浅谈@Aspect@Order各个通知的执行顺序
目录
- @Aspect@Order各个通知的执行顺序
- 代码
- 小结
- spring AspectJ order(顺序)
@Aspect@Order各个通知的执行顺序
两个切面类:【记录日志】和【判断参数】,分别对应顺序 @Order(0) 和@Order(1) 。
本文只是将重点说下 执行顺序 这么回事哈哈哈
代码
【业务类】
/**
* 登录控制器
*/
@Controller
public class LoginController {
//向外面抛出异常
public void loginWithThrow(String username, String password) throws Exception {
if (username == null || password == null) {
throw new Exception("登录信息不可为空啊");
}
System.out.println("LoginController#login...");
}
//抛出异常自己捕获的情况
public void loginWithTryCatch(String username, String password) {
try{
if (username == null || password == null) {
throw new Exception("登录信息不可为空啊");
}
System.out.println("LoginController#login...");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
【切面类】
/**
* 输出日志注解
*/
@Order(0)
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAspect {
//抽出共通的execution用的
//com.yuki.demo.aop.aspect 包或者子包下所有类的方法
@Pointcut("execution(* com.yuki.demo.aop.aspect..*.*(..))")
public void pointcut(){
}
//前置通知
// @Before("execution(public void com.yuki.demo.aop.aspect.LoginController.*(String,String))")
@Before("pointcut()")
public void before() {
System.out.println("LogAspect#before...");
}
//环绕通知
//ProceedingJoinPoint 只有环绕通知有
@Around("execution(public void com.yuki.demo.aop.aspect.LoginController.*(String,String))")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("LogAspectA#around开始...");
//代理方法的执行,如果没有joinPoint.proceed() ,则前置通知@Before 不会执行,其它的通知正常
joinPoint.proceed();
//执行方法之后,如果joinPoint.proceed() 抛出了异常,则该句不会执行,抛出异常后直接跳出了aroud方法了
System.out.println("LogAspectA#around结束...");
}
//后置通知(只要连接点被执行,不管是否抛出异常)
@After("execution(public void com.yuki.demo.aop.aspect.LoginController.*(String,String))")
public void after() {
System.out.println("LogAspect#after...");
}
//异常通知(只有在joinPoint.proceed()方法执行向外面抛出了异常,才会执行该通知)
@AfterThrowing("execution(public void com.yuki.demo.aop.aspect.LoginController.*(String,String))")
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("LogAspect#afterThrowing...");
}
//正常的返回通知通知(正常结束了才会执行该通知)
@AfterReturning("execution(public void com.yuki.demo.aop.aspect.LoginController.*(String,String))")
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("LogAspect#afterReturning...");
}
}
【切面类】
/**
* 判断请求参数的sign是否正确的 切面类
*/
@Order(1)
@Aspect
@Component
public class SignAspect {
@Around("execution(public void com.yuki.demo.aop.aspect.LoginController.*(String,String))")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("SignAspect#around开始...");
joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("SignAspect#around结束...");
}
}
【启动配置】
省略。。。非重点
【测试类】
@SpringBootTest
class AopApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private LoginController loginController;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
loginController.loginWithTryCatch("yuki", "1234");
}
}
【控制台输出】
LogAspectA#around开始...
LogAspect#before...
SignAspect#around开始...
LoginController#login...
SignAspect#around结束...
LogAspectA#around结束...
LogAspect#after...
LogAspect#afterReturning...
