Android 无障碍服务 performAction 调用过程分析
目录
- View 的 performClick 方法是同步的还是异步的?
- 总结
无障碍服务可以模拟一些用户操作,无障碍可以处理的对象,通过类 AccessibilityNodeInfo 表示,通过无障碍服务,可以通过它的 performAction 方法来触发一些 action ,包括:
ACTION_FOCUS // 获取焦点 ACTION_CLEAR_FOCUS // 清除焦点 ACTION_SELECT // 选中 ACTION_CLEAR_SELECTION // 清除选中状态 ACTION_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUS // 无障碍焦点 ACTION_CLEAR_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUS // 清除无障碍焦点 ACTION_CLICK // 点击 ACTION_LONG_CLICK // 长按 ACTION_NEXT_AT_MOVEMENT_GRANULARITY // 下一步移动 ACTION_PREVIOUS_AT_MOVEMENT_GRANULARITY // 上一步移动 ACTION_NEXT_HTML_ELEMENT // 下一个 html 元素 ACTION_PREVIOUS_HTML_ELEMENT // 上一个 html 元素 ACTION_SCROLL_FORWARD // 向前滑动 ACTION_SCROLL_BACKWARD // 向后滑动
他们都可以通过performAction方法进行处理:
// in AccessibilityNodeInfo
public boolean performAction(int action) {
enforceSealed();
if (!canPerformRequestOverConnection(mConnectionId, mWindowId, mSourceNodeId)) {
return false;
}
AccessibilityInteractionClient client = AccessibilityInteractionClient.getInstance();
return client.performAccessibilityAction(mConnectionId, mWindowId, mSourceNodeId,
action, null);
}
在这个方法中,第一步是检查 perform 是否可以通过 connection 请求,这里 connection 检查是根据通过 binder 通信传递过来的 id 检查连接是否正常。 然后通过AccessibilityInteractionClient对象,调用它的performAccessibilityAction方法去进行实际操作的。
AccessibilityInteractionClient
这个类是一个执行可访问性交互的单例,它可以根据 View 的快照查询远程的 View 层次结构,以及通过 View 层次结构,来请求对 View 执行某项操作。
基本原理:内容检索 API 从客户端的角度来看是同步的,但在内部它们是异步的。客户端线程调用系统请求操作并提供回调以接收结果,然后等待该结果的超时。系统强制执行安全性并将请求委托给给定的视图层次结构, 在该视图层次结构中发布消息(来自 Binder 线程),描述 UI 线程要执行的内容,其结果是通过上述回调传递的。但是,被阻塞的客户端线程和目标视图层次结构的主 UI 线程可以是同一个线程,例如无障碍服务和 Activity 在同一个进程中运行,因此它们在同一个主线程上执行。 在这种情况下,检索将会失败,因为 UI 线程在等待检索结果,会导致阻塞。 为了避免在进行调用时出现这种情况,客户端还会传递其进程和线程 ID,以便访问的视图层次结构可以检测发出请求的客户端是否正在其主 UI 线程中运行。 在这种情况下,视图层次结构,特别是对它执行 IPC 的绑定线程,不会发布要在 UI 线程上运行的消息,而是将其传递给单例交互客户端,通过该客户端发生所有交互,后者负责执行开始等待通过回调传递的异步结果之前的消息。在这种情况下,已经收到预期的结果,因此不执行等待。
上面是官方备注的描述,大概意思最好不要在主线程执行检索操作。
继续跟进它的performAccessibilityAction方法:
public boolean performAccessibilityAction(int connectionId, int accessibilityWindowId,
long accessibilityNodeId, int action, Bundle arguments) {
try {
IAccessibilityServiceConnection connection = getConnection(connectionId);
if (connection != null) {
final int interactionId = mInteractionIdCounter.getAndIncrement();
final long identityToken = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final boolean success;
try {
success = connection.performAccessibilityAction(
accessibilityWindowId, accessibilityNodeId, action, arguments,
interactionId, this, Thread.currentThread().getId()); // 【*】
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(identityToken);
}
if (success) {
return getPerformAccessibilityActionResultAndClear(interactionId);
}
}
} catch (RemoteException re) {
Log.w(LOG_TAG, "Error while calling remote performAccessibilityAction", re);
}
return false;
}
这里通过 getConnection(connectionId) 获取了一个 IAccessibilityServiceConnection 。
public static IAccessibilityServiceConnection getConnection(int connectionId) {
synchronized (sConnectionCache) {
