Java基础学习之Swing事件监听
一、初始代码架构
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Btn extends JFrame{
public static void main(String []args){
JFrame f = new JFrame("事件监听测试");
f.setBounds(0,0,300,400);
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
f.setVisible(false);
f.dispose();
System.exit(0);
}
});
Container page = f.getContentPane();
page.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
JButton btn = new JButton("打印");
page.add(btn);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
运行的结果
二、需求分析
想要点击按钮的时候在终端打印一行信息(比如"按钮被点击")
产品爸爸,提了新需求,不能实现也要创造办法实现的啦
2.1 写监听器
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Btn{
public static void main(String []args){
JFrame f = new JFrame("事件监听测试");
f.setBounds(0,0,300,400);
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
f.setVisible(false);
f.dispose();
System.exit(0);
}
});
Container page = f.getContentPane();
page.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
JButton btn = new JButton("打印");
/**
* 事件监听的使用步骤:
* 1. 创建监听听
* 2. 将监听器注册到按钮上
*
*/
btnListener bl = new btnListener();
btn.addActionListener(bl);
page.add(btn);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
class btnListener implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
System.out.println("按钮被点击了----");
}
}
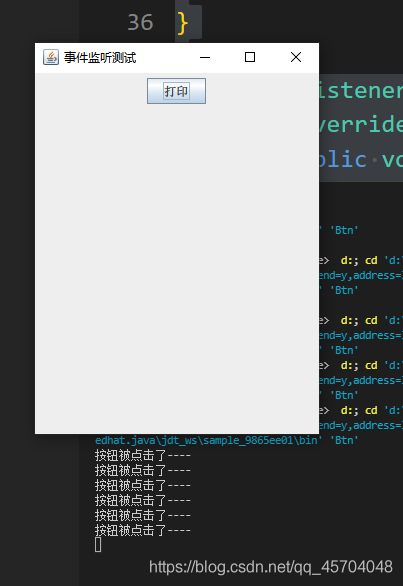
点击按钮的结果
2.2 发现问题
中规中矩地实现监听器地话,发现要另外写一个类实现
ActionListener接口地方法,使得代码架构显得比较臃肿。
2.3 使用匿名内部类优化代码
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Btn{
public static void main(String []args){
JFrame f = new JFrame("事件监听测试");
f.setBounds(0,0,300,400);
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
f.setVisible(false);
f.dispose();
System.exit(0);
}
});
Container page = f.getContentPane();
page.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
JButton btn = new JButton("打印");
/**
* 事件监听的使用步骤:
* 1. 创建监听听
* 2. 将监听器注册到按钮上
*
*/
ActionListener bl = new ActionListener(){
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
System.out.println("匿名内部类优化----");
}
};
btn.addActionListener(bl);
page.add(btn);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
class btnListener implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
System.out.println("按钮被点击了----");
}
}
2.4 优化完之后发现还是不是很优雅
因为每次监听都有重复代码
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
System.out.println("匿名内部类优化----");
}
2.5 使用Lambda表达式再优化
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Btn{
public static void main(String []args){
JFrame f = new JFrame("事件监听测试");
f.setBounds(0,0,300,400);
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
f.setVisible(false);
f.dispose();
System.exit(0);
}
});
Container page = f.getContentPane();
page.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
JButton btn = new JButton("打印");
/**
* 事件监听的使用步骤:
* 1. 创建监听听
* 2. 将监听器注册到按钮上
*
*/
// ActionListener bl = new ActionListener(){
// @Override
// public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
// System.out.println("匿名内部类优化----");
// }
// };
// btn.addActionListener(bl);
btn.addActionListener((e)->{
System.out.println("使用Lambda表达式优化");
});
page.add(btn);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
class btnListener implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
System.out.println("按钮被点击了----");
}
}
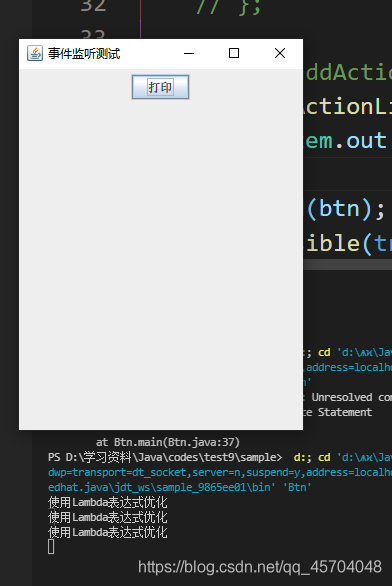
结果
2.6 最终的代码
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Btn{
public static void main(String []args){
JFrame f = new JFrame("事件监听测试");
f.setBounds(0,0,300,400);
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
f.setVisible(false);
f.dispose();
System.exit(0);
}
});
Container page = f.getContentPane();
page.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
JButton btn = new JButton("打印");
btn.addActionListener((e)->{
System.out.println("使用Lambda表达式优化");
});
page.add(btn);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
三、ActionListener接口源码
/*
* Copyright (c) 1996, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*/
package java.awt.event;
import java.util.EventListener;
/**
* The listener interface for receiving action events.
* The class that is interested in processing an action event
* implements this interface, and the object created with that
* class is registered with a component, using the component's
* {@code addActionListener} method. When the action event
* occurs, that object's {@code actionPerformed} method is
* invoked.
*
* @see ActionEvent
* @see <a href="https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/uiswing/events/actionlistener.html" rel="external nofollow" >How to Write an Action Listener</a>
*
* @author Carl Quinn
* @since 1.1
*/
public interface ActionListener extends EventListener {
/**
* Invoked when an action occurs.
* @param e the event to be processed
*/
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e);
}
到此这篇关于Java基础学习之Swing事件监听的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Swing事件监听内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!
赞 (0)

