我劝你谨慎使用Spring中的@Scheduled注解
目录
- 引言
- 1.@Scheduled失效原因
- 2.解析流程图
- 3.使用新的方法
- schedule定时任务修改表达式无效
引言
在一些业务场景中需要执行定时操作来完成一些周期性的任务,比如每隔一周删除一周前的某些历史数据以及定时进行某项检测任务等等。
在日常开发中比较简单的实现方式就是使用Spring的@Scheduled(具体使用方法不再赘述)注解。
但是在修改服务器时间时会导致定时任务不执行情况的发生,解决的办法是当修改服务器时间后,将服务进行重启就可以避免此现象的发生。
本文将主要探讨服务器时间修改导致@Scheduled注解失效的原因,同时找到在修改服务器时间后不重启服务的情况下,定时任务仍然正常执行的方法。
- @Scheduled失效原因分析
- 解析流程图
- 使用新的方法
1.@Scheduled失效原因
(1)首先我们一起看一下@Scheduled注解的源码,主要说明了注解可使用的参数形式,在注解中使用了Schedules这个类。
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Repeatable(Schedules.class)
public @interface Scheduled {
/**
* A cron-like expression, extending the usual UN*X definition to include
* triggers on the second as well as minute, hour, day of month, month
* and day of week. e.g. {@code "0 * * * * MON-FRI"} means once per minute on
* weekdays (at the top of the minute - the 0th second).
* @return an expression that can be parsed to a cron schedule
* @see org.springframework.scheduling.support.CronSequenceGenerator
*/
String cron() default "";
/**
* A time zone for which the cron expression will be resolved. By default, this
* attribute is the empty String (i.e. the server's local time zone will be used).
* @return a zone id accepted by {@link java.util.TimeZone#getTimeZone(String)},
* or an empty String to indicate the server's default time zone
* @since 4.0
* @see org.springframework.scheduling.support.CronTrigger#CronTrigger(String, java.util.TimeZone)
* @see java.util.TimeZone
*/
String zone() default "";
/**
* Execute the annotated method with a fixed period in milliseconds between the
* end of the last invocation and the start of the next.
* @return the delay in milliseconds
*/
long fixedDelay() default -1;
/**
* Execute the annotated method with a fixed period in milliseconds between the
* end of the last invocation and the start of the next.
* @return the delay in milliseconds as a String value, e.g. a placeholder
* @since 3.2.2
*/
String fixedDelayString() default "";
/**
* Execute the annotated method with a fixed period in milliseconds between
* invocations.
* @return the period in milliseconds
*/
long fixedRate() default -1;
/**
* Execute the annotated method with a fixed period in milliseconds between
* invocations.
* @return the period in milliseconds as a String value, e.g. a placeholder
* @since 3.2.2
*/
String fixedRateString() default "";
/**
* Number of milliseconds to delay before the first execution of a
* {@link #fixedRate()} or {@link #fixedDelay()} task.
* @return the initial delay in milliseconds
* @since 3.2
*/
long initialDelay() default -1;
/**
* Number of milliseconds to delay before the first execution of a
* {@link #fixedRate()} or {@link #fixedDelay()} task.
* @return the initial delay in milliseconds as a String value, e.g. a placeholder
* @since 3.2.2
*/
String initialDelayString() default "";
}
(2)接下来我们来看下,Spring容器是如何解析@Scheduled注解的。
public class ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
implements MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor, DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor,
Ordered, EmbeddedValueResolverAware, BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware,
SmartInitializingSingleton, ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent>, DisposableBean {
...
