Java实现矩形碰撞检测
本文实例为大家分享了Java实现矩形碰撞检测的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
第1种方法:通过检测一个矩形的4个顶点是否在另一个矩形的内部来完成。
通常由x和y坐标以及长度和宽度来确定一个矩形,因此又可以利用这四个参数来确定是否发生了碰撞。

相交的情况下一定会发生碰撞,如下图:
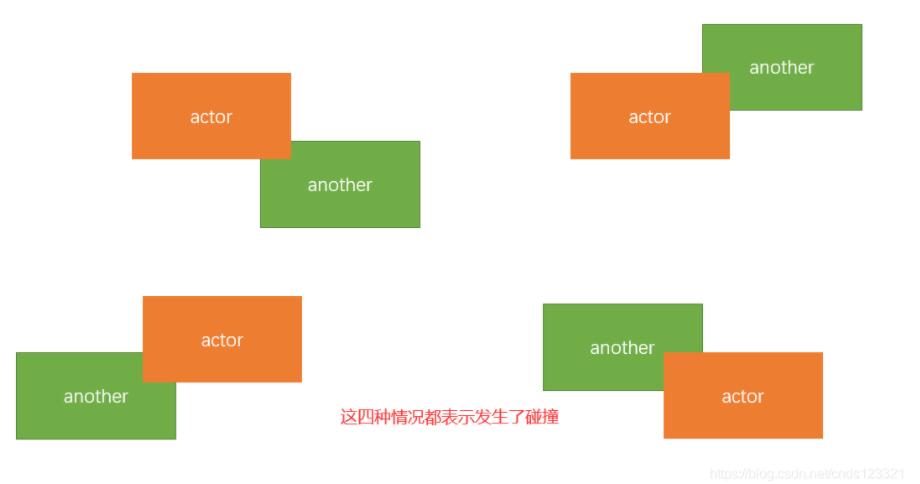
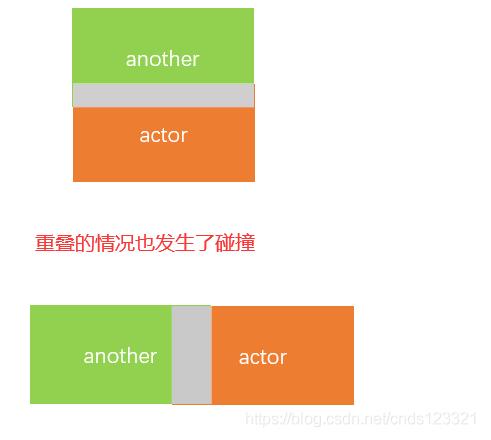
还有一类特殊的相交情况,就是重叠,如下图:
所以开发的碰撞检测类如下:
public class Actor {
int x, y, w, h;// 分别是x和y坐标,宽度和高度,构成一个矩形
public Actor() {
}
public Actor(int x, int y, int w, int h) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.w = w;
this.h = h;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public int getActorWidth() {
return w;
}
public int getActorHeight() {
return h;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Actor{" +
"x=" + x +
", y=" + y +
", w=" + w +
", h=" + h +
'}';
}
public boolean isCollidingWith(int px, int py) {
// px和py分别传入的是x坐标和y坐标
// 等号的情况就是考虑垂直重叠和水平重叠的情况
// 考虑的情况就是传入的坐标是否在当前的矩形范围内,只要满足下面所有条件就表示传入的坐标在当前矩形范围内,返回true
if (px >= getX() && px < getX() + getActorWidth() && py >= getY() && py < getY() + getActorHeight()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 碰撞检测,发生碰撞返回true,否则返回false
public boolean isCollidingWith(Actor another) {
// 判断矩形只要有任何一个点在另一个Actor所表示的矩形范围内,就表示发生了碰撞
if (isCollidingWith(another.getX(), another.getY()) ||
isCollidingWith(another.getX() + another.getActorWidth(), another.getY()) ||
