vue3:vue2中protoType更改为config.globalProperties问题
目录
- protoType替换为config.globalProperties
- Vue3 vs Vue2
- Vue3 的新组件
- 文件对比
- 全局 API
protoType替换为config.globalProperties
在main.js中:
vue2
Vue.prototype.$verson = '1.0.0'
使用
this.$verson
vue3
Vue.config.globalProperties.$verson = '1.0.0'
使用
<script setup lang="ts">
import {getCurrentInstance} from 'vue'
console.log(getCurrentInstance().appContext.config.globalProperties.$verson)
</script>
Vue3 vs Vue2
Vue3 的新组件
Fragment
Vue2 中:组件必须有一个根标签
Vue3 中:可以没有根标签,内部会添加根标签 <fragment> </fragment>
好处:减少标签层级,减少内存消耗
<template>
<h1>App</h1>
<p>superman</p>
</template>
<script>
export default { name: "App" };
</script>
Teleport
用于将组件的 HTML 结构移动到指定位置
用法:
① 用 Teleport 标签将需要移动的 HTML 结构包裹住
② 设置 to 属性,属性值为 选择器,以指定移动到的位置
默认情况下,子组件的 HTML 结构会显示到父组件的 HTML 结构里面;
使用 Teleport 标签包裹子组件的 HTML 标签,则能将该 HTML 结构显示到指定的位置
<template>
<div class="box">
<h1>App</h1>
<button @click="bol = !bol">显示 / 隐藏</button>
<Son v-if="bol" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from "vue";
import Son from "./components/Son.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { Son },
setup() {
let bol = ref(false);
return { bol };
},
};
</script>
<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: palevioletred;
position: relative;
}
</style>
<template>
<!-- 默认情况下,显示到 .box 里面 -->
<h2>Son</h2>
<!-- 通过 Teleport 标签,将 HTML 结构显示到 body 里面 -->
<Teleport to="body">
<h2>Teleport Son</h2>
</Teleport>
</template>
<script>
export default { name: "Son" };
</script>
Suspense
等待异步组件时,渲染一些额外的内容,提升用户体验感
用法:
① 在父组件中,异步引入组件:defineAsyncComponent + 懒加载
② 在子组件中,配置 Suspense 标签
③ 在 Suspense 标签内,用 template 标签设置具名插槽
default 插槽的内容:为异步引入的组件
fallback 插槽的内容:为加载时显示的内容
此时,异步引入的组件中 setup 可以是 async 函数
<template>
<div class="box">
<h1>App</h1>
<Suspense>
<!-- 需要显示的异步组件 -->
<template v-slot:default>
<Son></Son>
</template>
<!-- 异步组件显示之前,暂时先显示的内容 -->
<template #fallback>
加载中...
</template>
</Suspense>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 静态引入
// import Son from "./components/Son.vue";
// 异步引入
import { defineAsyncComponent } from 'vue';
const Son = defineAsyncComponent(() => import("./components/Son.vue"));
export default {
name: "App",
components: { Son },
};
</script>
<template>
<h2>Son: {{ p }}</h2>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Son",
// 此时 setup 也可以是 async 函数
async setup() {
let p = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("superman")
}, 1000);
});
return { p };
}
};
</script>
文件对比
main.js
Vue2
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
Vue3
引入的不再是 Vue 构造函数,而是工厂函数 createApp:
构造函数:通过 new 关键字调用,首字母大写
工厂函数:直接调用,首字母小写
createApp 返回:应用实例对象 (相当于 Vue2 中的 vm,但比 vm 轻)
可以在 createApp 之后链式调用其它方法
import { createApp } from 'vue' // 引入 createApp 方法
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
createApp(App).use(store).use(router).mount('#app') // 链式调用
store 文件
Vue2