return sConnectionCache.get(connectionId);
}
}
这里的 sConnectionCache 通过 AccessibilityInteractionClient 的addConnection添加数据的,addConnection在 AccessbilityService 创建初始化时调用的:
case DO_INIT: {
mConnectionId = message.arg1;
SomeArgs args = (SomeArgs) message.obj;
IAccessibilityServiceConnection connection = (IAccessibilityServiceConnection) args.arg1;
IBinder windowToken = (IBinder) args.arg2;
args.recycle();
if (connection != null) {
AccessibilityInteractionClient.getInstance(mContext).addConnection(mConnectionId, connection);
mCallback.init(mConnectionId, windowToken);
mCallback.onServiceConnected();
} else {
AccessibilityInteractionClient.getInstance(mContext).removeConnection(mConnectionId);
mConnectionId = AccessibilityInteractionClient.NO_ID;
AccessibilityInteractionClient.getInstance(mContext).clearCache();
mCallback.init(AccessibilityInteractionClient.NO_ID, null);
}
return;
}
也就是说,在 AccessbilityService 创建时,会将一个表示连接的对象存到 AccessibilityInteractionClient 的连接缓存中。
IAccessibilityServiceConnection
它是 AccessibilityManagerService 向 AccessbilityService 暴露的 AIDL 接口,提供给 AccessbilityService 调用AccessibilityManagerService 的能力。 上面的 performAction 流程中,调用到了 connection 的performAccessibilityAction方法。 而 IAccessibilityServiceConnection 有两个实现类,AccessibilityServiceConnectionImpl和AbstractAccessibilityServiceConnection,前者都是空实现,显然不是我们要调用到的地方,后者的performAccessibilityAction:
@Override
public boolean performAccessibilityAction(int accessibilityWindowId,
long accessibilityNodeId, int action, Bundle arguments, int interactionId,
IAccessibilityInteractionConnectionCallback callback, long interrogatingTid)
throws RemoteException {
final int resolvedWindowId;
synchronized (mLock) {
if (!hasRightsToCurrentUserLocked()) {
return false;
}
resolvedWindowId = resolveAccessibilityWindowIdLocked(accessibilityWindowId);
if (!mSecurityPolicy.canGetAccessibilityNodeInfoLocked(
mSystemSupport.getCurrentUserIdLocked(), this, resolvedWindowId)) {
return false;
}
}
if (!mSecurityPolicy.checkAccessibilityAccess(this)) {
return false;
}
return performAccessibilityActionInternal(
mSystemSupport.getCurrentUserIdLocked(), resolvedWindowId, accessibilityNodeId,
action, arguments, interactionId, callback, mFetchFlags, interrogatingTid);
}
最后的一行调用:
private boolean performAccessibilityActionInternal(int userId, int resolvedWindowId, long accessibilityNodeId, int action, Bundle arguments, int interactionId, IAccessibilityInteractionConnectionCallback callback, int fetchFlags, long interrogatingTid) {
RemoteAccessibilityConnection connection;
IBinder activityToken = null;
// 同步获取 connection
synchronized (mLock) {
connection = mA11yWindowManager.getConnectionLocked(userId, resolvedWindowId);
if (connection == null) {
return false;
}
final boolean isA11yFocusAction = (action == ACTION_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUS) || (action == ACTION_CLEAR_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUS);
if (!isA11yFocusAction) {
final WindowInfo windowInfo = mA11yWindowManager.findWindowInfoByIdLocked(resolvedWindowId);