isCollidingWith(another.getX(), another.getY() + another.getActorHeight()) ||
isCollidingWith(another.getX() + another.getActorWidth(), another.getY() + another.getActorHeight())) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Actor actor = new Actor(10, 10, 100, 150);
Actor another = new Actor(20, 50, 100, 150);
boolean collidingWith = actor.isCollidingWith(another);
System.out.println(collidingWith);
}
}
上面测试代码你不能很好的观察是否发生矩形碰撞了,所以写了下面这个界面,可以通过ASWD操作左边的矩形进行移动,通过上下左右键操作右边的矩形进行移动,效果如下图:
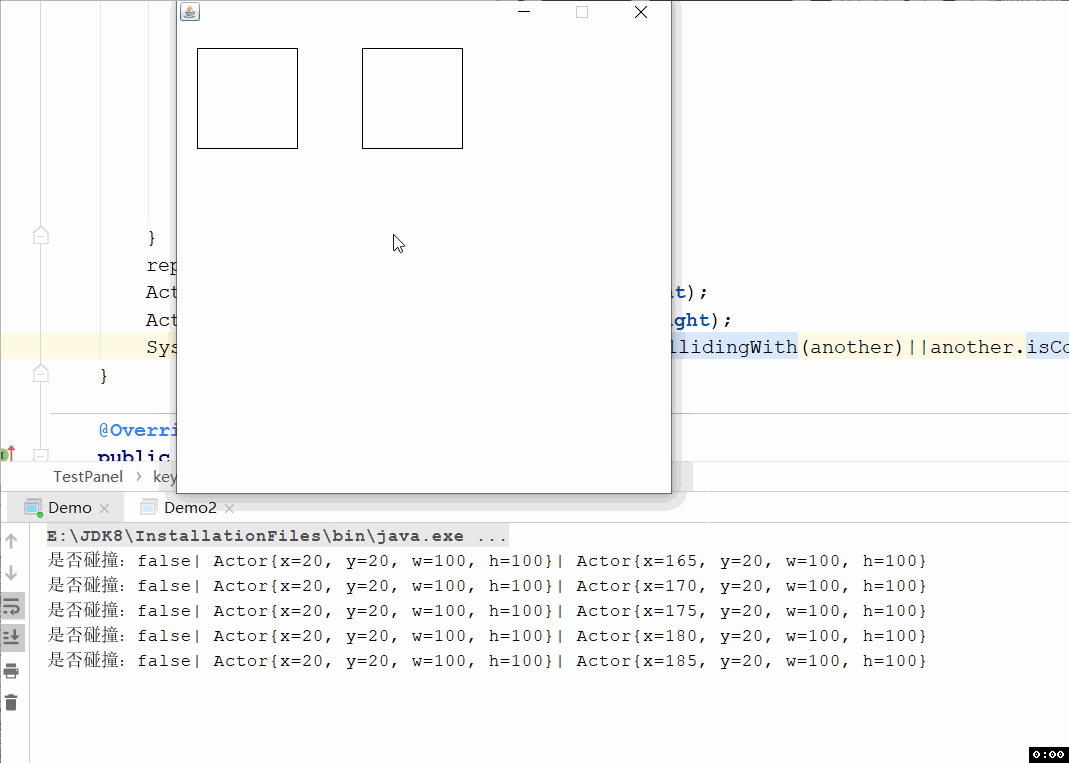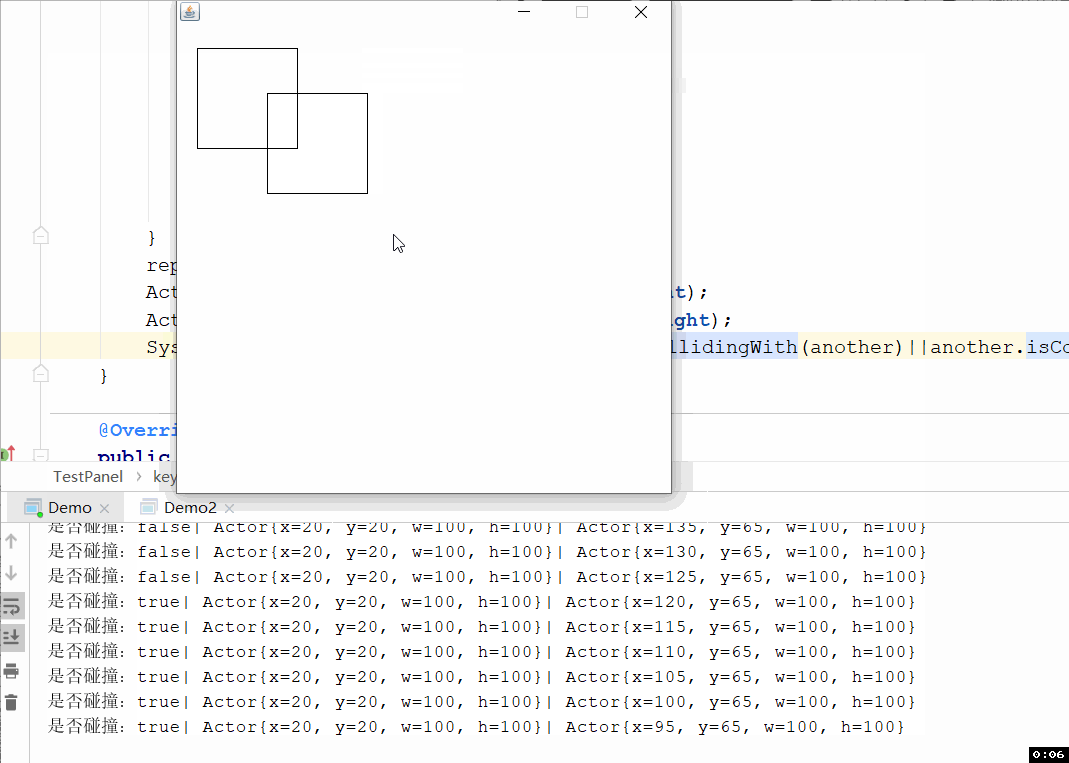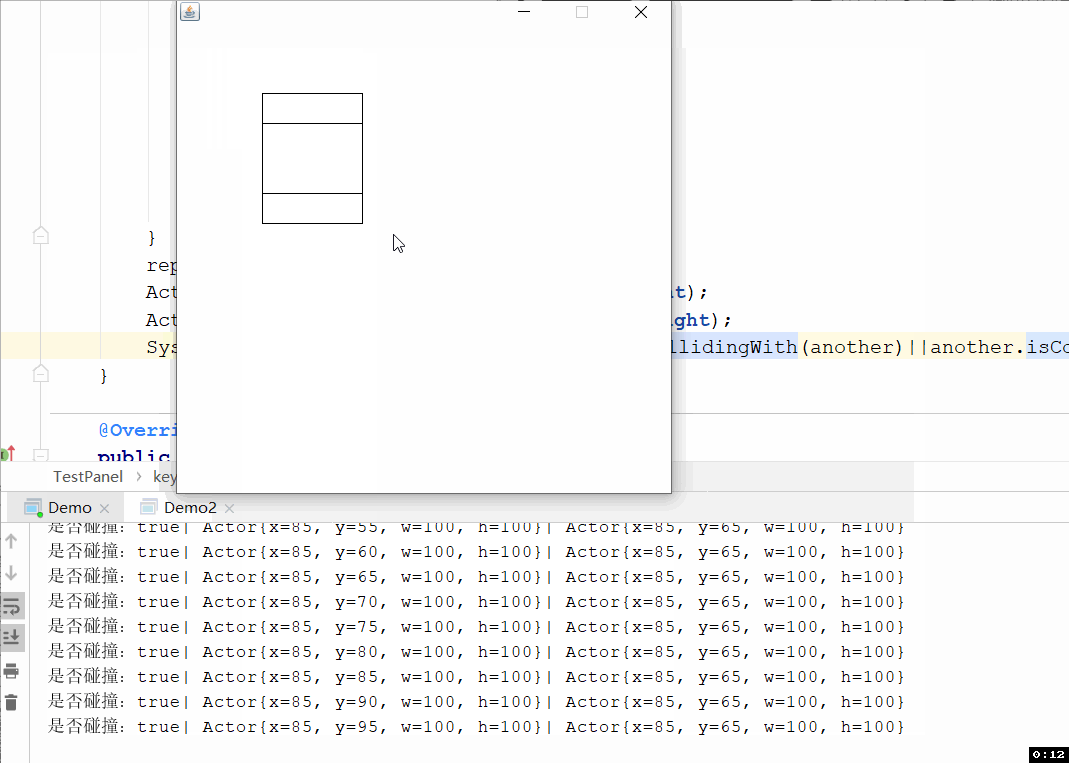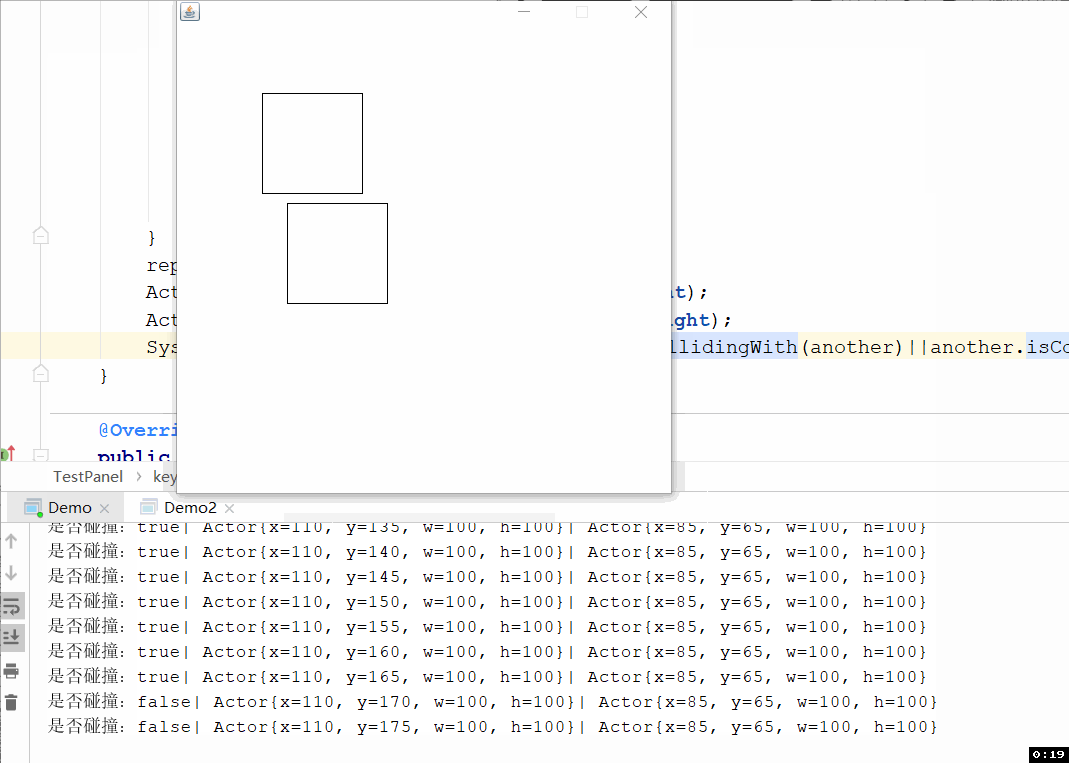
代码如下:
class TestPanel extends JPanel implements KeyListener {
private int x1 = 20, y1 = 20, x2 = 160, y2 = 20, width = 100, height = 100;
public TestPanel() {
// 设置焦点并且添加键盘事件监听器
setFocusable(true);
addKeyListener(this);
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics g) {
// 在进行绘制之前,一定要清除之前的图形
g.clearRect(0, 0, this.getWidth(), this.getHeight());// 先清除屏幕上原来的画
g.drawRect(x1, y1, width, height);
g.drawRect(x2, y2, width, height);
}
@Override
public void keyTyped(KeyEvent e) {
}
@Override
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
// 处理第一个矩形的移动
switch (e.getKeyCode()) {
case KeyEvent.VK_A:// 'A'键
