详解MyBatis resultType与resultMap中的几种返回类型
目录
- 一、返回集合
- 1.返回JavaBean集合
- 2.返回 Map 集合
- 二、返回 Map
- 1.一条记录
- 2.多条记录,需要指定 Map 的 Key 和 Value 的类型
- 三、返回 resultMap 自定义结果集封装
- 1.自定义 JavaBean 的封装
- 2.关联查询的封装,一对一,JavaBean 属性包含 JavaBean
- 3.关联查询的封装,一对多,JavaBean 属性包含 JavaBean 的集合
- 4.鉴别器discriminator
一、返回集合
1.返回JavaBean集合
public List<MyUser> selectMyUserByNameLike(String name);
<!-- resultType 集合内的元素类型 -->
<select id="selectMyUserByNameLike" resultType="myUser" parameterType="string">
select * from myuser where name like #{name}
</select>
测试方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
SqlSession session = null;
try {
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
MyUserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(MyUserMapper.class);
List<MyUser> myUsers = mapper.selectMyUserByNameLike("%a%");
System.out.println(myUsers);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (session != null) {
session.close();
}
}
}

2.返回 Map 集合
<!--public List<Map<String,Object>> getMyUser()--> <select id="getMyUser" resultType="map"> select * from myuser </select>

二、返回 Map
1.一条记录
public Map<String,Object> selectMyUserById(Integer id);
<select id="selectMyUserById" resultType="map" parameterType="integer">
select * from myuser where id = #{id}
</select>
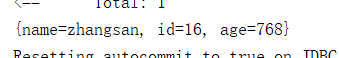
2.多条记录,需要指定 Map 的 Key 和 Value 的类型
// 指定 Map 的 Key 从记录中的 id 列获取
@MapKey("id")
public Map<String,MyUser> selectMyUserByGtId(Integer id);
<!-- resultType Map 中 value 的类型 -->
<select id="selectMyUserByGtId" resultType="myUser" parameterType="integer">
select * from myuser where id > #{id}
</select>

三、返回 resultMap 自定义结果集封装
关于自动映射封装的配置
<settings>
<!-- 自动映射有三种模式,NONE、PARTIAL、FULL。NONE 不启用自动映射,PARTIAL 只对非嵌套的 resultMap 进行自动映射,FULL 表示对所有的 resultMap 都进行自动映射。默认为 PARTIAL -->
<setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="PARTIAL"/>
<!-- 数据库字段下划线转Bean字段的驼峰命名 -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
<!-- 控制台打印SQL -->
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING" />
</settings>
默认数据库字段与 JavaBean 对应不上时可开启驼峰命名或查询时使用别名http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/sqlmap-xml.html
1.自定义 JavaBean 的封装
确认是否成功可以关掉 MyBatis 的自动映射
<setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="NONE"/>
public MyUser selectMyUserById(Integer id);
<!-- 自定义某个 javaBean 的封装规则
type:自定义规则中JavaBean类型的全路径,可用别名
id:唯一id方便引用 -->
<resultMap type="myUser" id="myUserResultMap">
<!-- 指定主键列的封装规则,用 id 标签定义主键会底层有优化
column:指定哪一列
property:指定对应的javaBean属性 -->
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<!-- 定义普通列封装规则 -->
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<!-- 其他不指定的列会自动封装:建议只要写 resultMap 就把全部的映射规则都写上 -->
<result column="age" property="age"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- 使用 resultMap,不使用 resultType -->
<select id="selectMyUserById" resultMap="myUserResultMap" parameterType="integer">
select * from myuser where id = #{id}
</select>
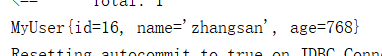
2.关联查询的封装,一对一,JavaBean 属性包含 JavaBean
public MyUser selectMyUserById(Integer id);
直接调用属性赋值
<resultMap type="myUser" id="myUserResultMap">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="age" property="age"/>
<!--直接属性封装-->
<result column="did" property="dept.id"/>
<result column="dname" property="dept.name"/>
</resultMap>
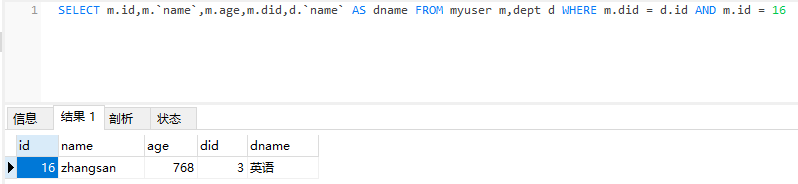
<select id="selectMyUserById" resultMap="myUserResultMap" parameterType="integer">
SELECT m.id, m.name, m.age, m.did, d.name AS dname FROM myuser m,dept d WHERE m.did = d.id AND m.id = #{id}
</select>