小结
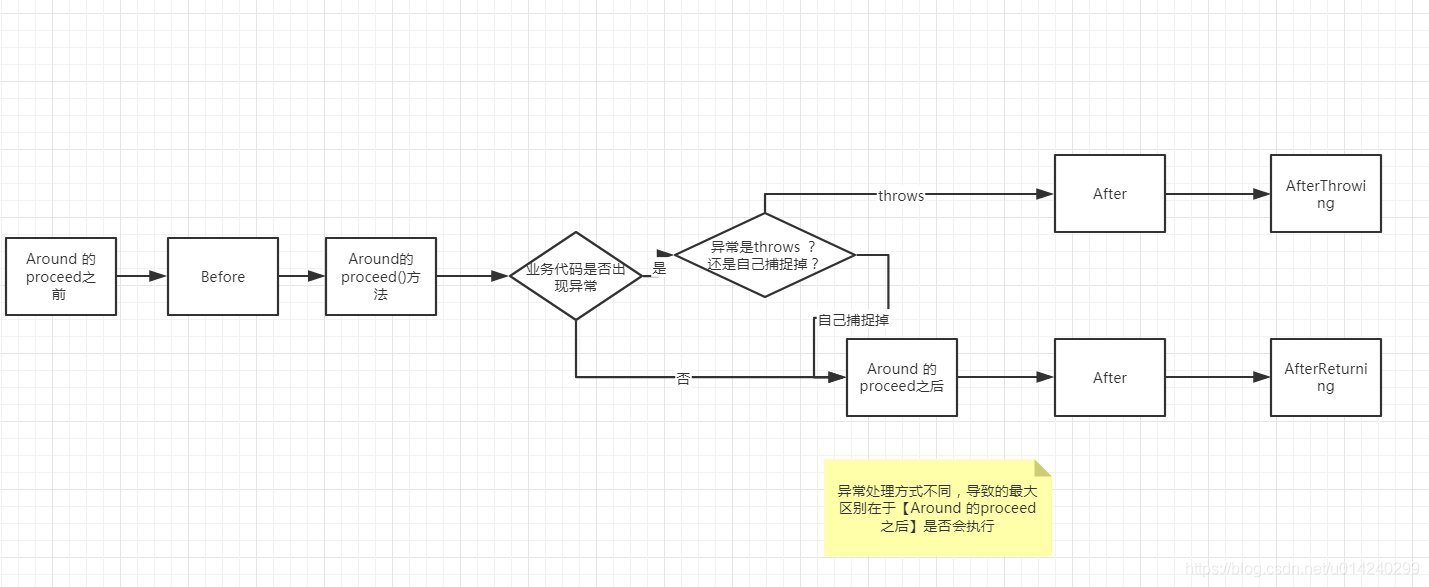
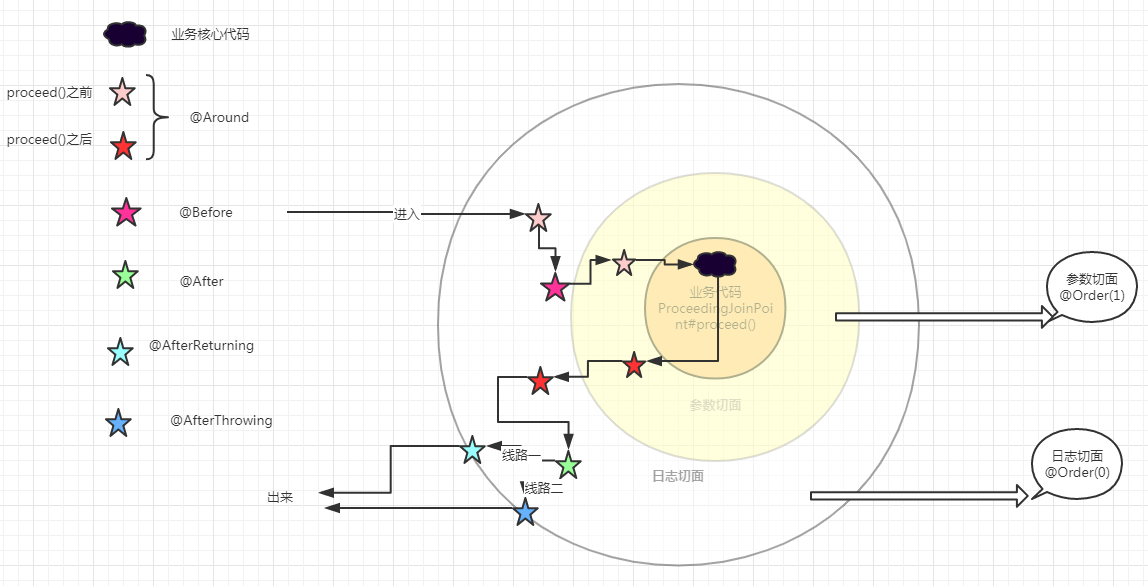
spring AspectJ order(顺序)
@Aspect
@Order(2)
public class HelloWorldAspectAnnotation {
/**
* JoinPoint接口
* @param joinPoint
*/
/*public interface JoinPoint {
String toString(); //连接点所在位置的相关信息
String toShortString(); //连接点所在位置的简短相关信息
String toLongString(); //连接点所在位置的全部相关信息
Object getThis(); //返回AOP代理对象
Object getTarget(); //返回目标对象
Object[] getArgs(); //返回被通知方法参数列表
Signature getSignature(); //返回当前连接点签名
SourceLocation getSourceLocation();//返回连接点方法所在类文件中的位置
String getKind(); //连接点类型
StaticPart getStaticPart(); //返回连接点静态部分
}*/
//定义前置通知,注意这里是sayHello2
//使用@Before进行前置通知声明,其中value用于定义切入点表达式或引用命名切入点
@Before(value="execution(* com.boventech..*.sayHello2(..))&& args(param)",argNames="param")
public void beforeAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint,String param) {
System.out.println(1);
System.out.println("=======================");
System.out.println("===param:" + param);
System.out.println("=======================");
System.out.println(joinPoint.getArgs().length);
System.out.println("=======================");
System.out.println(joinPoint.toString());
System.out.println("=======================");
System.out.println(joinPoint.getTarget());
System.out.println("=======================");
System.out.println(joinPoint.getThis());
System.out.println("=======================");
System.out.println("===========before advice");
}
/*value:指定切入点表达式或命名切入点;
pointcut:同样是指定切入点表达式或命名切入点,如果指定了将覆盖value属性指定的,pointcut具有高优先级;*/
@AfterReturning(value="execution(* com.boventech..*.sayHello2(..))&& args(param)",argNames="param",pointcut="execution(* com.boventech..*.sayHello2(..))&& args(param)")
public void afterFinallyAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint,String param) {
System.out.println("param:"+param);
System.out.println("===========");
System.out.println("===========after finally advice");
}
}
@Aspect