x1 -= 5;
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_D:// 'D'键
x1 += 5;
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_W:// 'W'键
y1 -= 5;
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_S://'S'键
y1 += 5;
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_LEFT://'LEFT'键
x2 -= 5;
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_RIGHT:// 'RIGHT'键
x2 += 5;
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_UP:// 'UP'键
y2 -= 5;
break;
case KeyEvent.VK_DOWN:// 'DOWN'键
y2 += 5;
break;
}
repaint();// 修改坐标后,重绘图形
// 判断是否碰撞,输出信息
Actor actor = new Actor(x1, y1, width, height);
Actor another = new Actor(x2, y2, width, height);
System.out.println("是否碰撞:" + (actor.isCollidingWith(another) || another.isCollidingWith(actor)) + "| " + actor + "| " + another);
}
@Override
public void keyReleased(KeyEvent e) {
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
frame.setLocation(200, 200);
frame.setSize(500, 500);
TestPanel panel = new TestPanel();
frame.setContentPane(panel);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.setResizable(false);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}
第2种方法:从相反的角度考虑,以前是处理什么时候相交,现在处理什么时候不会相交。如两个矩形a和b来判断4条边,假如a矩形在左边,b矩形在右边,那么可以判断左边a矩形的右边界在b矩形的左边界之外,同理,a的上边界需要在b的下边界以外,4条边都判断,则可以知道a矩形是否与b矩形相交。
