ASP.NET Core Authentication认证实现方法
追本溯源,从使用开始
首先看一下我们通常是如何使用微软自带的认证,一般在Startup里面配置我们所需的依赖认证服务,这里通过JWT的认证方式讲解
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddAuthentication(authOpt =>
{
authOpt.DefaultAuthenticateScheme = JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme;
authOpt.DefaultChallengeScheme = JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme;
})
.AddJwtBearer(o =>
{
o.TokenValidationParameters = new TokenValidationParameters
{
//配置自己所要验证的参数
};
});
}
我们来看一下源码AddAuthentication主要做了什么
public static class AuthenticationServiceCollectionExtensions
{
public static AuthenticationBuilder AddAuthentication( this IServiceCollection services, Action<AuthenticationOptions> configureOptions)
{
if (services == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (services));
if (configureOptions == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (configureOptions));
AuthenticationBuilder authenticationBuilder = services.AddAuthentication();
services.Configure<AuthenticationOptions>(configureOptions);
return authenticationBuilder;
}
public static AuthenticationBuilder AddAuthentication( this IServiceCollection services)
{
if (services == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (services));
services.AddAuthenticationCore();
services.AddDataProtection();
services.AddWebEncoders();
services.TryAddSingleton<ISystemClock, SystemClock>();
return new AuthenticationBuilder(services);
}
public static AuthenticationBuilder AddAuthentication(
this IServiceCollection services,
string defaultScheme)
{
return services.AddAuthentication((Action<AuthenticationOptions>) (o => o.DefaultScheme = defaultScheme));
}
.....
}
ConfigureServices方法基本都是服务的注册,基于微软的风格,这里的AddAuthenticationCore肯定是我们的认证服务注册方法,来看一下
public static class AuthenticationCoreServiceCollectionExtensions
{
/// <summary>
/// Add core authentication services needed for <see cref="T:Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.IAuthenticationService" />.
/// </summary>
public static IServiceCollection AddAuthenticationCore(
this IServiceCollection services)
{
if (services == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (services));
services.TryAddScoped<IAuthenticationService, AuthenticationService>();
services.TryAddSingleton<IClaimsTransformation, NoopClaimsTransformation>();
services.TryAddScoped<IAuthenticationHandlerProvider, AuthenticationHandlerProvider>();
services.TryAddSingleton<IAuthenticationSchemeProvider, AuthenticationSchemeProvider>();
return services;
}
/// <summary>
/// Add core authentication services needed for <see cref="T:Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.IAuthenticationService" />.
/// </summary>
public static IServiceCollection AddAuthenticationCore(
this IServiceCollection services,
Action<AuthenticationOptions> configureOptions)
{
if (services == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (services));
if (configureOptions == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (configureOptions));
services.AddAuthenticationCore();
services.Configure<AuthenticationOptions>(configureOptions);
return services;
}
}
我们看到这里主要注册了AuthenticationService, AuthenticationHandlerProvider, AuthenticationSchemeProvider这三个对象,如文章开头所说,追本溯源,从使用开始,我们先看一下这三个对象是如何在认证体系中使用的,且是如何发挥作用的。
从使用开始
看一下我们的认证管道构建
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
...
app.UseAuthentication();
...