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
modules: {}
})
Vue3
import { createStore } from 'vuex' // 引入 createStore 方法
export default createStore({
state: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
modules: {}
})
Vuex 的使用
先配置好 store 文件:
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
export default createStore({
state: {
name: "superman",
arr: [1, 2, 3]
},
mutations: {
muModify(state, val) {
console.log("commit muModify", val)
state.name += val
}
},
actions: {
acModify(context, val) {
console.log("dispatch acModify", val)
context.commit("muModify", val)
}
},
getters: {
getArr(state) {
return state.arr.map(item => item * 2)
}
},
modules: {}
})
Vue3 中需要通过 useStore 方法使用 vuex
<template>
<p>普通使用:</p>
<p>$store.state.name: {{ $store.state.name }}</p>
<p>$store.state.arr: {{ $store.state.arr }}</p>
<p>$store.getters.getArr: {{ $store.getters.getArr }}</p>
<hr />
<p>Vue 3:</p>
<p>name: {{ name }}</p>
<p>arr: {{ arr }}</p>
<p>getArr: {{ getArr }}</p>
<hr />
<button @click="coModify">coModify name</button> |
<button @click="diModify">diModify name</button>
</template>
<script>
import { useStore } from "vuex";
export default {
name: "App",
setup() {
// 通过 useStore 使用 Vuex
const store = useStore();
// 获取数据
let name = store.state.name;
let arr = store.state.arr;
let getArr = store.getters.getArr;
// 调用 dispatch 方法
function diModify() {
store.dispatch("acModify", "(Actions)");
}
// 调用 commit 方法
function coModify() {
store.commit("muModify", "(Mutations)");
}
return { name, arr, getArr, coModify, diModify };
},
};
</script>
但是,通过该方法获取的数据不是响应式的
响应式数据设置如下:需要配合 computed 方法使用
let name = computed(() => store.state.name); let arr = computed(() => store.state.arr); let getArr = computed(() => store.getters.getArr);
router 文件
Vue2
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Home from '../views/Home.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [{
path: '/',
name: 'Home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'About',
component: () => import('../views/About.vue')
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history', // 设置路由模式为 history
base: process.env.BASE_URL, // 根据 webpack 环境,设置 [根路径]
routes
})
export default router
Vue3
import {
createRouter, // 引入 createRouter 方法
createWebHistory // 引入 createWebHistory 方法
} from 'vue-router'
import Home from '../views/Home.vue'
const routes = [{
path: '/',
name: 'Home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'About',
component: () => import('../views/About.vue')
}
]
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(process.env.BASE_URL),
routes
})
export default router
vue-router 的使用
先配置 router 文件
import {
createRouter,
createWebHistory
} from 'vue-router'
import Home from '../views/Home.vue'
const routes = [{
path: '/',
name: 'Home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'About',
