C++模板以及实现vector实例详解
目录
- 函数模板
- 类模板
- Vector实现
- 简单的类模板实现代码及测试:
- win msvc编译器的实现:
- 容器的空间配置器
- 运算符重载与迭代器实现
- 最终vector的实现代码
- 总结
函数模板
函数模板:是不进行编译的,因为类型还不知道
模板的实例化:函数调用点进行实例化
模板函数:才是要被编译器所编译的
模板类型参数:typyname/class
模板非类型参数:模板非类型形参的详细阐述
模板的实参推演:可以根据用户传入的实参的类型,来推导出模板类型参数的具体
模板的特例化(专用化)的实例化
模板函数、模板的特例化和非模板函数的重载关系:候选的函数中,优先在精确匹配中选择,优先选择普通函数,特例性更强的模版函数次之,然后是模版函数的特化版本,最后才是泛化版本。
模板代码是不能声明在.h,实现在.cpp,模板代码调用之前,一定要看到模板定义的地方,这样的话,模板才能够正常的实例化,产生能够被编译器编译的代码。模板代码都是放在头文件中,然后在源文件中直接进行#include
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
//函数模板
template<typename T> //定义一个模板参数列表
bool compare(T a, T b) {//compare 是一个函数模板
std::cout << "template compare\n";
return a > b;
}
/*
在函数调用点,编译器用用户指定的类型,从原模板实例化一份函数代码出来:
模板函数:
bool compare<int>(int a, int b) {
return a > b;
}
bool compare<double>(double a, double b) {
return a > b;
}
*/
//模板特例化: 针对compare函数模板,提供const char * 类型的特例化版本
template<>
bool compare<const char *>(const char* a, const char * b) {
std::cout << "const char * compare\n";
return strcmp(a, b) > 0;
}
//非模板函数,普通函数
bool compare(const char* a, const char * b) {
std::cout << "normal compare\n";
return strcmp(a, b) > 0;
}
int main()
{
std::cout << compare<int>(1, 2) << std::endl;
std::cout << compare<double>(1, 2) << std::endl;
std::cout << compare(1, 2) << std::endl;//模板的实参推演 可以根据用户传入的实参的类型,来推导模板类型参数
//编译器优先把compare处理成函数名,没有的话,才去找compare模板
std::cout << compare("a", "b") << std::endl;//
return 0;
}
类模板
实现一个顺序栈
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
template<typename T>
class SeqStack
{
public:
//构造和析构函数名不加<T> 其他出现模板的地方都加上类型参数列表
SeqStack(int size = 10)
:pstack_(new T[size])
,top_(0)
,size_(size){
//初始化生成的指令更少,效率更高。仅调用默认构造函数(如果存在类成员)。赋值需要调用默认构造函数和赋值运算符
}
~SeqStack() {
if (pstack_) {
delete[] pstack_;
pstack_ = nullptr;
}
}
SeqStack(const SeqStack<T>& stack)
:top_(stack.top_),
size_(stack.size_){
pstack_ = new T[stack.size_];
for (int i = 0; i < top_; ++i) {
pstack_[i] = stack.pstack_[i];
}
}
SeqStack<T>& operator=(const SeqStack<T>&stack) {
if (this == &stack) {
return *this;
}
delete[] pstack_;
top_ = stack.top_;
size_ = stack.size_;
pstack_ = new T[stack.size_];
for (int i = 0; i < top_; ++i) {
pstack_[i] = stack.pstack_[i];
}
}
void push(const T& val) {
if (full()) {
resize();
}
pstack_[top_] = val;
top_++;
}
void pop() {
if (empty()) {
return;
}
top_--;
}
T top() const {
if (empty()) {
throw "stack is empty";
}
return pstack_[top_-1];
}
bool full() const {
return top_ == size_;
}
bool empty() const {
return top_ == 0;
}
protected:
private:
void resize() {
T * p = new T[size_ * 2];
for (int i = 0; i < top_; ++i) {
p[i] = pstack_[i];
}
size_ *= 2;
delete pstack_;
pstack_ = p;
}
T * pstack_;
int top_;
int size_;
};
int main()
{
SeqStack<int> stack;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
stack.push(i);
}
while (!stack.empty())
{
std::cout << stack.top() << " ";
stack.pop();
}
return 0;
}
