Java中用户向系统传递参数的三种基本方式实例分享
使用Main方法的参数传递方式
例示代码如下:
public class MainArgs
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(args.length);
for(String str : args){
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}
在运行 java程序后面跟的字符串(一个或多个 多个用空格隔开)jvm将会把这些一个或多个字符串赋给args数组。当字符串中包含空格时则需要将完整的一个字符串用“”括起来。如下示例:
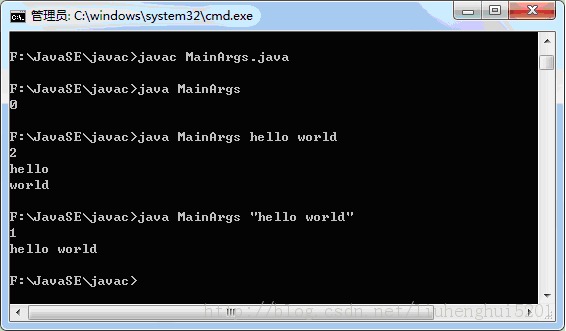
使用Scanner类进行用户输入:可以输入用户指定的数据类型
Scanner 使用分隔符模式将其输入分解为标记,默认情况下该分隔符模式与空白匹配。然后可以使用不同的 next 方法将得到的标记转换为不同类型的值。
例示代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.io.File;
public class ScannerKeyBoardTest
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
//readFileCon();
//test2();
//通过键盘输入指定类型
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
Long l = scan.nextLong();
System.out.println("l is "+l);
}
//读取任何的数据输入返回String
public static void test1(){
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
//使用 回车键 作为分隔符 默认使用 空格 制表键 回车作为分割付。
//scan.useDelimiter("\n");
while(scan.hasNext()){
System.out.println("next is " + scan.next());
}
}
//读取Long型数据的输入返回Long
public static void test2(){
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
//当输入的为 非 Long数值时 推出循环
while(scan.hasNextLong()){//阻塞式
//System.out.println("has over scan.nextLong() begin....");
System.out.println("next is " + scan.nextLong());
//System.out.println("scan.nextLong() over has begin....");
}
}
//读取文件中的内容 并打印到控制台
public static void readFileCon()throws Exception
{
Scanner scan = new Scanner(new File("ScannerKeyBoardTest.java"));
System.out.println("fileContent is:");
while(scan.hasNextLine()){
System.out.println(scan.nextLine());
}
}
}
使用BufferedReader类读取用户的输入:返回的只能是String类
例示代码如下
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
class BufferReaderKeyBoardTest
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String in = null;
while((in = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println("用户输入的是: "+in);
}
}
}