}
public static class AuthAppBuilderExtensions
{
public static IApplicationBuilder UseAuthentication( this IApplicationBuilder app)
{
if (app == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (app));
return app.UseMiddleware<AuthenticationMiddleware>();
}
}
这里使用了约定的注册方式UseMiddleware,并且指定使用中间件AuthenticationMiddleware
public class AuthenticationMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public AuthenticationMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, IAuthenticationSchemeProvider schemes)
{
if (next == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (next));
if (schemes == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (schemes));
this._next = next;
this.Schemes = schemes;
}
public IAuthenticationSchemeProvider Schemes { get; set; }
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
context.Features.Set<IAuthenticationFeature>((IAuthenticationFeature) new AuthenticationFeature()
{
OriginalPath = context.Request.Path,
OriginalPathBase = context.Request.PathBase
});
IAuthenticationHandlerProvider handlers = context.RequestServices.GetRequiredService<IAuthenticationHandlerProvider>();
foreach (AuthenticationScheme authenticationScheme in await this.Schemes.GetRequestHandlerSchemesAsync())
{
IAuthenticationRequestHandler handlerAsync = await handlers.GetHandlerAsync(context, authenticationScheme.Name) as IAuthenticationRequestHandler;
bool flag = handlerAsync != null;
if (flag)
flag = await handlerAsync.HandleRequestAsync();
if (flag)
return;
}
AuthenticationScheme authenticateSchemeAsync = await this.Schemes.GetDefaultAuthenticateSchemeAsync();
if (authenticateSchemeAsync != null)
{
AuthenticateResult authenticateResult = await context.AuthenticateAsync(authenticateSchemeAsync.Name); //实际的认证业务
if (authenticateResult?.Principal != null)
context.User = authenticateResult.Principal;
}
await this._next(context);
}
}
在继续往下之前,我们先看一下这个认证中间件的作用结果,当认证通过时,在HttpContext的User属性(ClaimPrincipal)赋予身份标识,所以在后续的请求管道中都是基于认证结果中的身份标识做鉴权,这个我们会在后面的实际操作中会提到。
言归正传,在这里引出了我们的两个对象AuthenticationHandlerProvider,AuthenticationSchemeProvider。
重要对象讲解
IAuthenticationSchemeProvider
从名字来看,IAuthenticationSchemeProvider的作用应该是提供Scheme的,这也是Provider在微软的风格里面起的作用(类似于工厂模式)。
这个Scheme是什么呢?很明显,在Framework时代,也是有基于不同Scheme验证的,比如Bearer,Cookie,在Aspnet Core中定义不同的Scheme代表着不同的认证处理方式,具体体现是在每个Scheme中包含对应的IAuthenticationHandler类型的Handler,由它来完成跟自身Scheme相关的认证处理。如果没有定义会怎么样?仔细看上面这块源码,只有当AuthenticationScheme不为空时才会做认证,否则一旦在Controller打上鉴权标签[Authorize],将会直接返回401,所以我们必须指定自己的Scheme。
那么我们在哪里指定我们的Scheme类似呢?我们先返回到ConfigureService的AddJwtBearer,使用过的朋友们肯定知道,这里获取的Scheme是我们在ConfigureService通过Addxxx scheme指定的Scheme类型。这里我们是使用JWT的
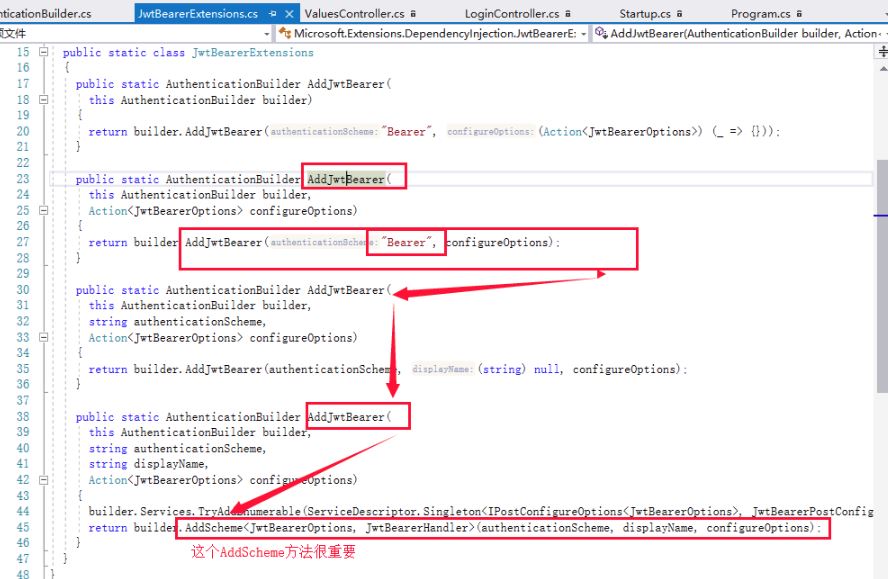
在这里指定了TOptions 为JwtBearerOptions,而THandler为JwtBearerHandler。
public virtual AuthenticationBuilder AddScheme<TOptions, THandler>(
string authenticationScheme,
string displayName,
Action<TOptions> configureOptions)
where TOptions : AuthenticationSchemeOptions, new()
where THandler : AuthenticationHandler<TOptions>
{
return this.AddSchemeHelper<TOptions, THandler>(authenticationScheme, displayName, configureOptions);
}
private AuthenticationBuilder AddSchemeHelper<TOptions, THandler>(
string authenticationScheme,
string displayName,
Action<TOptions> configureOptions)
where TOptions : class, new()
where THandler : class, IAuthenticationHandler
{
this.Services.Configure<AuthenticationOptions>((Action<AuthenticationOptions>) (o => o.AddScheme(authenticationScheme, (Action<AuthenticationSchemeBuilder>) (scheme =>
{
scheme.HandlerType = typeof (THandler);
scheme.DisplayName = displayName;
}))));
if (configureOptions != null)
this.Services.Configure<TOptions>(authenticationScheme, configureOptions);