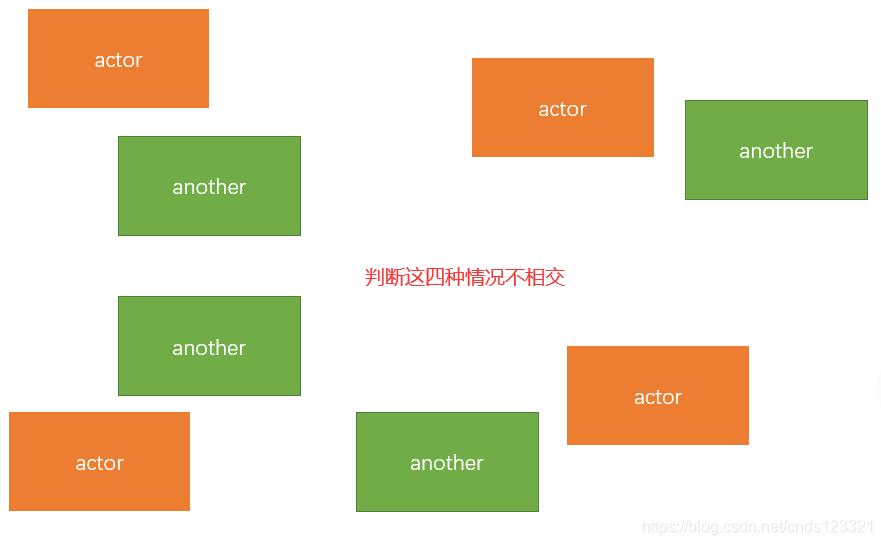
方法如下:
/**
* 判断两个矩形是否会发生碰撞
*
* @param ax 矩形a的x坐标
* @param ay 矩形a的y坐标
* @param aw 矩形a的宽度
* @param ah 矩形a的高度
* @param bx 矩形b的x坐标
* @param by 矩形b的y坐标
* @param bw 矩形b的宽度
* @param bh 矩形b的高度
* @return 如果发生碰撞则返回true,否则返回false
*/
public boolean isCollidingWith(int ax, int ay, int aw, int ah, int bx, int by, int bw, int bh) {
if (ay > by + bh || by > ay + ah || ax > bx + bw || bx > ax + aw) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
第3种方法:是方法2的变异,我们保存两个矩形的左上和右下两个坐标的坐标值,然后对两个坐标的一个对比就可以得出两个矩形是否相交。
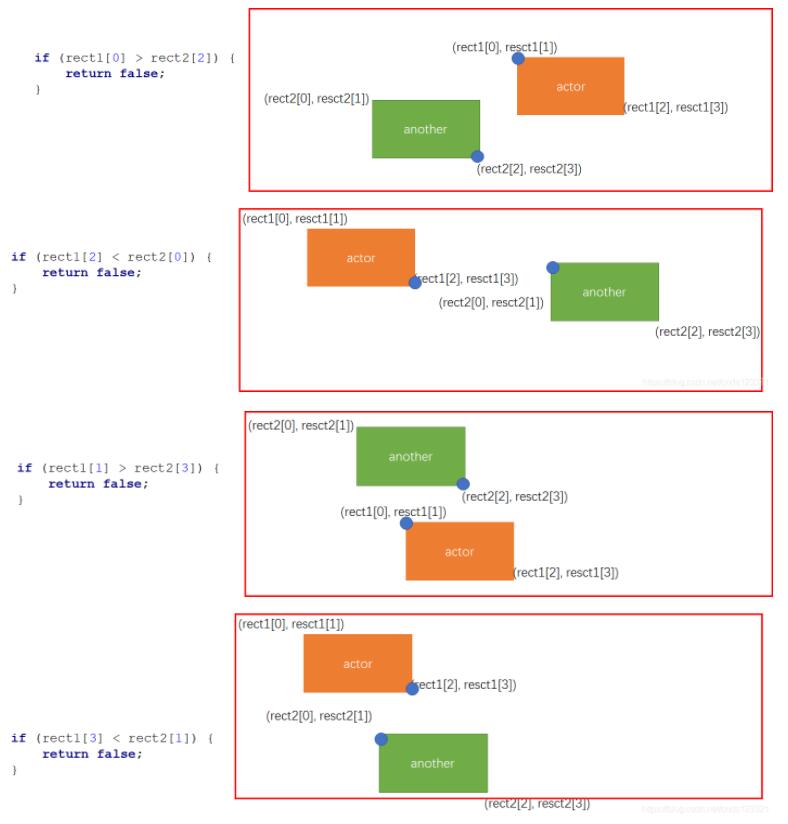
/**
* rect1[0]:矩形1左上角x坐标
* rect1[1]:矩形1左上角y坐标
* rect1[2]:矩形1右下角x坐标
* rect1[3]:矩形1右下角y坐标
* rect2[0]:矩形2左上角x坐标
* rect2[1]:矩形2左上角y坐标
* rect2[2]:矩形2右下角x坐标
* rect2[3]:矩形2右下角y坐标
*
* @param rect1 第一个矩形的左上角坐标和右下角坐标数组
* @param rect2 第二个矩形的左上角坐标和右下角坐标数组
* @return 如果发生碰撞则返回true,否则返回false
*/
public static boolean isCollidingWith(int rect1[], int rect2[]) {
if (rect1[0] > rect2[2]) {
return false;
}
if (rect1[2] < rect2[0]) {
return false;
}
if (rect1[1] > rect2[3]) {
return false;
}
if (rect1[3] < rect2[1]) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
最后Actor类的完整代码如下:
public class Actor {
int x, y, w, h;// 分别是x和y坐标,宽度和高度,构成一个矩形
public Actor() {
}
public Actor(int x, int y, int w, int h) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.w = w;
