// 向上冒泡,找到合适位置
this.siftUp();
}
dequeue() {
if (!this.size) return null;
const val = this.arr.shift();
const rep = this.arr.pop();
this.arr.splice(0, 0, rep);
this.siftDown();
}
get size() {
return this.arr.length;
}
siftUp() {
// 新元素索引
let index = this.size - 1;
// 根据完全二叉树的规则,这里我们可以依据元素索引index的值,获得他对应父节点的索引值
const parent = (i) => Math.floor((i - 1) / 2);
if (parent(index) >= 0 && this.comparator(parent(index), index) < 0) {
// 如果父节点存在,并且对比值比当前值小,则交互位置
this.swap(parent(index), index);
index = parent(index);
}
}
siftDown() {
let curr = 0;
const left = (i) => 2 * i + 1;
const right = (i) => 2 * i + 2;
const getTopChild = (i) => {
// 如果右节点存在,并且右节点值比左节点值大
return (right(i) < this.size && this.comparator(left(i), right(i)) < 0)
? right(i) : left(i);
};
// 左节点存在,并且当前节点的值,小于子节点中大的那个值,交换
while (left(curr) < this.size && this.comparator(curr, getTopChild(curr)) < 0) {
const next = getTopChild(curr);
this.swap(curr, next);
curr = next;
}
}
// 交换位置
swap(iFrom, iTo) {
[this.arr[iFrom], this.arr[iTo]] = [this.arr[iTo], this.arr[iFrom]];
}
}
const heap = new Heap();
heap.enqueue(56);
heap.enqueue(18);
heap.enqueue(20);
heap.enqueue(40);
heap.enqueue(30);
heap.enqueue(22);
console.log('heapify: ', heap.arr.join(', '));
heap.dequeue();
console.log('step 1: ', heap.arr.join(', '));
heap.dequeue();
console.log('step 2: ', heap.arr.join(', '));
heap.dequeue();
console.log('step 3: ', heap.arr.join(', '));
// heapify: 56, 40, 22, 18, 30, 20
// step 1: 40, 30, 22, 18, 20
// step 2: 30, 20, 22, 18
// step 3: 22, 20, 18
如上面代码所示,数据进入队列是无序的,但在出队列的时候,总是能找到最大那个。这样也实现了一个优先队列。
小顶堆在 React Scheduler 事务调度的包应用
Scheduler 存在两个队列,timerQueue(未就绪任务队列) 和 taskQueue(就绪任务队列)。当有新的未就绪任务被注册,就会 push 到 timerQueue 中,并根据开始时间重新排列任务顺序。
push 方法是在一个叫 schedulerMinHeap.js 的文件中基于最小堆(min-heap)来实现的。schedulerMinHeap 源码
export function push(heap: Heap, node: Node): void {
const index = heap.length;
heap.push(node);
siftUp(heap, node, index);
}
看到代码中,在 push 之后,调用了 siftUp 来重新整理顺序
function siftUp(heap, node, i) {
let index = i;
while (index > 0) {
const parentIndex = (index - 1) >>> 1;
const parent = heap[parentIndex];
if (compare(parent, node) > 0) {
// The parent is larger. Swap positions.
heap[parentIndex] = node;
heap[index] = parent;
index = parentIndex;
} else {
// The parent is smaller. Exit.
return;
}
}
}
这里计算 parentIndex 是用了位移的方法(等价于除以 2 再去尾),帅!
最后
数据结构还有很多内容,这里只是简单的说了两种,为了能引导大家去学习其他更复杂的数据结构知识。真正的掌握数据结构,并把它应用于实际工作中,对我们非常重要。
到此这篇关于Javascript数据结构之栈和队列的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关js栈和队列内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