}
Spring容器加载完bean之后,postProcessAfterInitialization将拦截所有以@Scheduled注解标注的方法。
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) {
Class<?> targetClass = AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(bean);
if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(targetClass)) {
//获取含有@Scheduled注解的方法
Map<Method, Set<Scheduled>> annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetClass,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<Set<Scheduled>>) method -> {
Set<Scheduled> scheduledMethods = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedRepeatableAnnotations(
method, Scheduled.class, Schedules.class);
return (!scheduledMethods.isEmpty() ? scheduledMethods : null);
});
if (annotatedMethods.isEmpty()) {
this.nonAnnotatedClasses.add(targetClass);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No @Scheduled annotations found on bean class: " + bean.getClass());
}
}
else {
// 循环处理包含@Scheduled注解的方法
annotatedMethods.forEach((method, scheduledMethods) ->
scheduledMethods.forEach(scheduled -> processScheduled(scheduled, method, bean)));
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(annotatedMethods.size() + " @Scheduled methods processed on bean '" + beanName +
"': " + annotatedMethods);
}
}
}
return bean;
}
再往下继续看,Spring是如何处理带有@Schedule注解的方法的。processScheduled获取scheduled类参数,之后根据参数类型、相应的延时时间、对应的时区将定时任务放入不同的任务列表中。
protected void processScheduled(Scheduled scheduled, Method method, Object bean) {
try {
Assert.isTrue(method.getParameterCount() == 0,
"Only no-arg methods may be annotated with @Scheduled");
//获取调用的方法
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, bean.getClass());
//处理线程
Runnable runnable = new ScheduledMethodRunnable(bean, invocableMethod);
boolean processedSchedule = false;
String errorMessage =
"Exactly one of the 'cron', 'fixedDelay(String)', or 'fixedRate(String)' attributes is required";
Set<ScheduledTask> tasks = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
// Determine initial delay
long initialDelay = scheduled.initialDelay();
String initialDelayString = scheduled.initialDelayString();
if (StringUtils.hasText(initialDelayString)) {
Assert.isTrue(initialDelay < 0, "Specify 'initialDelay' or 'initialDelayString', not both");
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
initialDelayString = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(initialDelayString);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initialDelayString)) {
try {
initialDelay = parseDelayAsLong(initialDelayString);
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid initialDelayString value \"" + initialDelayString + "\" - cannot parse into long");
}
}
}
// 获取cron参数
String cron = scheduled.cron();
if (StringUtils.hasText(cron)) {
String zone = scheduled.zone();
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
cron = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(cron);
zone = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(zone);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(cron)) {
Assert.isTrue(initialDelay == -1, "'initialDelay' not supported for cron triggers");
processedSchedule = true;
TimeZone timeZone;
if (StringUtils.hasText(zone)) {
timeZone = StringUtils.parseTimeZoneString(zone);
}
else {
timeZone = TimeZone.getDefault();
}
//加入到定时任务列表中
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleCronTask(new CronTask(runnable, new CronTrigger(cron, timeZone))));
}
}
// At this point we don't need to differentiate between initial delay set or not anymore
if (initialDelay < 0) {
initialDelay = 0;
}
// Check fixed delay
long fixedDelay = scheduled.fixedDelay();
if (fixedDelay >= 0) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedDelayTask(new FixedDelayTask(runnable, fixedDelay, initialDelay)));
}
String fixedDelayString = scheduled.fixedDelayString();
if (StringUtils.hasText(fixedDelayString)) {
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
fixedDelayString = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(fixedDelayString);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(fixedDelayString)) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
try {
fixedDelay = parseDelayAsLong(fixedDelayString);
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid fixedDelayString value \"" + fixedDelayString + "\" - cannot parse into long");
}
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedDelayTask(new FixedDelayTask(runnable, fixedDelay, initialDelay)));
}
}
// 执行频率的类型为long
long fixedRate = scheduled.fixedRate();
if (fixedRate >= 0) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedRateTask(new FixedRateTask(runnable, fixedRate, initialDelay)));
}
String fixedRateString = scheduled.fixedRateString();
if (StringUtils.hasText(fixedRateString)) {
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
fixedRateString = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(fixedRateString);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(fixedRateString)) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
try {
fixedRate = parseDelayAsLong(fixedRateString);
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid fixedRateString value \"" + fixedRateString + "\" - cannot parse into long");
}
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedRateTask(new FixedRateTask(runnable, fixedRate, initialDelay)));
}
}
// Check whether we had any attribute set
Assert.isTrue(processedSchedule, errorMessage);
// Finally register the scheduled tasks
synchronized (this.scheduledTasks) {
Set<ScheduledTask> registeredTasks = this.scheduledTasks.get(bean);
if (registeredTasks == null) {
registeredTasks = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
this.scheduledTasks.put(bean, registeredTasks);
}
registeredTasks.addAll(tasks);
}
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Encountered invalid @Scheduled method '" + method.getName() + "': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
满足条件时将定时任务添加到定时任务列表中,在加入任务列表的同时对定时任务进行注册。ScheduledTaskRegistrar这个类为Spring容器的定时任务注册中心。以下为ScheduledTaskRegistrar部分源码,主要说明该类中包含的属性。Spring容器通过线程处理注册的定时任务。
public class ScheduledTaskRegistrar implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private TaskScheduler taskScheduler;
private ScheduledExecutorService localExecutor;
private List<TriggerTask> triggerTasks;
private List<CronTask> cronTasks;
private List<IntervalTask> fixedRateTasks;
private List<IntervalTask> fixedDelayTasks;
private final Map<Task, ScheduledTask> unresolvedTasks = new HashMap<Task, ScheduledTask>(16);
private final Set<ScheduledTask> scheduledTasks = new LinkedHashSet<ScheduledTask>(16);
......