this.Services.AddTransient<THandler>();
return this;
}
注意这里TOptions 是需要继承AuthenticationSchemeOptions的,在这里是JwtBearerOptions,而THandler是AuthenticationHandler<TOptions>类型的Handler,在这里是JwtBearerHandler。

我们回到Scheme的分析继续往下,首先看一下AuthenticationScheme的定义
public class AuthenticationScheme
{
/// <summary>Constructor.</summary>
public AuthenticationScheme(string name, string displayName, Type handlerType)
{
if (name == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (name));
if (handlerType == (Type) null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (handlerType));
if (!typeof (IAuthenticationHandler).IsAssignableFrom(handlerType))
throw new ArgumentException("handlerType must implement IAuthenticationHandler.");
this.Name = name;
this.HandlerType = handlerType;
this.DisplayName = displayName;
}
/// <summary>The name of the authentication scheme.</summary>
public string Name { get; }
/// <summary>
/// The display name for the scheme. Null is valid and used for non user facing schemes.
/// </summary>
public string DisplayName { get; }
/// <summary>
/// The <see cref="T:Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.IAuthenticationHandler" /> type that handles this scheme.
/// </summary>
public Type HandlerType { get; }
}
在这里可以看到,如果要使用Aspnet Core自身的认证体系,需先注册Scheme,并且该Scheme必须指定一个类型为IAuthenticationHandler的Handler,否则会抛出异常。(这个其实在AddxxxScheme的时候已经指定了AuthenticationHandler)
我们再看一下IAuthenticationSchemeProvider的GetRequestHandlerSchemesAsync方法做了什么
public virtual Task<IEnumerable<AuthenticationScheme>> GetRequestHandlerSchemesAsync()
{
return Task.FromResult<IEnumerable<AuthenticationScheme>>((IEnumerable<AuthenticationScheme>) this._requestHandlers);
}
这东西返回了_requestHandlers,这是什么?看代码
public class AuthenticationSchemeProvider : IAuthenticationSchemeProvider
{
private readonly object _lock = new object();
private readonly AuthenticationOptions _options;
private readonly IDictionary<string, AuthenticationScheme> _schemes;
private readonly List<AuthenticationScheme> _requestHandlers;
/// <summary>
/// Creates an instance of <see cref="T:Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.AuthenticationSchemeProvider" />
/// using the specified <paramref name="options" />,
/// </summary>
public AuthenticationSchemeProvider(IOptions<AuthenticationOptions> options)
: this(options, (IDictionary<string, AuthenticationScheme>) new Dictionary<string, AuthenticationScheme>((IEqualityComparer<string>) StringComparer.Ordinal))
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Creates an instance of <see cref="T:Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.AuthenticationSchemeProvider" />
/// using the specified <paramref name="options" /> and <paramref name="schemes" />.
/// </summary>
protected AuthenticationSchemeProvider(
IOptions<AuthenticationOptions> options,
IDictionary<string, AuthenticationScheme> schemes)
{
this._options = options.Value;
IDictionary<string, AuthenticationScheme> dictionary = schemes;
if (dictionary == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof (schemes));
this._schemes = dictionary;
this._requestHandlers = new List<AuthenticationScheme>();
foreach (AuthenticationSchemeBuilder scheme in this._options.Schemes)
this.AddScheme(scheme.Build());
}
public virtual void AddScheme(AuthenticationScheme scheme)
{
if (this._schemes.ContainsKey(scheme.Name))
throw new InvalidOperationException("Scheme already exists: " + scheme.Name);
lock (this._lock)
{
if (this._schemes.ContainsKey(scheme.Name))
throw new InvalidOperationException("Scheme already exists: " + scheme.Name);
if (typeof (IAuthenticationRequestHandler).IsAssignableFrom(scheme.HandlerType))
this._requestHandlers.Add(scheme);
this._schemes[scheme.Name] = scheme;
}
}
.....
