pytorch如何获得模型的计算量和参数量
方法1 自带
pytorch自带方法,计算模型参数总量
total = sum([param.nelement() for param in model.parameters()])
print("Number of parameter: %.2fM" % (total/1e6))
或者
total = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters())
print("Total params: %.2fM" % (total/1e6))
方法2 编写代码
计算模型参数总量和模型计算量
def count_params(model, input_size=224):
# param_sum = 0
with open('models.txt', 'w') as fm:
fm.write(str(model))
# 计算模型的计算量
calc_flops(model, input_size)
# 计算模型的参数总量
model_parameters = filter(lambda p: p.requires_grad, model.parameters())
params = sum([np.prod(p.size()) for p in model_parameters])
print('The network has {} params.'.format(params))
# 计算模型的计算量
def calc_flops(model, input_size):
def conv_hook(self, input, output):
batch_size, input_channels, input_height, input_width = input[0].size()
output_channels, output_height, output_width = output[0].size()
kernel_ops = self.kernel_size[0] * self.kernel_size[1] * (self.in_channels / self.groups) * (
2 if multiply_adds else 1)
bias_ops = 1 if self.bias is not None else 0
params = output_channels * (kernel_ops + bias_ops)
flops = batch_size * params * output_height * output_width
list_conv.append(flops)
def linear_hook(self, input, output):
batch_size = input[0].size(0) if input[0].dim() == 2 else 1
weight_ops = self.weight.nelement() * (2 if multiply_adds else 1)
bias_ops = self.bias.nelement()
flops = batch_size * (weight_ops + bias_ops)
list_linear.append(flops)
def bn_hook(self, input, output):
list_bn.append(input[0].nelement())
def relu_hook(self, input, output):
list_relu.append(input[0].nelement())
def pooling_hook(self, input, output):
batch_size, input_channels, input_height, input_width = input[0].size()
output_channels, output_height, output_width = output[0].size()
kernel_ops = self.kernel_size * self.kernel_size
bias_ops = 0
params = output_channels * (kernel_ops + bias_ops)
flops = batch_size * params * output_height * output_width
list_pooling.append(flops)
def foo(net):
childrens = list(net.children())
if not childrens:
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Conv2d):
net.register_forward_hook(conv_hook)
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Linear):
net.register_forward_hook(linear_hook)
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.BatchNorm2d):
net.register_forward_hook(bn_hook)
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.ReLU):
net.register_forward_hook(relu_hook)
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.MaxPool2d) or isinstance(net, torch.nn.AvgPool2d):
net.register_forward_hook(pooling_hook)
return
for c in childrens:
foo(c)
multiply_adds = False
list_conv, list_bn, list_relu, list_linear, list_pooling = [], [], [], [], []
foo(model)
if '0.4.' in torch.__version__:
if assets.USE_GPU:
input = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(torch.rand(2, 3, input_size, input_size).cuda())
else:
input = torch.FloatTensor(torch.rand(2, 3, input_size, input_size))
else:
input = Variable(torch.rand(2, 3, input_size, input_size), requires_grad=True)
_ = model(input)
total_flops = (sum(list_conv) + sum(list_linear) + sum(list_bn) + sum(list_relu) + sum(list_pooling))