if (windowInfo != null) activityToken = windowInfo.activityToken;
}
final AccessibilityWindowInfo a11yWindowInfo = mA11yWindowManager.findA11yWindowInfoByIdLocked(resolvedWindowId);
if (a11yWindowInfo != null && a11yWindowInfo.isInPictureInPictureMode() && mA11yWindowManager.getPictureInPictureActionReplacingConnection() != null && !isA11yFocusAction) {
connection = mA11yWindowManager.getPictureInPictureActionReplacingConnection();
}
}
// 通过 connection 调用到远程服务的performAccessibilityAction
final int interrogatingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final long identityToken = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
// 无论操作是否成功,它都是由用户操作的无障碍服务生成的,因此请注意用户Activity。
mPowerManager.userActivity(SystemClock.uptimeMillis(), PowerManager.USER_ACTIVITY_EVENT_ACCESSIBILITY, 0);
if (action == ACTION_CLICK || action == ACTION_LONG_CLICK) {
mA11yWindowManager.notifyOutsideTouch(userId, resolvedWindowId);
}
if (activityToken != null) {
LocalServices.getService(ActivityTaskManagerInternal.class).setFocusedActivity(activityToken);
}
connection.getRemote().performAccessibilityAction(accessibilityNodeId, action, arguments, interactionId, callback, fetchFlags, interrogatingPid, interrogatingTid);
} catch (RemoteException re) {
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.e(LOG_TAG, "Error calling performAccessibilityAction: " + re);
}
return false;
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(identityToken);
}
return true;
}
在这个方法中,通过 connection 调用到了远端的 performAccessibilityAction 方法。
关键的一行是:
connection.getRemote().performAccessibilityAction(accessibilityNodeId, action, arguments, interactionId, callback, fetchFlags, interrogatingPid, interrogatingTid);
这里的 connection 类型定义成了RemoteAccessibilityConnection。
RemoteAccessibilityConnection
RemoteAccessibilityConnection 是AccessibilityWindowManager的内部类,它的getRemote()返回类型是IAccessibilityInteractionConnection。
AccessibilityWindowManager
此类为 AccessibilityManagerService 提供 API 来管理 AccessibilityWindowInfo 和 WindowInfos。
IAccessibilityInteractionConnection
这是一个 AIDL 中定义的接口,用来进行 给定 window 中 AccessibilityManagerService 和 ViewRoot 之间交互的接口。
也就是说getRemote(). performAccessibilityAction(...)最终来到了 ViewRootImpl 中。
AccessibilityInteractionConnection
ViewRootImpl 中存在一个内部类AccessibilityInteractionConnection,它是这个 ViewAncestor 提供给 AccessibilityManagerService 的一个接口,后者可以与这个 ViewAncestor 中的视图层次结构进行交互。
它的performAccessibilityAction实现是:
@Override
public void performAccessibilityAction(long accessibilityNodeId, int action, Bundle arguments, int interactionId, IAccessibilityInteractionConnectionCallback callback, int flags, int interrogatingPid, long interrogatingTid) {
ViewRootImpl viewRootImpl = mViewRootImpl.get();
if (viewRootImpl != null && viewRootImpl.mView != null) {
viewRootImpl.getAccessibilityInteractionController().performAccessibilityActionClientThread(accessibilityNodeId, action, arguments,
interactionId, callback, flags, interrogatingPid, interrogatingTid);
} else {
// We cannot make the call and notify the caller so it does not wait.
