spring控制事务的三种方式小结
目录
- 方式一:编码方式(需要修改源代码,基本不会用)
- 方式二:xml配置(不需要改动代码,直接配置xml)
- 方式三:注解
- spring是如何控制事务的?
首先准备环境,目录结构如下
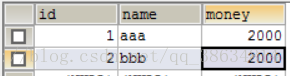
数据库准备
业务层代码
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Resource(name = "accountDao")
AccountDao accountDao;
public void transfer(Integer from, Integer to, Float money) {
accountDao.subMoney(from,money);
int i = 1/0; //此处引发异常
accountDao.addMoney(to,money);
}
}
持久层代码
public class AccountDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport implements AccountDao {
public void addMoney(Integer id, Float money) {
getJdbcTemplate().update("update account set money=money+? where id=?", money , id);
}
public void subMoney(Integer id, Float money) {
getJdbcTemplate().update("update account set money=money-? where id=?", money , id);
}
}
测试代码
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class Test {
@Resource(name="accountService")
private AccountService accountService;
@org.junit.Test
public void test(){
accountService.transfer(1,2,100f);
}
}
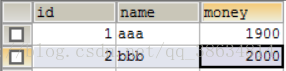
运行结果
现在来用三种方式进行事务控制
方式一:编码方式(需要修改源代码,基本不会用)
添加事务管理类和事务模板类
<!-- 事务核心管理器,封装了所有事务操作. 依赖于连接池 -->
<bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" >
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" ></property>
</bean>
<!-- 事务模板对象 -->
<bean name="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate" >
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" ></property>
</bean>
修改业务层代码
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Resource(name = "accountDao")
AccountDao accountDao;
@Resource(name="transactionTemplate")
private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
public void transfer(final Integer from, final Integer to, final Float money) {
transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() {
@Override
protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus status) {
accountDao.subMoney(from,money);
int i = 1/0;
accountDao.addMoney(to,money);
}
});
}
}
方式二:xml配置(不需要改动代码,直接配置xml)
<!-- 配置事务通知 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager" >
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 以方法为单位,指定方法应用什么事务属性
isolation:隔离级别
propagation:传播行为
read-only:是否只读
-->
<tx:method name="find*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true" />
<tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 配置织入 -->
<aop:config >
<!-- 配置切点表达式 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.swun.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))" id="txPc"/>
<!-- 配置切面 : 通知+切点
advice-ref:通知的名称
pointcut-ref:切点的名称
-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPc" />
</aop:config>
方式三:注解
首先开启注解管理aop事务,然后打注解
<!-- 开启使用注解管理aop事务 -->
<tx:annotation-driven/>
/*
* 该注解可以打在方法上,也可以打在类上
*/
@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly=false)
public void transfer(final Integer from, final Integer to, final Float money) {
accountDao.subMoney(from,money);
int i = 1/0;
accountDao.addMoney(to,money);
}
spring是如何控制事务的?
Spring 的事务,可以说是 Spring AOP 的一种实现。
AOP面向切面编程,即在不修改源代码的情况下,对原有功能进行扩展,通过代理类来对具体类进行操作。
spring是一个容器,通过spring这个容器来对对象进行管理,根据配置文件来实现spring对对象的管理。
spring的事务声明有两种方式,编程式和声明式。spring主要是通过“声明式事务”的方式对事务进行管理,即在配置文件中进行声明,通过AOP将事务切面切入程序,最大的好处是大大减少了代码量。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。
赞 (0)