Vector实现

vector 的本质是一个数组,在vector 中需要有三个指针:
_first :指向数组的起始位置
_last:指向已经存放的最后一个元素的下一个位置
_end:指向数组长度的末尾元素的下一个位置。
数组的容量=_end-_first
数组中存放的元素个数=_last-_first
数组是否为空:_first == _last
数组是否已满:_last == _end
简单的类模板实现代码及测试:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
template<typename T>
class vector
{
public:
vector(int size = 10)
{
_first = new T[size];
_last = _first;
_end = _first + size;
}
~vector()
{
delete[]_first;
_first = _end = _last = nullptr;
}
vector(const vector<T>& rhs)
{
int size = rhs._end - rhs._first;
_first = new T[size];
int len = rhs._last - rhs._first;
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
_first[i] = rhs._first[i];
}
_last = _first + len;
_end = _first + size;
}
vector<T>& operator=(const vector<T>& rhs)
{
if (this == &rhs)
return *this;
delete[]_first;
int size = rhs._end - rhs._first;
_first = new T[size];
int len = rhs._last - rhs._first;
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
_first[i] = rhs._first[i];
}
_last = _first + len;
_end = _first + size;
return *this;
}
void push_back(const T& val) // 向容器末尾添加元素
{
if (full())
expand();
*_last++ = val;
}
void pop_back() // 从容器末尾删除元素
{
if (empty())
return;
--_last;
}
T back()const // 返回容器末尾的元素的值
{
return *(_last - 1);
}
bool full()const { return _last == _end; }
bool empty()const { return _first == _last; }
int size()const { return _last - _first; }
private:
T* _first; // 指向数组起始的位置
T* _last; // 指向数组中有效元素的后继位置
T* _end; // 指向数组空间的后继位置
void expand() // 容器的二倍扩容
{
int size = _end - _first;
T *ptmp = new T[2 * size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
ptmp[i] = _first[i];
}
delete[]_first;
_first = ptmp;
_last = _first + size;
_end = _first + 2 * size;
}
};
class Test
{
public:
Test() { std::cout << "Test()" << std::endl; }
Test& operator=(const Test&t) { std::cout << "operator=" << std::endl; return *this; }
~Test() { std::cout << "~Test()" << std::endl; }
Test(const Test&) { std::cout << "Test(const Test&)" << std::endl; }
};
int main()
{
Test t1, t2;
std::cout << "vector<Test> vec" << std::endl;
vector<Test> vec;
std::cout << "vector<Test> vec; push_back" << std::endl;
vec.push_back(t1);
vec.push_back(t2);
std::cout << "vector<Test> vec; pop_back" << std::endl;
vec.pop_back();
return 0;
}

问题:在我们实现的vector构造函数中,使用new T[size] :它做了两件事情
(1)开辟内存空间
(2)调用T类型的默认构造函数构造对象
其中第二步是一种浪费,因为我还没在vector 添加元素,提前构造一遍对象 然后在析构时候是否纯属多余。
同时:在实现pop_back()时,存在内存泄漏
void pop_back() // 从容器末尾删除元素
{
if (empty())
return;
--_last;
}
T
仅仅将_last指针 --,并没有释放Test申请的资源。需要调用对象的析构函数
win msvc编译器的实现:
// CLASS TEMPLATE vector
template<class _Ty,
class _Alloc = allocator<_Ty>>
class vector
: public _Vector_alloc<_Vec_base_types<_Ty, _Alloc>>
{ // varying size array of values
private:
using _Mybase = _Vector_alloc<_Vec_base_types<_Ty, _Alloc>>;
using _Alty = typename _Mybase::_Alty;
using _Alty_traits = typename _Mybase::_Alty_traits;
......