}
ScheduledTaskRegistrar类中在处理定时任务时会调用scheduleCronTask方法初始化定时任务。
public ScheduledTask scheduleCronTask(CronTask task) {
ScheduledTask scheduledTask = this.unresolvedTasks.remove(task);
boolean newTask = false;
if (scheduledTask == null) {
scheduledTask = new ScheduledTask();
newTask = true;
}
if (this.taskScheduler != null) {
scheduledTask.future = this.taskScheduler.schedule(task.getRunnable(), task.getTrigger());
}
else {
addCronTask(task);
this.unresolvedTasks.put(task, scheduledTask);
}
return (newTask ? scheduledTask : null);
}
在ThreadPoolTaskShcedule这个类中,进行线程池的初始化。在创建线程池时会创建 DelayedWorkQueue()阻塞队列,定时任务会被提交到线程池,由线程池进行相关的操作,线程池初始化大小为1。当有多个线程需要执行时,是需要进行任务等待的,前面的任务执行完了才可以进行后面任务的执行。
@Override
protected ExecutorService initializeExecutor(
ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler) {
this.scheduledExecutor = createExecutor(this.poolSize, threadFactory, rejectedExecutionHandler);
if (this.removeOnCancelPolicy) {
if (this.scheduledExecutor instanceof ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor) {
((ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor) this.scheduledExecutor).setRemoveOnCancelPolicy(true);
}
else {
logger.info("Could not apply remove-on-cancel policy - not a Java 7+ ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor");
}
}
return this.scheduledExecutor;
}
根本原因,jvm启动之后会记录系统时间,然后jvm根据CPU ticks自己来算时间,此时获取的是定时任务的基准时间。如果此时将系统时间进行了修改,当Spring将之前获取的基准时间与当下获取的系统时间进行比对时,就会造成Spring内部定时任务失效。因为此时系统时间发生变化了,不会触发定时任务。
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule() {
synchronized (this.triggerContextMonitor) {
this.scheduledExecutionTime = this.trigger.nextExecutionTime(this.triggerContext);
if (this.scheduledExecutionTime == null) {
return null;
}
//获取时间差
long initialDelay = this.scheduledExecutionTime.getTime() - System.currentTimeMillis();
this.currentFuture = this.executor.schedule(this, initialDelay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return this;
}
}
2.解析流程图
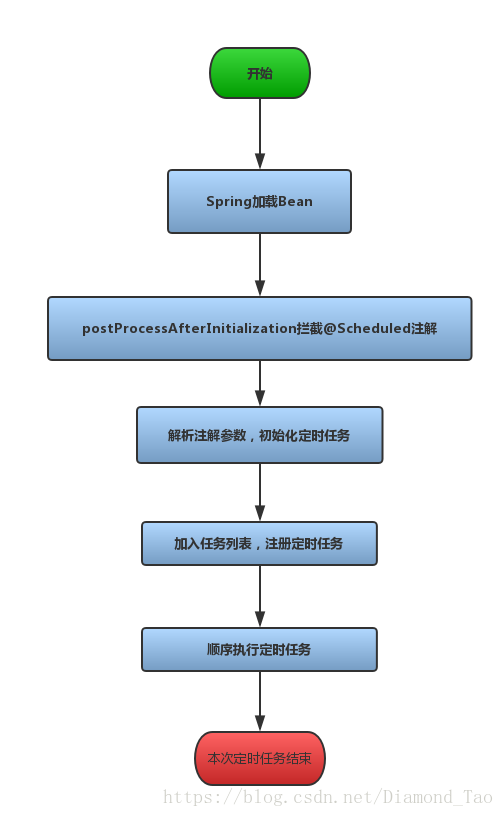
3.使用新的方法
为了避免使用@Scheduled注解,在修改服务器时间导致定时任务不执行情况的发生。在项目中需要使用定时任务场景的情况下,使ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor进行替代,它任务的调度是基于相对时间的,原因是它在任务的内部 存储了该任务距离下次调度还需要的时间(使用的是基于 System.nanoTime实现的相对时间 ,不会因为系统时间改变而改变,如距离下次执行还有10秒,不会因为将系统时间调前6秒而变成4秒后执行)。
schedule定时任务修改表达式无效
真是鬼了。 就那么个cron表达式,难道还能错了。
对了无数遍,cron表达式没问题。 但就是无效。
扩展下思路,有没有用到zookeeper,zookeeper是会缓存配置信息的。
看了下,果然是缓存了。 清空后,重启项目有效了。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

