剖析Android Activity侧滑返回的实现原理
简介
使用侧滑Activity返回很常见,例如微信就用到了。那么它是怎么实现的呢。本文带你剖析一下实现原理。我在github上找了一个star有2.6k的开源,我们分析他是怎么实现的
//star 2.6k 'com.r0adkll:slidableactivity:2.0.5'
Slidr使用示例
它的使用很简单,首先要设置透明的窗口背景
<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar">
<!-- Customize your theme here. -->
<item name="android:textAllCaps">false</item>
<item name="android:windowActionBar">false</item>
<item name="windowActionBar">false</item>
<item name="windowNoTitle">true</item>
<item name="colorPrimary">@color/colorPrimary</item>
<item name="colorPrimaryDark">@color/colorPrimaryDark</item>
<item name="colorAccent">@color/colorAccent</item>
<item name="android:windowIsTranslucent">true</item>
<item name="android:windowBackground">@android:color/transparent</item>
</style>
然后
//setContent(View view)后 Slidr.attach(this);

下面可以从三个步骤看其原理
步骤一 重新包裹界面
Slidr.class
public static SlidrInterface attach(final Activity activity, final int statusBarColor1, final int statusBarColor2){
//0 创建滑动嵌套界面SliderPanel
final SliderPanel panel = initSliderPanel(activity, null);
//7 Set the panel slide listener for when it becomes closed or opened
// 监听回调
panel.setOnPanelSlideListener(new SliderPanel.OnPanelSlideListener() {
...
//open close等
});
// Return the lock interface
return initInterface(panel);
}
private static SliderPanel initSliderPanel(final Activity activity, final SlidrConfig config) {
//3 获取decorview
ViewGroup decorView = (ViewGroup)activity.getWindow().getDecorView();
//4 获取我们布局的内容并删除
View oldScreen = decorView.getChildAt(0);
decorView.removeViewAt(0);
//5 Setup the slider panel and attach it to the decor
// 建立滑动嵌套视图SliderPanel并且添加到DecorView中
SliderPanel panel = new SliderPanel(activity, oldScreen, config);
panel.setId(R.id.slidable_panel);
oldScreen.setId(R.id.slidable_content);
//6 把我们的界面布局添加到SliderPanel,并且把SliderPanel添加到decorView中
panel.addView(oldScreen);
decorView.addView(panel, 0);
return panel;
}
步骤二 使用ViewDragHelper.class处理滑动手势
SliderPanel.class
private void init(){
...
//1 ViewDragHelper创建
mDragHelper = ViewDragHelper.create(this, mConfig.getSensitivity(), callback);
mDragHelper.setMinVelocity(minVel);
mDragHelper.setEdgeTrackingEnabled(mEdgePosition);
//2 Setup the dimmer view 添加用于指示滑动过程的View到底层
mDimView = new View(getContext());
mDimView.setBackgroundColor(mConfig.getScrimColor());
mDimView.setAlpha(mConfig.getScrimStartAlpha());
addView(mDimView);
}
步骤三 在ViewDragHelper.Callback中处理我们的界面的拖动
我们首先明确ViewDragHelper仅仅是处理ParentView与它子View的关系,不会一直遍历到最顶层的View。ViewDragHelper的捕获capture是这样实现的
@Nullable
public View findTopChildUnder(int x, int y) {
final int childCount = mParentView.getChildCount();
for (int i = childCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final View child = mParentView.getChildAt(mCallback.getOrderedChildIndex(i));
if (x >= child.getLeft() && x < child.getRight()
&& y >= child.getTop() && y < child.getBottom()) {
return child;
}
}
return null;
}
