手把手教你vue实现动态路由
目录
- 1、什么是动态路由?
- 2、动态路由的好处
- 3、动态路由如何实现
- 总结
1、什么是动态路由?
动态路由,动态即不是写死的,是可变的。我们可以根据自己不同的需求加载不同的路由,做到不同的实现及页面的渲染。动态的路由存储可分为两种,一种是将路由存储到前端。另一种则是将路由存储到数据库。动态路由的使用一般结合角色权限控制一起使用。
总结:
1)路由可变,不是写死的,动态加载
2)存储分两种:存前端,存数据库
2、动态路由的好处
使用动态路由可以跟灵活,无需手工维护,我们可以使用一个页面对路由进行维护。如果将路由存储到数据库,还可以增加安全性。
总结:
1)灵活,无需手工维护
2)增加安全性
3、动态路由如何实现
在此以路由存储在数据库为例
流程:一般我们在登录的时候,根据登录用户的角色返回此角色可以访问的页面的路由,前端将路由存储到vuex(vuex存储的数据必须可持久的,不要一刷新页面就不见),我们在路由前置守卫处动态添加拿到的路由,对页面进行渲染。
1)此为我的router目录,index.js对路由添加,守卫拦截等处理。static-route.js为前端定义的静态路由,不需要动态加载的,如登陆页面,忘记密码页面,404页面等。


index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import $cookies from 'vue-cookies'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import store from '../store'
import staticRoute from './static-route.js'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
routes: staticRoute //staticRoute为静态路由,不需动态添加
})
let isToken = true
router.beforeEach(async (to, from, next) => {
//定义isToken为true和vuex不为空时添加路由
if (isToken && store.state.routers.routers.length != 0) {
//从vuex中获取动态路由
const accessRouteses = await store.state.routers.routers;
//动态路由循环解析和添加
accessRouteses.forEach(v => {
v.children = routerChildren(v.children);
v.component = routerCom(v.component);
router.addRoute(v); //添加
})
isToken = false //将isToken赋为 false ,否则会一直循环,崩溃
next({
...to, // next({ ...to })的目的,是保证路由添加完了再进入页面 (可以理解为重进一次)
replace: true, // 重进一次, 不保留重复历史
})
} else {
if (to.name == null) {
next("/404")
} else {
if (to.meta.title) { //判断是否有标题
document.title = to.meta.title //给相应页面添加标题
}
next()
}
}
})
function routerCom(path) { //对路由的component解析
return (resolve) => require([`@/views/${path}`], resolve);
}
function routerChildren(children) { //对子路由的component解析
children.forEach(v => {
v.component = routerCom(v.component);
if (v.children != undefined) {
v.children = routerChildren(v.children)
}
})
return children
}
export default router
2)登陆成功后将获取到的动态路由存储到vuex
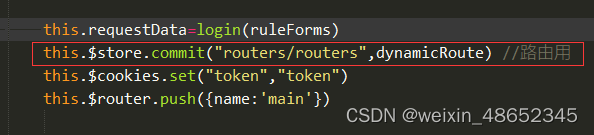
vuex—>index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
//数据持久化
import createPersistedState from "vuex-persistedstate";
Vue.use(Vuex)
const routers = {
namespaced: true,
state: () => ({
routers:"",
}),
mutations: {
routers(state, newsdata) {
state.routers = newsdata
},
},
actions: {
routers(context) {
context.commit('routers')
},
},
getters: {
routers(state) {
console.log("getters", state)
return state.routers
},
}
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
routers: routers,
},
// 数据持久化
plugins: [createPersistedState({
//key是存储数据的键名
key: 'routersData',
//paths是存储state中的那些数据,如果是模块下具体的数据需要加上模块名称,如user.token
paths: ["routers.routers"]
})]
})
export default store
