JPA之@EnableJpaAuditing注解使用
目录
- @EnableJpaAuditing注解使用
- 如何实现自动填充功能,即如何使用审计?
- Springboot启用Spring Data JPA Auditing(审计功能)
- Auditing功能简介
- 如何启用
- 使用CreatedBy和LastModifiedBy时
@EnableJpaAuditing注解使用
在Spring JPA中,支持在字段或方法上进行注解 @CreateDate、@CreatedBy、@LastModifiedDate、@LastModifiedBy。具体含义:
@CreateDate:表示该字段是创建时间字段,在这个实体被insert的时候,会自动填充创建的时间,不用手动填充该字段。@CreatedBy:表示该字段是创建人字段,在这个实体被insert的时候,会自动填充创建人字段,不用手动填充。@LastModifiedDate、@LastModifiedBy同理。
如何实现自动填充功能,即如何使用审计?
1、在Xxx Application 启动类上添加 @EnableJpaAuditing:开启审计功能。
@EnableScheduling
@EnableJpaAuditing //利用jpa可以给MySQL列属性自动赋值,例如一些创建时间,修改时间
@EnableEurekaClient
@SpringBootApplication
public class CouponTemplateApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CouponTemplateApplication.class, args);
}
/**
* 测试中如果无法自动识别,可能是包路径的问题,采用手动声明bean的方式
* @return
*/
@Bean
public UserAuditor setUserAuditorAware(){
return new UserAuditor();
}
}
2、实体类上添加 @EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class):开启实体类监听。
3、在需要的字段上加上 @CreatedDate、@CreatedBy、@LastModifiedDate、@LastModifiedBy 等注解。
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Entity //实体类
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class) //监听器,自动赋值创建时间
@Table(name = "coupon_template")
@JsonSerialize(using = CouponTemplateSerialize.class) //绑定自定义的序列化器
public class CouponTemplate implements Serializable {
/** 自增主键 */
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id",nullable = false)
@Basic //指定属于我们数据表的一个列,相反的@Transient,表示该列不属于数据表
private Integer id;
/** 是否是可用状态 */
@Column(name = "available",nullable = false)
private Boolean available;
/** 是否过期 */
@Column(name = "expired",nullable = false)
private Boolean expired;
/** 优惠券名称 */
@Column(name = "name",nullable = false)
private String name;
/** 优惠券 logo */
@Column(name = "logo",nullable = false)
private String logo;
/** 优惠券描述 */
@Column(name = "intro",nullable = false)
private String desc;
/** 优惠券模板 创建时间
* 使用@CreateDate注解在插入的时候,自动生成创建时间,与监听注解有关
* */
@CreatedDate
@Column(name = "create_time",nullable = false)
private Date createTime;
}
4、实现 AuditorAware 接口来返回你需要插入的值。重点!