print(' + Number of FLOPs: %.2fM' % (total_flops / 1e6 / 2))
方法3 thop
需要安装thop
pip install thop
调用方法:计算模型参数总量和模型计算量,而且会打印每一层网络的具体信息
from thop import profile input = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224) flops, params = profile(model, inputs=(input,)) print(flops) print(params)
或者
from torchvision.models import resnet50
from thop import profile
# model = resnet50()
checkpoints = '模型path'
model = torch.load(checkpoints)
model_name = 'yolov3 cut asff'
input = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
flops, params = profile(model, inputs=(input, ),verbose=True)
print("%s | %.2f | %.2f" % (model_name, params / (1000 ** 2), flops / (1000 ** 3)))#这里除以1000的平方,是为了化成M的单位,
注意:输入必须是四维的
提高输出可读性, 加入一下代码。
from thop import clever_format macs, params = clever_format([flops, params], "%.3f")
方法4 torchstat
from torchstat import stat from torchvision.models import resnet50, resnet101, resnet152, resnext101_32x8d model = resnet50() stat(model, (3, 224, 224)) # (3,224,224)表示输入图片的尺寸
使用torchstat这个库来查看网络模型的一些信息,包括总的参数量params、MAdd、显卡内存占用量和FLOPs等。需要安装torchstat:
pip install torchstat
方法5 ptflops
作用:计算模型参数总量和模型计算量
安装方法:pip install ptflops
或者
pip install --upgrade git+https://github.com/sovrasov/flops-counter.pytorch.git
使用方法
import torchvision.models as models
import torch
from ptflops import get_model_complexity_info
with torch.cuda.device(0):
net = models.resnet18()
flops, params = get_model_complexity_info(net, (3, 224, 224), as_strings=True, print_per_layer_stat=True) #不用写batch_size大小,默认batch_size=1
print('Flops: ' + flops)
print('Params: ' + params)
或者
from torchvision.models import resnet50
import torch
import torchvision.models as models
# import torch
from ptflops import get_model_complexity_info
# model = models.resnet50() #调用官方的模型,
checkpoints = '自己模型的path'
model = torch.load(checkpoints)
model_name = 'yolov3 cut'
flops, params = get_model_complexity_info(model, (3,320,320),as_strings=True,print_per_layer_stat=True)
print("%s |%s |%s" % (model_name,flops,params))
注意,这里输入一定是要tuple类型,且不需要输入batch,直接输入输入通道数量与尺寸,如(3,320,320) 320为网络输入尺寸。
输出为网络模型的总参数量(单位M,即百万)与计算量(单位G,即十亿)
方法6 torchsummary
安装:pip install torchsummary
使用方法:
from torchsummary import summary ... summary(your_model, input_size=(channels, H, W))
作用:
1、每一层的类型、shape 和 参数量
2、模型整体的参数量
3、模型大小,和 fp/bp 一次需要的内存大小,可以用来估计最佳 batch_size
补充:pytorch计算模型算力与参数大小
ptflops介绍
这个脚本设计用于计算卷积神经网络中乘法-加法操作的理论数量。它还可以计算参数的数量和打印给定网络的每层计算成本。
支持layer:Conv1d/2d/3d,ConvTranspose2d,BatchNorm1d/2d/3d,激活(ReLU, PReLU, ELU, ReLU6, LeakyReLU),Linear,Upsample,Poolings (AvgPool1d/2d/3d、MaxPool1d/2d/3d、adaptive ones)
安装要求:Pytorch >= 0.4.1, torchvision >= 0.2.1
get_model_complexity_info()
get_model_complexity_info是ptflops下的一个方法,可以计算出网络的算力与模型参数大小,并且可以输出每层的算力消耗。
栗子
以输出Mobilenet_v2算力信息为例:
from ptflops import get_model_complexity_info from torchvision import models net = models.mobilenet_v2() ops, params = get_model_complexity_info(net, (3, 224, 224), as_strings=True, print_per_layer_stat=True, verbose=True)
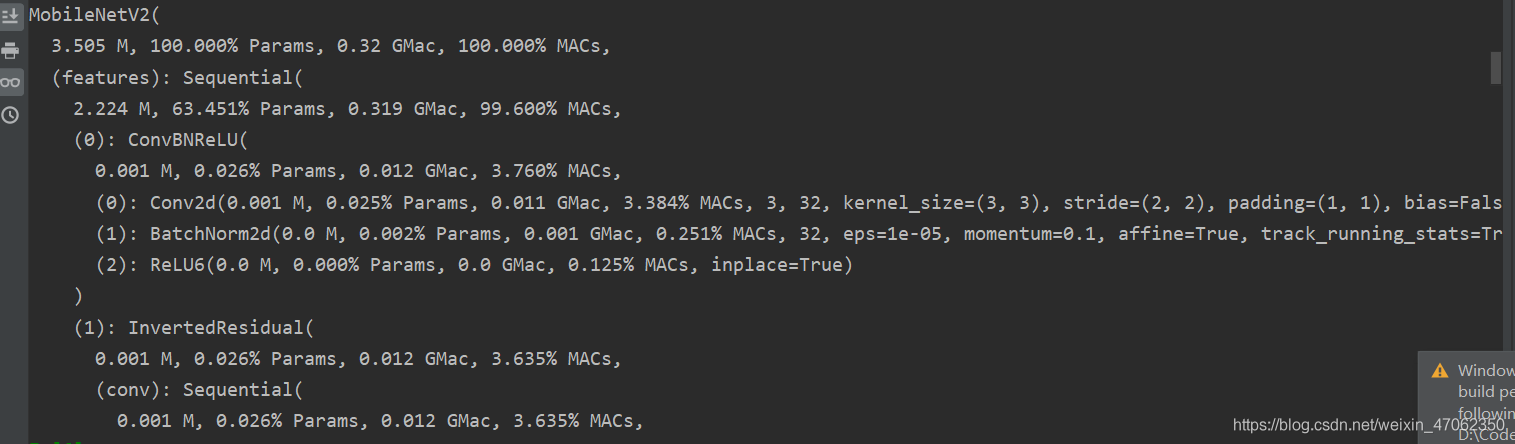
从图中可以看到,MobileNetV2在输入图像尺寸为(3, 224, 224)的情况下将会产生3.505MB的参数,算力消耗为0.32G,同时还打印出了每个层所占用的算力,权重参数数量。当然,整个模型的算力大小与模型大小也被存到了变量ops与params中。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