重点在SliderPanel.class的ViewDragHelper.Callback callback的实现,作者实现实现了很多个方向的滑动处理mLeftCallback、mRightCallback、mTopCallback、mBottomCallback、mVerticalCallback、mHorizontalCallback, 我们取mLeftCallback来分析
private ViewDragHelper.Callback mLeftCallback = new ViewDragHelper.Callback() {
//捕获View
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId) {
boolean edgeCase = !mConfig.isEdgeOnly() || mDragHelper.isEdgeTouched(mEdgePosition, pointerId);
//像前面说的,我们的内容是最上层子View,mDecorView这里指的是我们的contentView
return child.getId() == mDecorView.getId() && edgeCase;
}
//拖动, 最终是通过view.offsetLeftAndRight(offset)实现移动
@Override
public int clampViewPositionHorizontal(View child, int left, int dx) {
return clamp(left, 0, mScreenWidth);
}
//滑动范围
@Override
public int getViewHorizontalDragRange(View child) {
return mScreenWidth;
}
//释放处理,判断是滚回屏幕
@Override
public void onViewReleased(View releasedChild, float xvel, float yvel) {
super.onViewReleased(releasedChild, xvel, yvel);
int left = releasedChild.getLeft();
int settleLeft = 0;
int leftThreshold = (int) (getWidth() * mConfig.getDistanceThreshold());
boolean isVerticalSwiping = Math.abs(yvel) > mConfig.getVelocityThreshold();
if(xvel > 0){
if(Math.abs(xvel) > mConfig.getVelocityThreshold() && !isVerticalSwiping){
settleLeft = mScreenWidth;
}else if(left > leftThreshold){
settleLeft = mScreenWidth;
}
}else if(xvel == 0){
if(left > leftThreshold){
settleLeft = mScreenWidth;
}
}
//滚动到left=0(正常布局) 或者 滚动到left=mScreenWidth(滚出屏幕)关闭Activity
mDragHelper.settleCapturedViewAt(settleLeft, releasedChild.getTop());
invalidate();
}
//转换位置百分比,确定指示层的透明度
@Override
public void onViewPositionChanged(View changedView, int left, int top, int dx, int dy) {
super.onViewPositionChanged(changedView, left, top, dx, dy);
float percent = 1f - ((float)left / (float)mScreenWidth);
if(mListener != null) mListener.onSlideChange(percent);
// Update the dimmer alpha
applyScrim(percent);
}
//回调到Slidr处理Activity状态
@Override
public void onViewDragStateChanged(int state) {
super.onViewDragStateChanged(state);
if(mListener != null) mListener.onStateChanged(state);
switch (state){
case ViewDragHelper.STATE_IDLE:
if(mDecorView.getLeft() == 0){
// State Open
if(mListener != null) mListener.onOpened();
}else{
// State Closed 这里回调到Slidr处理activity.finish()
if(mListener != null) mListener.onClosed();
}
break;
case ViewDragHelper.STATE_DRAGGING:
break;
case ViewDragHelper.STATE_SETTLING:
break;
}
}
};
对于mDragHelper.settleCapturedViewAt(settleLeft, releasedChild.getTop());内部是使用Scroller.class辅助滚动,所以要在SliderPanel中重写View.computeScroll()
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
super.computeScroll();
if(mDragHelper.continueSettling(true)){
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(this);
}
}
总结
整体方案如下图所示
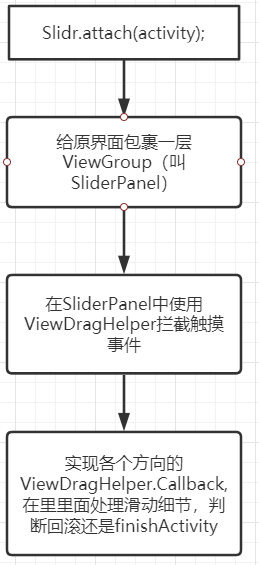
总体来看原理并不复杂, 就是通过ViewDragHelper对View进行拖动。
以上就是Android Activity侧滑返回的实现原理的详细内容,更多关于Activity侧滑返回的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!
赞 (0)