系统的实现,除了数据类型外,还有一个allocator,它将开辟空间和构造对象分离开。
而这,也就是空间配置器做的工作;
容器的空间配置器
空间配置器主要有四个功能:
- 内存开辟 allocate(底层调用malloc);
- 内存释放 deallocate(底层调用free);
- 对象构造 construct(调用构造函数);
- 对象析构 destroy(调用析构函数
// 定义容器的空间配置器,和C++标准库的allocator实现一样
template<typename T>
struct Allocator
{
T* allocate(size_t size) // 负责内存开辟
{
return (T*)malloc(sizeof(T) * size);
}
void deallocate(void* p) // 负责内存释放
{
free(p);
}
void construct(T* p, const T& val) // 负责对象构造
{
new (p) T(val); // 定位new
}
void destroy(T* p) // 负责对象析构
{
p->~T(); // ~T()代表了T类型的析构函数
}
};
修改后的vector
#include <iostream>
// 定义容器的空间配置器,和C++标准库的allocator实现一样
template<typename T>
class Allocator
{
public:
T* allocate(size_t size) // 负责内存开辟
{
return (T*)malloc(sizeof(T) * size);
}
void deallocate(void* p) // 负责内存释放
{
free(p);
}
void construct(T* p, const T& val) // 负责对象构造
{
new (p) T(val); // 定位new
}
void destroy(T* p) // 负责对象析构
{
p->~T(); // ~T()代表了T类型的析构函数
}
};
template<typename T, typename Alloc = Allocator<T>>
class vector
{
public:
vector(int size = 10)
{
// 需要把内存开辟和对象构造分开处理
_first = _allocator.allocate(size);
_last = _first;
_end = _first + size;
}
~vector()
{
// 析构容器有效的元素,然后释放_first指针指向的堆内存
for (T* p = _first; p != _last; ++p)
{
_allocator.destroy(p); // 把_first指针指向的数组的有效元素进行析构操作
}
_allocator.deallocate(_first); // 释放堆上的数组内存
_first = _last = _end = nullptr;
}
vector(const vector<T>& rhs)
{
int size = rhs._end - rhs._first;
_first = _allocator.allocate(size);
int len = rhs._last - rhs._first;
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
_allocator.construct(_first + i, rhs._first[i]);
}
_last = _first + len;
_end = _first + size;
}
vector<T>& operator=(const vector<T>& rhs)
{
if (this == &rhs)
return *this;
for (T* p = _first; p != _last; ++p)
{
_allocator.destroy(p); // 把_first指针指向的数组的有效元素进行析构操作
}
_allocator.deallocate(_first);
int size = rhs._end - rhs._first;
_first = _allocator.allocate(size);
int len = rhs._last - rhs._first;
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
_allocator.construct(_first + i, rhs._first[i]);
}
_last = _first + len;
_end = _first + size;
return *this;
}
void push_back(const T& val) // 向容器末尾添加元素
{
if (full())
expand();
_allocator.construct(_last, val);
_last++;
}
void pop_back() // 从容器末尾删除元素
{
if (empty())
return;
// 不仅要把_last指针--,还需要析构删除的元素
--_last;
_allocator.destroy(_last);
}
T back()const // 返回容器末尾的元素的值
{
return *(_last - 1);
}
bool full()const { return _last == _end; }
bool empty()const { return _first == _last; }
int size()const { return _last - _first; }
private:
T* _first; // 指向数组起始的位置
T* _last; // 指向数组中有效元素的后继位置
T* _end; // 指向数组空间的后继位置
Alloc _allocator; // 定义容器的空间配置器对象
void expand() // 容器的二倍扩容
{
int size = _end - _first;
T* ptmp = _allocator.allocate(2 * size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
_allocator.construct(ptmp + i, _first[i]);
}
for (T* p = _first; p != _last; ++p)
{
_allocator.destroy(p);
}
_allocator.deallocate(_first);
_first = ptmp;
_last = _first + size;
_end = _first + 2 * size;
}
};
class Test
{
public:
Test() { std::cout << "Test()" << std::endl; }
Test& operator=(const Test&t) { std::cout << "operator=" << std::endl; return *this; }
~Test() { std::cout << "~Test()" << std::endl; }
Test(const Test&) { std::cout << "Test(const Test&)" << std::endl; }
};
int main()
{
Test t1, t2;
std::cout << "vector<Test> vec" << std::endl;
vector<Test> vec;
std::cout << "vector<Test> vec; push_back" << std::endl;
vec.push_back(t1);
vec.push_back(t2);
std::cout << "vector<Test> vec; pop_back" << std::endl;
vec.pop_back();
std::cout << "end" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
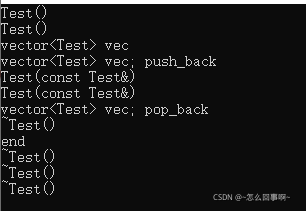
现在的效果就和msvc实现的vector相同了
运算符重载与迭代器实现
/************************************************************************/
/*
迭代器一般实现成容器的嵌套类型
*/
/************************************************************************/
class iterator
{
public:
iterator(T*p=nullptr) :_ptr(p) {}
iterator(const iterator& iter) :_ptr(iter._ptr) {}
//前置++
iterator& operator++() {
_ptr++;
return *this;
}
//后置++
iterator operator++(int) {
iterator tmp(*this);
_ptr++;
return tmp;
}
//解引用
T& operator*() {
return *_ptr;
}
// !=
bool operator!=(const iterator& iter)const {
return _ptr != iter._ptr;
}
private:
T * _ptr;
};
//迭代器方法
iterator begin() { return iterator(_first); }