}
这东西就是把我们在认证注册服务中指定的scheme,通过解析出的AuthenticationSchemeProvider 的构造函数加载来的,进而返回一系列的List<AuthenticationScheme>,OK拿到这些scheme之后有什么用呢?这里引出了我们的第二个对象AuthenticationHandlerProvider,下面我们来了解一下。
IAuthenticationHandlerProvider
我们看到,AuthenticationMiddleware中用到了IAuthenticationHandlerProvider的GetHandlerAsync方法,那我们先看一下这个方法的作用
public class AuthenticationHandlerProvider : IAuthenticationHandlerProvider
{
private Dictionary<string, IAuthenticationHandler> _handlerMap = new Dictionary<string, IAuthenticationHandler>((IEqualityComparer<string>) StringComparer.Ordinal);
/// <summary>Constructor.</summary>
public AuthenticationHandlerProvider(IAuthenticationSchemeProvider schemes)
{
this.Schemes = schemes;
}
/// <summary>
/// The <see cref="T:Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.IAuthenticationHandlerProvider" />.
/// </summary>
public IAuthenticationSchemeProvider Schemes { get; }
/// <summary>Returns the handler instance that will be used.</summary>
public async Task<IAuthenticationHandler> GetHandlerAsync( HttpContext context, string authenticationScheme)
{
if (this._handlerMap.ContainsKey(authenticationScheme))
return this._handlerMap[authenticationScheme];
AuthenticationScheme schemeAsync = await this.Schemes.GetSchemeAsync(authenticationScheme);
if (schemeAsync == null)
return (IAuthenticationHandler) null;
IAuthenticationHandler handler = (context.RequestServices.GetService(schemeAsync.HandlerType) ?? ActivatorUtilities.CreateInstance(context.RequestServices, schemeAsync.HandlerType)) as IAuthenticationHandler;
if (handler != null)
{
await handler.InitializeAsync(schemeAsync, context);
this._handlerMap[authenticationScheme] = handler;
}
return handler;
}
}
在创建Handler的时候,是先从AuthenticationScheme中获取,如果不存在则通过ActivatorUtilities创建。 获取到Handle后,将会放在_handlerMap字典里面,当下次获取Handler的时候,将直接从缓存中获取。
IAuthenticationService
这个对象是在AuthenticationMiddleware中最后才用到的,而且是基于HttpContext的扩展被调用
public static class AuthenticationHttpContextExtensions
{
public static Task<AuthenticateResult> AuthenticateAsync(this HttpContext context, string scheme) =>
context.RequestServices.GetRequiredService<IAuthenticationService>().AuthenticateAsync(context, scheme);
....
}
这里主要调用了IAuthenticationService的AuthenticateAsync方法,看一下这个方法做了什么
public class AuthenticationService : IAuthenticationService
{
public IAuthenticationSchemeProvider Schemes { get; }
public IAuthenticationHandlerProvider Handlers { get; }
public IClaimsTransformation Transform { get; }
public virtual async Task<AuthenticateResult> AuthenticateAsync(HttpContext context, string scheme)
{
if (scheme == null)
{
var scheme = (await this.Schemes.GetDefaultAuthenticateSchemeAsync())?.Name;
if (scheme == null)
throw new InvalidOperationException($"No authenticationScheme was specified, and there was no DefaultAuthenticateScheme found.");
}
var handler = await Handlers.GetHandlerAsync(context, scheme);
if(handler == null)
throw await this.CreateMissingHandlerException(scheme);
AuthenticateResult result = await handler.AuthenticateAsync();
if (result != null && result.Succeeded)
return AuthenticateResult.Success(new AuthenticationTicket(await Transform.TransformAsync(result.Principal), result.Properties, result.Ticket.AuthenticationScheme));
return result;
}
}
这里其实就是我们在前面讲的根据Scheme获取对应的AuthenticationHandler,然后调用AuthenticateAsync()方法,这个方法调用了核心方法HandleAuthenticateOnceAsync,然后再调用HandleAuthenticateAsync()这个核心的认证方法。