this.h = h;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public int getActorWidth() {
return w;
}
public int getActorHeight() {
return h;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Actor{" +
"x=" + x +
", y=" + y +
", w=" + w +
", h=" + h +
'}';
}
public boolean isCollidingWith(int px, int py) {
// px和py分别传入的是x坐标和y坐标
// 等号的情况就是考虑垂直重叠和水平重叠的情况
// 考虑的情况就是传入的坐标是否在当前的矩形范围内,只要满足下面所有条件就表示传入的坐标在当前矩形范围内,返回true
if (px >= getX() && px < getX() + getActorWidth() && py >= getY() && py < getY() + getActorHeight()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 碰撞检测,发生碰撞返回true,否则返回false
public boolean isCollidingWith(Actor another) {
// 判断矩形只要有任何一个点在另一个Actor所表示的矩形范围内,就表示发生了碰撞
if (isCollidingWith(another.getX(), another.getY()) ||
isCollidingWith(another.getX() + another.getActorWidth(), another.getY()) ||
isCollidingWith(another.getX(), another.getY() + another.getActorHeight()) ||
isCollidingWith(another.getX() + another.getActorWidth(), another.getY() + another.getActorHeight())) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判断两个矩形是否会发生碰撞
*
* @param ax 矩形a的x坐标
* @param ay 矩形a的y坐标
* @param aw 矩形a的宽度
* @param ah 矩形a的高度
* @param bx 矩形b的x坐标
* @param by 矩形b的y坐标
* @param bw 矩形b的宽度
* @param bh 矩形b的高度
* @return 如果发生碰撞则返回true,否则返回false