使用association
<resultMap type="com.bean.MyUser" id="myUserResultMap">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="age" property="age"/>
<!-- association 指定联合的 javaBean 对象
property="dept":指定哪个属性是联合的对象
javaType:指定这个属性对象的类型[不能省略] -->
<association property="dept" javaType="com.bean.Dept">
<id column="did" property="id"/>
<result column="dname" property="name"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
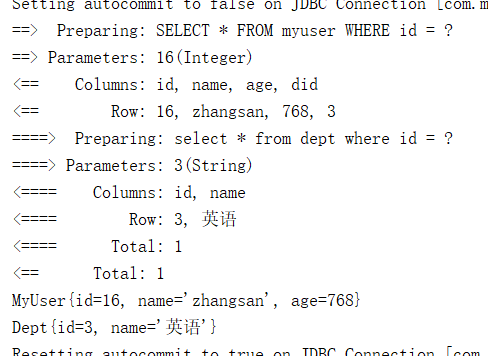
<select id="selectMyUserById" resultMap="myUserResultMap" parameterType="integer">
SELECT m.id, m.name, m.age, m.did, d.name AS dname FROM myuser m,dept d WHERE m.did = d.id AND m.id = #{id}
</select>
使用association 二次查询,即有两条 SQL
<resultMap id="myUserResultMap" type="com.bean.MyUser">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="age" property="age"/>
<!-- association 定义关联对象的封装规则
select:当前属性是调用 select 指定的方法查出的结果
column:将哪一列的值传给这个方法 -->
<association property="dept" select="com.dao.DeptMapper.selectDeptById" column="did"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectMyUserById" resultMap="myUserResultMap" parameterType="integer">
SELECT * FROM myuser WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- namespace 对应接口文件的全路径 -->
<mapper namespace="com.dao.DeptMapper">
<select id="selectDeptById" resultType="dept" parameterType="string">
select * from dept where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
开启懒加载:在没有使用 Dept 的属性时,则只会加载 MyUser 的属性。即只会发送一条 SQL 语句,要使用Dept 属性时才会发送第二条 SQL。不会一次性发送两条 SQL
<!-- 延迟加载的全局开关。当开启时,所有关联对象都会延迟加载。 特定关联关系中可通过设置fetchType属性来覆盖该项的开关状态。默认false --> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <!-- 当开启时,任何方法的调用都会加载该对象的所有属性。否则,每个属性会按需加载。默认false (true in ≤3.4.1) --> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
3.关联查询的封装,一对多,JavaBean 属性包含 JavaBean 的集合
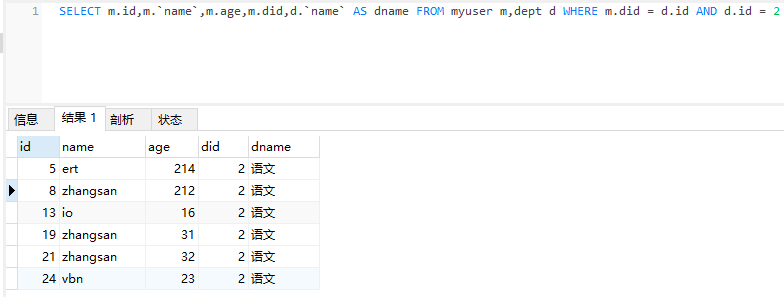
使用association
public Dept getDeptById(Integer id);
<resultMap type="com.bean.Dept" id="MyDept">
<id column="did" property="id"/>
<result column="dname" property="name"/>
<!-- collection 定义关联集合类型的属性封装规则
ofType 指定集合里面元素的类型 -->
<collection property="myUsers" ofType="com.bean.MyUser">
<!-- 定义集合中元素的封装规则 -->
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="age" property="age"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="getDeptById" resultMap="MyDept">
SELECT m.id,m.name,m.age,m.did,d.name AS dname FROM myuser m,dept d WHERE m.did = d.id AND d.id = #{id}
</select>