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class UserAuditor implements AuditorAware<String> {
/**
* 获取当前创建或修改的用户
* @return
*/
@Override
public Optional<String> getCurrentAuditor() {
UserDetails user;
try {
user = (UserDetails) SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
return Optional.ofNullable(user.getUsername());
}catch (Exception e){
return Optional.empty();
}
}
}
Springboot启用Spring Data JPA Auditing(审计功能)
Auditing功能简介
先贴上Spring Data JPA的官方文档
项目中每条数据在创建修改的时候,我们都需要记录它创建人,创建时间,修改人,修改时间。如果每次新增的时候都去手动set,代码冗余且显得很不友好
spring data JPA 为我们提供了审计功能,英文是 Auditing
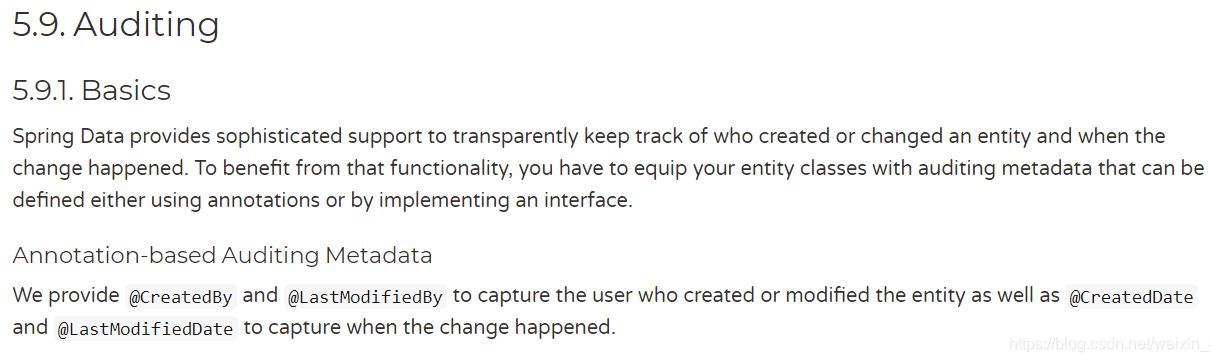
Auditing包括了四个注解,从名字就能看出它们的作用
@CreatedBy:创建人,在这个实体被insert的时候,会设置值@LastModifiedBy:最后一次修改人,在这个实体每次被更新的时候,会设置值@CreatedDate:创建时间,在这个实体被insert的时候,会设置值@LastModifiedDate:最后一次修改时间,在这个实体每次被更新的时候,会设置值
如何启用
1.启动类上加@EnableJpaAuditing注解
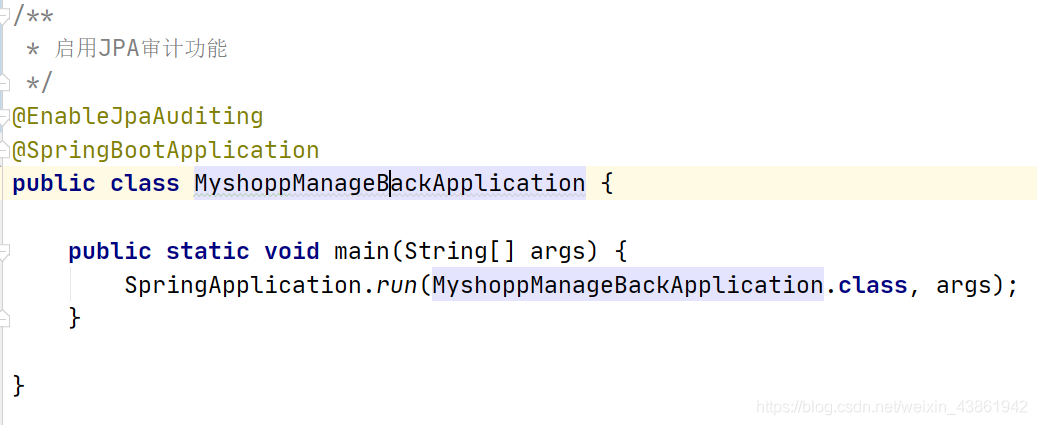
2.实体类上加@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)

3.属性上面使用对应注解

使用CreatedBy和LastModifiedBy时
JPA并不知道你的这个字段的值是什么,需要自己实现AuditorAware接口
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.domain.AuditorAware;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import java.util.Optional;
/**
* 使用@CreatedBy或@LastModifiedBy 则必须实现AuditorAware接口重写getCurrentAuditor方法
* 在定义使用@CreatedBy或@LastModifiedBy时,属性类型必须与AuditorAware接口的泛型类型相同
*/
@Configuration
public class SpringSecurityAuditorAware implements AuditorAware<String> {
@Override
public Optional<String> getCurrentAuditor() {
UserDetails userDetails;
try {
userDetails = (UserDetails)SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
return Optional.ofNullable(userDetails.getUsername());
}catch (Exception e){
return Optional.empty();
}
}
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。
赞 (0)