*/
public boolean isCollidingWith(int ax, int ay, int aw, int ah, int bx, int by, int bw, int bh) {
if (ay > by + bh || by > ay + ah || ax > bx + bw || bx > ax + aw) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* isCollidingWith方法的重载方法
*
* @param a
* @param b
* @return
*/
public boolean isCollidingWith(Actor a, Actor b) {
return isCollidingWith(a.getX(), a.getY(), a.getActorWidth(), a.getActorHeight(), b.getX(), b.getY(), b.getActorWidth(), b.getActorHeight());
}
/**
* rect1[0]:矩形1左上角x坐标
* rect1[1]:矩形1左上角y坐标
* rect1[2]:矩形1右下角x坐标
* rect1[3]:矩形1右下角y坐标
* rect2[0]:矩形2左上角x坐标
* rect2[1]:矩形2左上角y坐标
* rect2[2]:矩形2右下角x坐标
* rect2[3]:矩形2右下角y坐标
*
* @param rect1 第一个矩形的左上角坐标和右下角坐标数组
* @param rect2 第二个矩形的左上角坐标和右下角坐标数组
* @return 如果发生碰撞则返回true,否则返回false
*/
public static boolean isCollidingWith(int rect1[], int rect2[]) {
if (rect1[0] > rect2[2]) {
return false;
}
if (rect1[2] < rect2[0]) {
return false;
}
if (rect1[1] > rect2[3]) {
return false;
}
if (rect1[3] < rect2[1]) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Actor actor = new Actor(10, 10, 100, 150);
Actor another = new Actor(20, 50, 100, 150);
boolean collidingWith = actor.isCollidingWith(another);
System.out.println(collidingWith);
}
}
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。
赞 (0)