关闭懒加载,使用二次查询
public Dept getDeptByIdStep(Integer did);
<!-- Collection 分段查询 -->
<resultMap type="com.bean.Dept" id="MyDeptStep">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<collection property="myUsers" select="com.dao.MyUserMapper.selectMyUserByDid"
column="{did=id}" fetchType="eager"/>
<!-- column 要处理复合主键或传递多个值过去:可以将多列的值封装 Map 传递,指定多个列名通过 column="{prop1=col1,prop2=col2}"
语法来传递给嵌套查询语句。这会引起 prop1 和 prop2 以参数对象形式来设置给目标嵌套查询语句
fetchType="lazy":是否延迟加载,优先级高于全局配置,lazy:延迟,eager:立即 -->
</resultMap>
<select id="getDeptByIdStep" resultMap="MyDeptStep">
select * from dept where id = #{id}
</select>
public List<MyUser> selectMyUserByDid(Integer dId);
<select id="selectMyUserByDid" resultType="myUser">
select * from myuser where dId = #{did}
</select>

4.鉴别器discriminator
<!--public MyUser selectMyUserById(Integer id);-->
<select id="selectMyUserById" resultMap="MyEmpDis" parameterType="integer">
SELECT * FROM myuser WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
<resultMap id="MyEmpDis" type="com.bean.MyUser">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="age" property="age"/>
<!-- column:指定判定的列名 javaType:列值对应的java类型 -->
<discriminator javaType="integer" column="age">
<!-- 21岁 封装课程至 JavaBean -->
<case value="21" resultType="com.bean.MyUser">
<association property="dept" select="com.dao.DeptMapper.selectDeptById" column="did"/>
</case>
<!-- 33岁 不封装课程至 JavaBean 且把 age 赋值给 id -->
<case value="33" resultType="com.bean.MyUser">
<result column="age" property="id"/>
</case>
</discriminator>
</resultMap>
<!--public Dept selectDeptById(Integer id);-->
<select id="selectDeptById" resultType="dept" parameterType="string">
select * from dept where id = #{id}
</select>


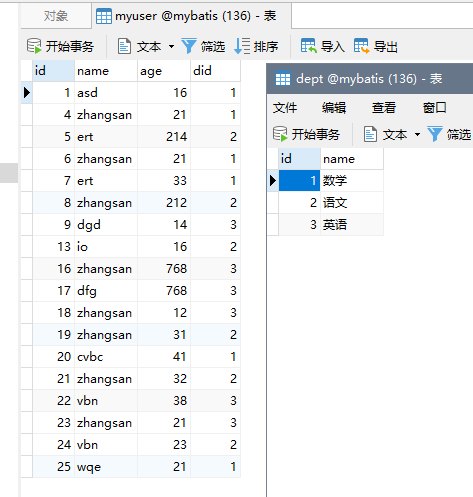
上面测试中使用的实体类与数据
public class Dept {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private List<MyUser> myUsers;
public class MyUser {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Dept dept;
https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/sqlmap-xml.html
到此这篇关于详解MyBatis resultType与resultMap中的几种返回类型的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关MyBatis resultType与resultMap返回类型内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!
赞 (0)