@Order(1)
public class HelloWorldAspectAnnotation2 {
/**
* JoinPoint接口
* @param joinPoint
*/
/*public interface JoinPoint {
String toString(); //连接点所在位置的相关信息
String toShortString(); //连接点所在位置的简短相关信息
String toLongString(); //连接点所在位置的全部相关信息
Object getThis(); //返回AOP代理对象
Object getTarget(); //返回目标对象
Object[] getArgs(); //返回被通知方法参数列表
Signature getSignature(); //返回当前连接点签名
SourceLocation getSourceLocation();//返回连接点方法所在类文件中的位置
String getKind(); //连接点类型
StaticPart getStaticPart(); //返回连接点静态部分
}*/
//定义前置通知,注意这里是sayHello2
//使用@Before进行前置通知声明,其中value用于定义切入点表达式或引用命名切入点
@Before(value="execution(* com.boventech..*.sayHello2(..))&& args(param)",argNames="param")
public void beforeAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint,String param) {
System.out.println(2);
System.out.println("=======================");
}
/*value:指定切入点表达式或命名切入点;
pointcut:同样是指定切入点表达式或命名切入点,如果指定了将覆盖value属性指定的,pointcut具有高优先级;*/
@AfterReturning(value="execution(* com.boventech..*.sayHello2(..))&& args(param)",argNames="param",pointcut="execution(* com.boventech..*.sayHello2(..))&& args(param)")
public void afterFinallyAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint,String param) {
System.out.println("order:" + 2);
}
}
public class AopAnnotationTest {
@Test
public void testHelloworld() {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/helloWorld2.xml");
IHelloWorld2Service helloworldService =ctx.getBean("helloWorld2Service", IHelloWorld2Service.class);
String param = "12";
helloworldService.sayHello2(param);
}
}
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<bean id="helloWorld2Service" class="com.boventech.learning.serviceImpl.HelloWorld2ServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="aspect"
class="com.boventech.learning.aspect.HelloWorldAspectAnnotation"/>
<bean id="aspect2"
class="com.boventech.learning.aspect.HelloWorldAspectAnnotation2"/>
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。
赞 (0)