try {
callback.setPerformAccessibilityActionResult(false, interactionId);
} catch (RemoteException re) {
/* best effort - ignore */
}
}
}
内部又是通过代理调用 ,ViewRootImpl 的 getAccessibilityInteractionController() 返回了一个 AccessibilityInteractionController 对象。
AccessibilityInteractionController
它的 performAccessibilityActionClientThread :
public void performAccessibilityActionClientThread(long accessibilityNodeId, int action,
Bundle arguments, int interactionId,
IAccessibilityInteractionConnectionCallback callback, int flags, int interrogatingPid,
long interrogatingTid) {
Message message = mHandler.obtainMessage();
message.what = PrivateHandler.MSG_PERFORM_ACCESSIBILITY_ACTION;
message.arg1 = flags;
message.arg2 = AccessibilityNodeInfo.getAccessibilityViewId(accessibilityNodeId);
SomeArgs args = SomeArgs.obtain();
args.argi1 = AccessibilityNodeInfo.getVirtualDescendantId(accessibilityNodeId);
args.argi2 = action;
args.argi3 = interactionId;
args.arg1 = callback;
args.arg2 = arguments;
message.obj = args;
scheduleMessage(message, interrogatingPid, interrogatingTid, CONSIDER_REQUEST_PREPARERS);
}
组装了一个 message ,并通过 scheduleMessage 方法去执行:
private void scheduleMessage(Message message, int interrogatingPid, long interrogatingTid, boolean ignoreRequestPreparers) {
if (ignoreRequestPreparers || !holdOffMessageIfNeeded(message, interrogatingPid, interrogatingTid)) {
if (interrogatingPid == mMyProcessId && interrogatingTid == mMyLooperThreadId
&& mHandler.hasAccessibilityCallback(message)) {
AccessibilityInteractionClient.getInstanceForThread(
interrogatingTid).setSameThreadMessage(message);
} else {
if (!mHandler.hasAccessibilityCallback(message) && Thread.currentThread().getId() == mMyLooperThreadId) {
mHandler.handleMessage(message);
} else {
mHandler.sendMessage(message);
}
}
}
}
这里实际上,如果是在主线程,则处理消息,如果不是,则发送消息到主线程处理。handler 的类型是 PrivateHandler ,在 AccessibilityInteractionController 内部定义。
它的处理消息方法的实现是:
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message message) {
final int type = message.what;
switch (type) {
// ...
case MSG_PERFORM_ACCESSIBILITY_ACTION: {
performAccessibilityActionUiThread(message);
} break;
// ...
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown message type: " + type);
}
}
执行到了 performAccessibilityActionUiThread(message); :
private void performAccessibilityActionUiThread(Message message) {
// ...
boolean succeeded = false;
try {
// ...
final View target = findViewByAccessibilityId(accessibilityViewId);
if (target != null && isShown(target)) {
mA11yManager.notifyPerformingAction(action);
if (action == R.id.accessibilityActionClickOnClickableSpan) {
// 单独处理这个 hidden action
succeeded = handleClickableSpanActionUiThread(target, virtualDescendantId, arguments);
} else {
AccessibilityNodeProvider provider = target.getAccessibilityNodeProvider();
if (provider != null) {
succeeded = provider.performAction(virtualDescendantId, action, arguments);
} else if (virtualDescendantId == AccessibilityNodeProvider.HOST_VIEW_ID) {
succeeded = target.performAccessibilityAction(action, arguments);
}
}
mA11yManager.notifyPerformingAction(0);
}
} finally {
try {
mViewRootImpl.mAttachInfo.mAccessibilityFetchFlags = 0;
callback.setPerformAccessibilityActionResult(succeeded, interactionId);
} catch (RemoteException re) {
/* ignore - the other side will time out */
}
}
}
在这个流程中,分为三种情况去真正执行 performAction :
1. action == R.id.accessibilityActionClickOnClickableSpan
private boolean handleClickableSpanActionUiThread(
View view, int virtualDescendantId, Bundle arguments) {
Parcelable span = arguments.getParcelable(ACTION_ARGUMENT_ACCESSIBLE_CLICKABLE_SPAN);
if (!(span instanceof AccessibilityClickableSpan)) {
return false;
}
// Find the original ClickableSpan if it's still on the screen