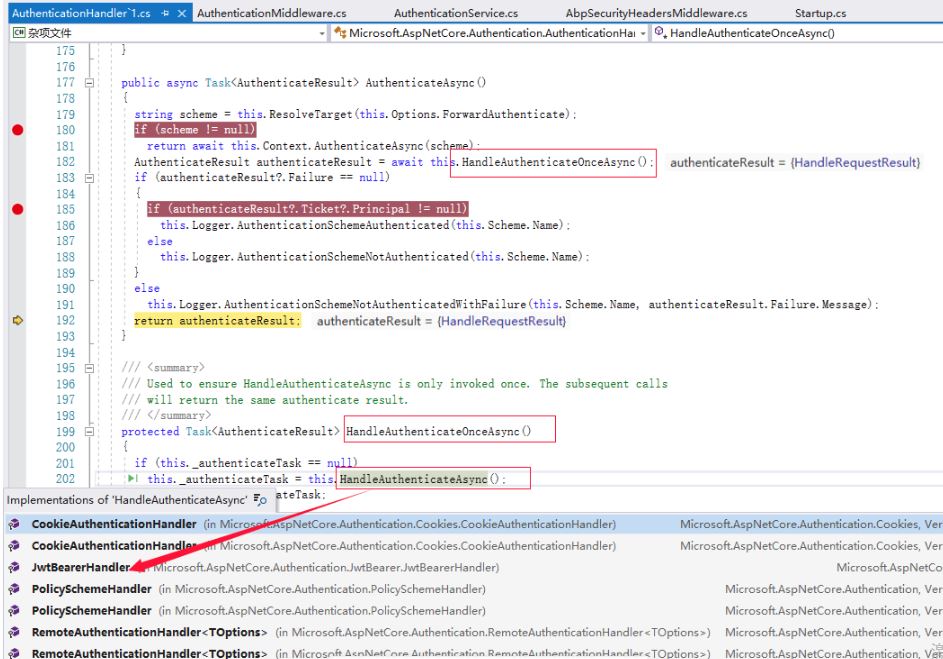
从上图看到这个HandleAuthenticateAsync是个抽象方法,我们的子类都需要实现这个方法的动作,基于本文的例子,我们看一下JwtBearerHandler的一个实际认证。
public class JwtBearerHandler : AuthenticationHandler<JwtBearerOptions>
{
protected override async Task<AuthenticateResult> HandleAuthenticateAsync()
{
JwtBearerHandler jwtBearerHandler = this;
string token = (string) null;
object obj;
AuthenticationFailedContext authenticationFailedContext;
int num;
try
{
MessageReceivedContext messageReceivedContext = new MessageReceivedContext(jwtBearerHandler.Context, jwtBearerHandler.Scheme, jwtBearerHandler.Options);
await jwtBearerHandler.Events.MessageReceived(messageReceivedContext);
if (messageReceivedContext.Result != null)
return messageReceivedContext.Result;
token = messageReceivedContext.Token;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(token))
{
string header = (string) jwtBearerHandler.Request.Headers["Authorization"];
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(header))
return AuthenticateResult.NoResult();
if (header.StartsWith("Bearer ", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
token = header.Substring("Bearer ".Length).Trim();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(token))
return AuthenticateResult.NoResult();
}
if (jwtBearerHandler._configuration == null && jwtBearerHandler.Options.ConfigurationManager != null)
{
OpenIdConnectConfiguration configurationAsync = await jwtBearerHandler.Options.ConfigurationManager.GetConfigurationAsync(jwtBearerHandler.Context.RequestAborted);
jwtBearerHandler._configuration = configurationAsync;
}
TokenValidationParameters validationParameters1 = jwtBearerHandler.Options.TokenValidationParameters.Clone();
if (jwtBearerHandler._configuration != null)
{
string[] strArray = new string[1]
{
jwtBearerHandler._configuration.Issuer
};
TokenValidationParameters validationParameters2 = validationParameters1;
IEnumerable<string> validIssuers = validationParameters1.get_ValidIssuers();
object obj1 = (validIssuers != null ? (object) validIssuers.Concat<string>((IEnumerable<string>) strArray) : (object) null) ?? (object) strArray;
validationParameters2.set_ValidIssuers((IEnumerable<string>) obj1);
TokenValidationParameters validationParameters3 = validationParameters1;
IEnumerable<SecurityKey> issuerSigningKeys = validationParameters1.get_IssuerSigningKeys();
IEnumerable<SecurityKey> securityKeys = (issuerSigningKeys != null ? issuerSigningKeys.Concat<SecurityKey>((IEnumerable<SecurityKey>) jwtBearerHandler._configuration.get_SigningKeys()) : (IEnumerable<SecurityKey>) null) ?? (IEnumerable<SecurityKey>) jwtBearerHandler._configuration.get_SigningKeys();
validationParameters3.set_IssuerSigningKeys(securityKeys);
}
List<Exception> exceptionList = (List<Exception>) null;
foreach (ISecurityTokenValidator securityTokenValidator in (IEnumerable<ISecurityTokenValidator>) jwtBearerHandler.Options.SecurityTokenValidators)
{
if (securityTokenValidator.CanReadToken(token))
{
SecurityToken securityToken;
ClaimsPrincipal claimsPrincipal;
try
{
claimsPrincipal = securityTokenValidator.ValidateToken(token, validationParameters1, ref securityToken);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
jwtBearerHandler.Logger.TokenValidationFailed(ex);
if (jwtBearerHandler.Options.RefreshOnIssuerKeyNotFound && jwtBearerHandler.Options.ConfigurationManager != null && ex is SecurityTokenSignatureKeyNotFoundException)