我的动态路由模板
//动态路由
const dynamicRoute = [{
"path": "/main",
"name": "main",
"redirect": "/main/index",
"component": "main/main.vue",
"children": [{
"path": "index",
"name": "index",
"component": "index/index.vue",
"meta": {
"name": "index",
"title": "首页",
"icon": "el-icon-location",
"menu":true //true为菜单栏
}
},
{
"path": "Configuration",
"name": "Configuration",
"redirect": "Configuration/route",
"component": "Configuration/index.vue",
"roles": ['developer', "admin"], // developer、admin角色的用户才能访问该页面
"meta": {
"title": "配置",
"icon": "el-icon-location",
"menu":true
},
"children": [{
"path": "route",
"name": "route",
"component": "Configuration/route/index.vue",
"meta": {
"title": "菜单",
"icon": "",
"menu":true
},
}, {
"path": "user",
"name": "user",
"component": "Configuration/user/index.vue",
"meta": {
"title": "用户管理",
"icon": "el-icon-location",
"menu":true
},
},
{
"path": "admin",
"name": "admin",
"component": "Configuration/admin/index.vue",
"meta": {
"title": "管理员管理",
"icon": "",
"menu":true
},
},
{
"path": "userEdit",
"name": "userEdit",
"component": "Configuration/user/user-Edit.vue",
"meta": {
"title": "编辑用户",
"icon": "",
"menu":false
},
},
]
},
{
"path": "check",
"name": "check",
"redirect": "check/user",
"component": "check/index.vue",
"roles": ['developer', "admin", "check"], // developer、admin角色的用户才能访问该页面
"meta": {
"title": "审核",
"icon": "el-icon-location",
"menu":true
},
"children": [{
"path": "user",
"name": "checkUser",
"component": "check/check-user/index.vue",
"meta": {
"title": "用户实名审核",
"icon": "el-icon-location",
"menu":true
}
},
{
"path": "enterprise",
"name": "checkEnterprise",
"component": "check/check-enterprise/index.vue",
"meta": {
"title": "企业认证审核",
"icon": "el-icon-location",
"menu":true
},
},
{
"path": "checkNormImage",
"name": "checkNormImage",
"component": "check/check-norm-image/index.vue",
"meta": {
"title": "标准照认证审核",
"icon": "el-icon-location",
"menu":true
},
},
{
"path": "checkHiringJobs",
"name": "checkHiringJobs",
"component": "check/check-hiring-Jobs/index.vue",
"meta": {
"title": "求职、招聘认证审核",
"icon": "el-icon-location",
"menu":true
},
}
]
}
]
}, ]
export default dynamicRoute
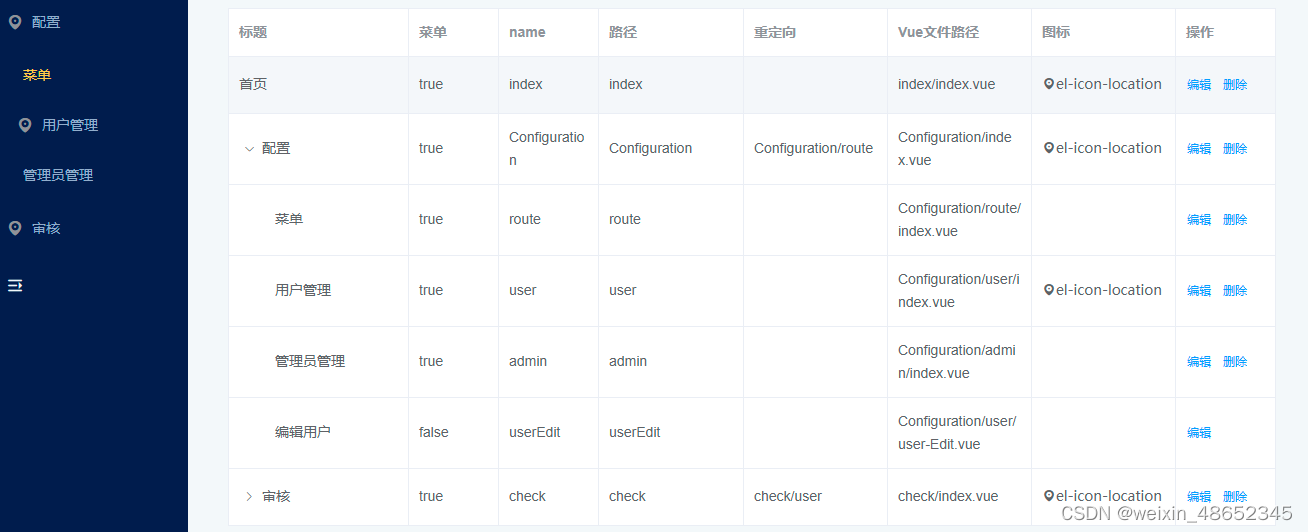
路由管理界面(可能有不完善的地方)
讲一讲遇到的坑及注意点
1)“component”: “check/check-norm-image/index.vue”, 用字符串再在解析,不要像静态路由一样。否则第一次进去可以,刷新就变空白
2)此处为重要的一点,直接用next()不行
next({
...to, // next({ ...to })的目的,是保证路由添加完了再进入页面 (可以理解为重进一次)
replace: true, // 重进一次, 不保留重复历史
})
3)由于添加完路由还会重复执行一遍路由守卫,所有必须确保不要一直死循环添加路由。否则直接崩溃。这里我用的是isToken变量确保不循环。
总结
到此这篇关于vue实现动态路由的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关vue实现动态路由内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