AccessibilityNodeInfo infoWithSpan = null;
AccessibilityNodeProvider provider = view.getAccessibilityNodeProvider();
if (provider != null) {
infoWithSpan = provider.createAccessibilityNodeInfo(virtualDescendantId);
} else if (virtualDescendantId == AccessibilityNodeProvider.HOST_VIEW_ID) {
infoWithSpan = view.createAccessibilityNodeInfo();
}
if (infoWithSpan == null) {
return false;
}
// Click on the corresponding span
ClickableSpan clickableSpan = ((AccessibilityClickableSpan) span).findClickableSpan(
infoWithSpan.getOriginalText());
if (clickableSpan != null) {
clickableSpan.onClick(view);
return true;
}
return false;
}
2. View. AccessibilityNodeProvider != null
当能够通过 View 获取到 AccessibilityNodeProvider 对象是,通过它的 performAction 方法,去执行真正的调用,它的真正调用在 AccessibilityNodeProviderCompat中,这个 Compat 的实现在ExploreByTouchHelper中的内部类MyNodeProvider中:
@Override
public boolean performAction(int virtualViewId, int action, Bundle arguments) {
return ExploreByTouchHelper.this.performAction(virtualViewId, action, arguments);
}
在 ExploreByTouchHelper 中继续查看:
boolean performAction(int virtualViewId, int action, Bundle arguments) {
switch (virtualViewId) {
case HOST_ID:
return performActionForHost(action, arguments);
default:
return performActionForChild(virtualViewId, action, arguments);
}
}
private boolean performActionForHost(int action, Bundle arguments) {
return ViewCompat.performAccessibilityAction(mHost, action, arguments);
}
private boolean performActionForChild(int virtualViewId, int action, Bundle arguments) {
switch (action) {
case AccessibilityNodeInfoCompat.ACTION_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUS:
return requestAccessibilityFocus(virtualViewId);
case AccessibilityNodeInfoCompat.ACTION_CLEAR_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUS:
return clearAccessibilityFocus(virtualViewId);
case AccessibilityNodeInfoCompat.ACTION_FOCUS:
return requestKeyboardFocusForVirtualView(virtualViewId);
case AccessibilityNodeInfoCompat.ACTION_CLEAR_FOCUS:
return clearKeyboardFocusForVirtualView(virtualViewId);
default:
return onPerformActionForVirtualView(virtualViewId, action, arguments);
}
}
前者调用到了 ViewCompat :
public static boolean performAccessibilityAction(@NonNull View view, int action,
Bundle arguments) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 16) {
return view.performAccessibilityAction(action, arguments);
}
return false;
}
然后是 View 的 :
public boolean performAccessibilityAction(int action, Bundle arguments) {
if (mAccessibilityDelegate != null) {
return mAccessibilityDelegate.performAccessibilityAction(this, action, arguments);
} else {
return performAccessibilityActionInternal(action, arguments);
}
}
mAccessibilityDelegate.performAccessibilityAction的实现是:
public boolean performAccessibilityAction(View host, int action, Bundle args) {
return host.performAccessibilityActionInternal(action, args);
}
也是调用到了 View 的performAccessibilityActionInternal 。 performAccessibilityActionInternal 的实现是:
// in View.java
public boolean performAccessibilityActionInternal(int action, Bundle arguments) {
if (isNestedScrollingEnabled()
&& (action == AccessibilityNodeInfo.ACTION_SCROLL_BACKWARD
|| action == AccessibilityNodeInfo.ACTION_SCROLL_FORWARD
|| action == R.id.accessibilityActionScrollUp
|| action == R.id.accessibilityActionScrollLeft
|| action == R.id.accessibilityActionScrollDown
|| action == R.id.accessibilityActionScrollRight)) {
if (dispatchNestedPrePerformAccessibilityAction(action, arguments)) {
return true;
}
}
switch (action) {
case AccessibilityNodeInfo.ACTION_CLICK: {
if (isClickable()) {
performClickInternal();
return true;
}
} break;
case AccessibilityNodeInfo.ACTION_LONG_CLICK: {
if (isLongClickable()) {
performLongClick();
return true;
}
} break;
// ...