component: () => import('../views/About.vue')
}
]
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(process.env.BASE_URL),
routes
})
export default router
Vue3 中需要通过 useRoute 方法使用 vue-router
<template>
<router-link to="/">Home</router-link> |
<router-link to="/about">About</router-link>
<router-view />
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
};
</script>
<template>
<h1>About</h1>
</template>
<script>
import {
useRoute,
useRouter,
onBeforeRouteLeave,
onBeforeRouteUpdate,
} from "vue-router";
export default {
name: "About",
setup() {
// 当前路由对象
let route = useRoute();
console.log("route", route);
// 总路由对象
let router = useRouter(router);
console.log("router", router);
// 路由守卫
onBeforeRouteLeave(() => {
console.log("onBeforeRouteLeave:离开路由时触发");
});
onBeforeRouteUpdate(() => {
console.log("onBeforeRouteUpdate:复用路由时触发");
});
return {};
},
};
</script>
<template>
<h1>Home</h1>
</template>
<script>
export default { name: "Home" };
</script>
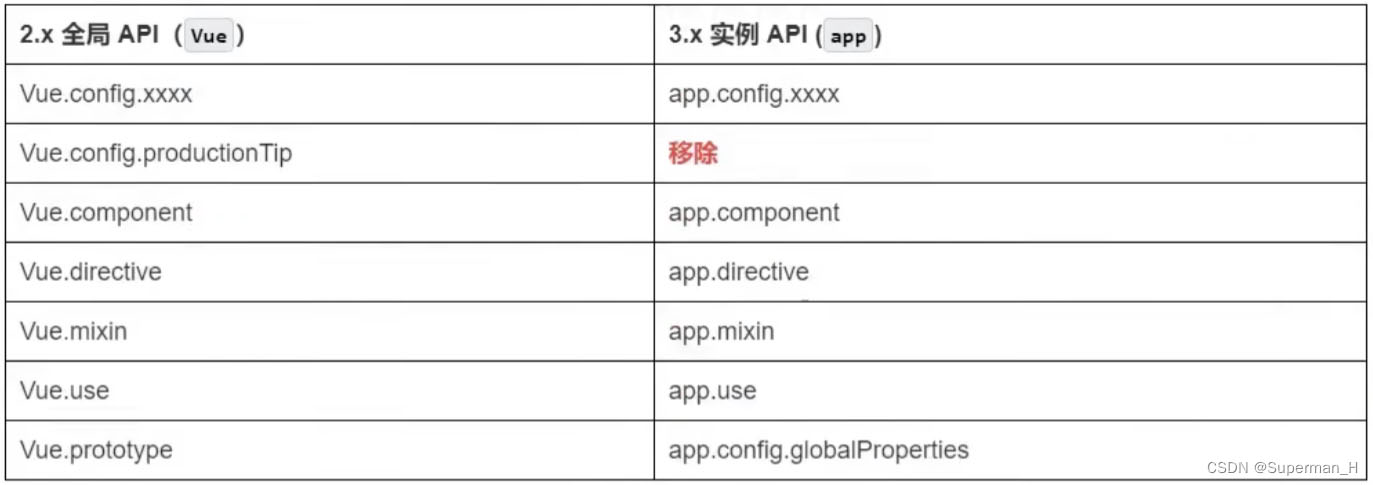
全局 API
在 Vue3 中,全局和内部 API 都经过了重构
全局 API 现在只能作为 ES 模块构建的命名导出进行访问
import { nextTick } from 'vue'
nextTick(() => {
// 一些和DOM有关的东西
})
Vue.XXX → app.XXX
全局 directive
Vue2 - Vue.directive("自定义指令名", 配置对象)
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.directive("focus", {
bind() {
console.log("指令与元素绑定时触发");
},
inserted(el) {
console.log("指令所在元素插入页面时触发");
el.focus();
},
update(el) {
console.log("模板重新渲染时触发");
el.focus();
}
});
new Vue({ render: h => h(App) }).$mount('#app')
也可以使用简写(回调函数执行完后,DOM 才会插入到页面中):
Vue.directive("focus", (el, msg) => {
console.log(el, msg); // el:挂载的元素;val:挂载的信息
console.log(msg.value); // 获取指令的属性值
});
Vue3 - app.directive("自定义指令名", 配置对象)
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
const app = createApp(App)
// 自定义指令,指令具有一组生命周期钩子:
app.directive('myIns', {
// 在绑定元素的 attribute 或事件监听器被应用之前调用
created() {},
// 在绑定元素的父组件挂载之前调用
beforeMount() {},
// 在绑定元素的父组件挂载之后调用
mounted() {},
// 在包含组件的 VNode 更新之前调用
beforeUpdate() {},
// 在包含组件的 VNode 及其子组件的 VNode 更新之后调用
updated() {},
// 在绑定元素的父组件卸载之前调用
beforeUnmount() {},
// 在绑定元素的父组件卸载之后调用
unmounted() {}
});
app.mount('#app')
钩子函数接收 2 个参数:
el:指令绑定到的元素,可用于直接操作 DOM。eg:el.focus()binding:配置对象instance:使用指令的组件实例value:传递给指令的值oldValue:先前的值,仅在 beforeUpdate 和 updated 中可用。无论值是否有更改都可用arg:传递给指令的参数(如果有的话)eg:v-my-directive:foo 中,arg 为 "foo"。modifiers:修饰符对象(如果有的话)eg:v-my-directive.foo.bar 中,修饰符对象为 {foo: true,bar: true}dir:配置对象本身
全局属性
- 全局属性:在任何组件中都可以访问
- 与组件的属性发生命名冲突时,组件的属性优先级更高
Vue2 - Vue.prototype
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.prototype.$myData = "superman" // 设置全局属性
new Vue({ render: h => h(App) }).$mount('#app')
Vue3 - app.config.globalProperties
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
const app = createApp(App)
app.config.globalProperties.$myData = "superman" // 设置全局属性
app.mount('#app')
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