iterator end() { return iterator(_last);}
//运算符重载[]
T& operator[](int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size()) {
throw "OutofRangeException";
}
return _first[index];
}
最终vector的实现代码
#include <iostream>
// 定义容器的空间配置器,和C++标准库的allocator实现一样
template<typename T>
class Allocator
{
public:
T* allocate(size_t size) // 负责内存开辟
{
return (T*)malloc(sizeof(T) * size);
}
void deallocate(void* p) // 负责内存释放
{
free(p);
}
void construct(T* p, const T& val) // 负责对象构造
{
new (p) T(val); // 定位new
}
void destroy(T* p) // 负责对象析构
{
p->~T(); // ~T()代表了T类型的析构函数
}
};
template<typename T, typename Alloc = Allocator<T>>
class vector
{
public:
vector(int size = 10)
{
// 需要把内存开辟和对象构造分开处理
_first = _allocator.allocate(size);
_last = _first;
_end = _first + size;
}
~vector()
{
// 析构容器有效的元素,然后释放_first指针指向的堆内存
for (T* p = _first; p != _last; ++p)
{
_allocator.destroy(p); // 把_first指针指向的数组的有效元素进行析构操作
}
_allocator.deallocate(_first); // 释放堆上的数组内存
_first = _last = _end = nullptr;
}
vector(const vector<T>& rhs)
{
int size = rhs._end - rhs._first;
_first = _allocator.allocate(size);
int len = rhs._last - rhs._first;
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
_allocator.construct(_first + i, rhs._first[i]);
}
_last = _first + len;
_end = _first + size;
}
vector<T>& operator=(const vector<T>& rhs)
{
if (this == &rhs)
return *this;
for (T* p = _first; p != _last; ++p)
{
_allocator.destroy(p); // 把_first指针指向的数组的有效元素进行析构操作
}
_allocator.deallocate(_first);
int size = rhs._end - rhs._first;
_first = _allocator.allocate(size);
int len = rhs._last - rhs._first;
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
_allocator.construct(_first + i, rhs._first[i]);
}
_last = _first + len;
_end = _first + size;
return *this;
}
void push_back(const T& val) // 向容器末尾添加元素
{
if (full())
expand();
_allocator.construct(_last, val);
_last++;
}
void pop_back() // 从容器末尾删除元素
{
if (empty())
return;
// 不仅要把_last指针--,还需要析构删除的元素
--_last;
_allocator.destroy(_last);
}
T back()const // 返回容器末尾的元素的值
{
return *(_last - 1);
}
bool full()const { return _last == _end; }
bool empty()const { return _first == _last; }
int size()const { return _last - _first; }
//运算符重载[]
T& operator[](int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size()) {
throw "OutofRangeException";
}
return _first[index];
}
/************************************************************************/
/*
迭代器一般实现成容器的嵌套类型
*/
/************************************************************************/
class iterator
{
public:
iterator(T*p=nullptr) :_ptr(p) {}
iterator(const iterator& iter) :_ptr(iter._ptr) {}
//前置++
iterator& operator++() {
_ptr++;
return *this;
}
//后置++
iterator operator++(int) {
iterator tmp(*this);
_ptr++;
return tmp;
}
//解引用
T& operator*() {
return *_ptr;
}
// !=
bool operator!=(const iterator& iter)const {
return _ptr != iter._ptr;
}
private:
T * _ptr;
};
//迭代器方法
iterator begin() { return iterator(_first); }
iterator end() { return iterator(_last);}
private:
T* _first; // 指向数组起始的位置
T* _last; // 指向数组中有效元素的后继位置
T* _end; // 指向数组空间的后继位置
Alloc _allocator; // 定义容器的空间配置器对象
void expand() // 容器的二倍扩容
{
int size = _end - _first;
T* ptmp = _allocator.allocate(2 * size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
_allocator.construct(ptmp + i, _first[i]);
}
for (T* p = _first; p != _last; ++p)
{
_allocator.destroy(p);
}
_allocator.deallocate(_first);
_first = ptmp;
_last = _first + size;
_end = _first + 2 * size;
}
};
class Test
{
public:
Test() { std::cout << "Test()" << std::endl; }
Test& operator=(const Test&t) { std::cout << "operator=" << std::endl; return *this; }
~Test() { std::cout << "~Test()" << std::endl; }
Test(const Test&) { std::cout << "Test(const Test&)" << std::endl; }
};
int main()
{
Test t1, t2;
std::cout << "vector<Test> vec" << std::endl;
vector<Test> vec;
std::cout << "vector<Test> vec; push_back" << std::endl;
vec.push_back(t1);
vec.push_back(t2);
std::cout << "vector<Test> vec; pop_back" << std::endl;
vec.pop_back();
std::cout << "end" << std::endl;
vector<Test>::iterator it = vec.begin();
for (; it != vec.end(); ++it) {
std::cout << "iterator" << " ";
}
return 0;
}
总结
到此这篇关于C++模板以及实现vector的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++模板以及实现vector内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