}
return false;
}
以 AccessibilityNodeInfo.ACTION_CLICK 为例,内部调用是:
private boolean performClickInternal() {
// Must notify autofill manager before performing the click actions to avoid scenarios where
// the app has a click listener that changes the state of views the autofill service might
// be interested on.
notifyAutofillManagerOnClick();
return performClick();
}
这样就调用到了 View 的点击事件。
3. View. AccessibilityNodeProvider == null && virtualDescendantId == AccessibilityNodeProvider.HOST_VIEW_ID
target.performAccessibilityAction(action, arguments);
这里 target 是个 View, 也是走的 View 的 performAccessibilityAction ,和上面流程一样。
View 的 performClick 方法是同步的还是异步的?
public boolean performClick() {
// We still need to call this method to handle the cases where performClick() was called
// externally, instead of through performClickInternal()
notifyAutofillManagerOnClick();
final boolean result;
final ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnClickListener != null) {
playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants.CLICK);
li.mOnClickListener.onClick(this);
result = true;
} else {
result = false;
}
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_CLICKED);
notifyEnterOrExitForAutoFillIfNeeded(true);
return result;
}
同步的。
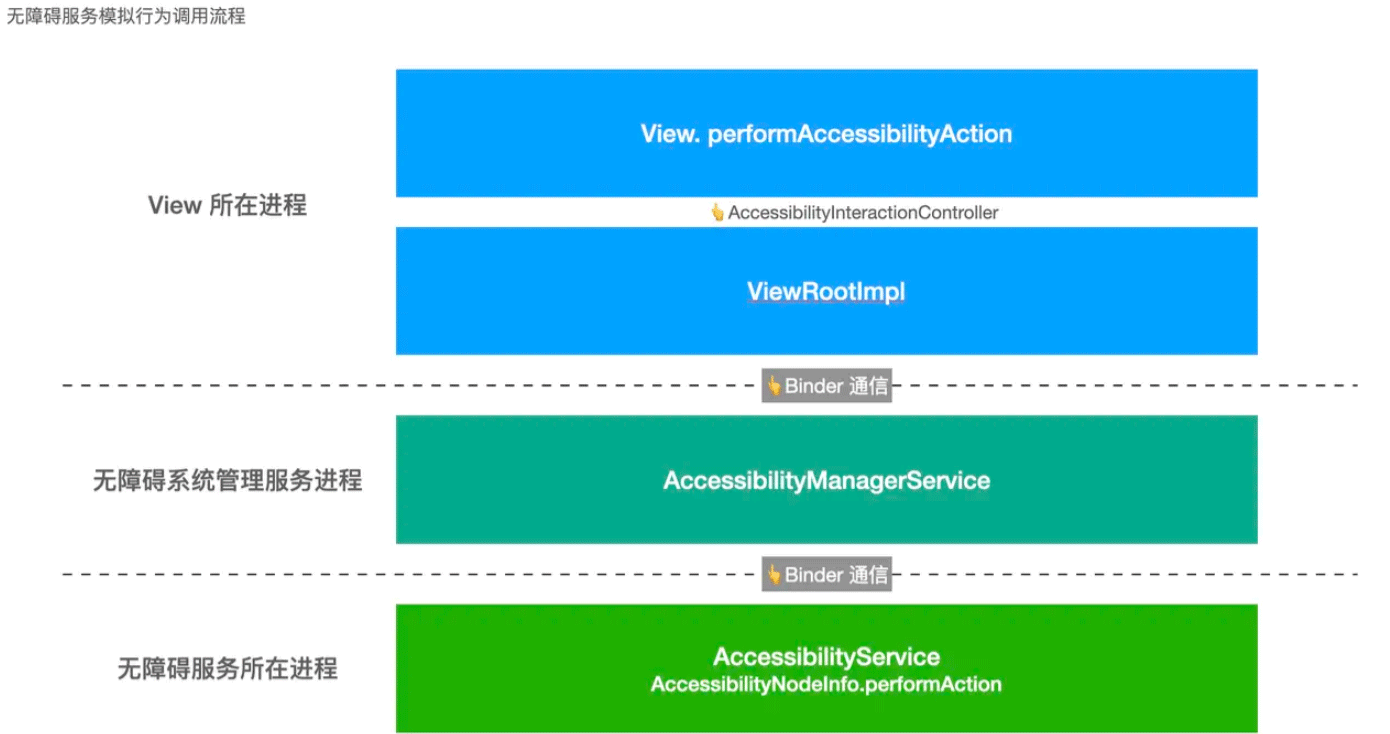
总结
到此这篇关于Android 无障碍服务 performAction 调用过程分析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Android performAction 内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