jwtBearerHandler.Options.ConfigurationManager.RequestRefresh();
if (exceptionList == null)
exceptionList = new List<Exception>(1);
exceptionList.Add(ex);
continue;
}
jwtBearerHandler.Logger.TokenValidationSucceeded();
TokenValidatedContext validatedContext = new TokenValidatedContext(jwtBearerHandler.Context, jwtBearerHandler.Scheme, jwtBearerHandler.Options);
validatedContext.Principal = claimsPrincipal;
validatedContext.SecurityToken = securityToken;
TokenValidatedContext tokenValidatedContext = validatedContext;
await jwtBearerHandler.Events.TokenValidated(tokenValidatedContext);
if (tokenValidatedContext.Result != null)
return tokenValidatedContext.Result;
if (jwtBearerHandler.Options.SaveToken)
tokenValidatedContext.Properties.StoreTokens((IEnumerable<AuthenticationToken>) new AuthenticationToken[1]
{
new AuthenticationToken()
{
Name = "access_token",
Value = token
}
});
tokenValidatedContext.Success();
return tokenValidatedContext.Result;
}
}
if (exceptionList == null)
return AuthenticateResult.Fail("No SecurityTokenValidator available for token: " + token ?? "[null]");
authenticationFailedContext = new AuthenticationFailedContext(jwtBearerHandler.Context, jwtBearerHandler.Scheme, jwtBearerHandler.Options)
{
Exception = exceptionList.Count == 1 ? exceptionList[0] : (Exception) new AggregateException((IEnumerable<Exception>) exceptionList)
};
await jwtBearerHandler.Events.AuthenticationFailed(authenticationFailedContext);
return authenticationFailedContext.Result == null ? AuthenticateResult.Fail(authenticationFailedContext.Exception) : authenticationFailedContext.Result;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
obj = (object) ex;
num = 1;
}
if (num == 1)
{
Exception ex = (Exception) obj;
jwtBearerHandler.Logger.ErrorProcessingMessage(ex);
authenticationFailedContext = new AuthenticationFailedContext(jwtBearerHandler.Context, jwtBearerHandler.Scheme, jwtBearerHandler.Options)
{
Exception = ex
};
await jwtBearerHandler.Events.AuthenticationFailed(authenticationFailedContext);
if (authenticationFailedContext.Result != null)
return authenticationFailedContext.Result;
Exception source = obj as Exception;
if (source == null)
throw obj;
ExceptionDispatchInfo.Capture(source).Throw();
authenticationFailedContext = (AuthenticationFailedContext) null;
}
obj = (object) null;
token = (string) null;
AuthenticateResult authenticateResult;
return authenticateResult;
}
}
这个方法有点长,主要是从Request.Headers里面获取Authorization的Bearer出来解析,再在AddJwtBearer中传入的委托参数JwtBearerOptions的TokenValidationParameters属性作为依据进行对比来进行认证是否通过与否。
总结
本文对 ASP.NET Core 的认证流程做了一个源码分析流程介绍,由于是源码分析篇,所以可能会比较枯燥和苦涩难懂。在后面的真正使用过程中,然后再结合本篇的一个总结流程,相信大家会逐渐开朗。
- 在Startup类中的ConfigureServices方法通过添加AddAuthentication注册我们最主要的三个对象AuthenticationService, AuthenticationHandlerProvider, AuthenticationSchemeProvider
- 通过AddAuthentication返回的AuthenticationBuilder 通过AddJwtBearer(或者AddCookie)来指定Scheme类型和需要验证的参数
- 在Startup类中的Configure方法通过添加UseAuthentication注册认证中间件
- 在认证过程中,通过AuthenticationSchemeProvider获取正确的Scheme,在AuthenticationService中通过Scheme和AuthenticationHandlerProvider获取正确的AuthenticationHandler,最后通过对应的AuthenticationHandler的AuthenticateAsync方法进行认证流程
到此这篇关于ASP.NET Core Authentication认证实现方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关ASP.NET Core Authentication认证内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

