Spring Boot整合RabbitMQ开发实战详解
这篇文章主要讲基本的整合。先把代码跑起来,再说什么高级特性。
RabbitMQ 中的一些术语
如果你打开 RabbitMQ web 控制台,你会发现其中有一个 Exhanges 不好理解。下面简单说明一下。
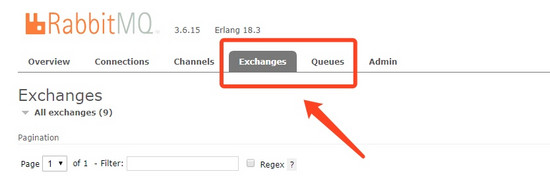
交换器(Exchange)
交换器就像路由器,我们先是把消息发到交换器,然后交换器再根据路由键(routingKey)把消息投递到对应的队列。(明白这个概念很重要,后面的代码里面充分体现了这一点)
队列(Queue)
队列很好理解,就不用解释了。
绑定(Binding)
交换器怎么知道把这条消息投递到哪个队列呢?这就需要用到绑定了。大概就是:使用某个路由键(routingKey)把某个队列(Queue)绑定到某个交换器(Exchange),这样交换器就知道根据路由键把这条消息投递到哪个队列了。(后面的代码里面充分体现了这一点)
加入 RabbitMQ maven 依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId> </dependency>
再加入另外一个依赖(这个依赖可省略,主要是用来简化代码)
<dependency> <groupId>cn.hutool</groupId> <artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId> <version>4.0.2</version> </dependency>
RabbitMQConfig.java 配置
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {
public final static String QUEUE_NAME = "spring-boot-queue";
public final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "spring-boot-exchange";
public final static String ROUTING_KEY = "spring-boot-key";
// 创建队列
@Bean
public Queue queue() {
return new Queue(QUEUE_NAME);
}
// 创建一个 topic 类型的交换器
@Bean
public TopicExchange exchange() {
return new TopicExchange(EXCHANGE_NAME);
}
// 使用路由键(routingKey)把队列(Queue)绑定到交换器(Exchange)
@Bean
public Binding binding(Queue queue, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with(ROUTING_KEY);
}
@Bean
public ConnectionFactory connectionFactory() {
CachingConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new CachingConnectionFactory("127.0.0.1", 5672);
connectionFactory.setUsername("guest");
connectionFactory.setPassword("guest");
return connectionFactory;
}
@Bean
public RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory);
}
}
生产者
直接调用 rabbitTemplate 的 convertAndSend 方法就可以了。从下面的代码里也可以看出,我们不是把消息直接发送到队列里面的,而是先发送到了交换器,交换器再根据路由键把我们的消息投递到对应的队列。
@RestController
public class ProducerController {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@GetMapping("/sendMessage")
public Object sendMessage() {
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
String value = new DateTime().toString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Console.log("send message {}", value);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitMQConfig.EXCHANGE_NAME, RabbitMQConfig.ROUTING_KEY, value);
}
}).start();
return "ok";
}
}
消费者
消费者也很简单,只需要对应的方法上加入 @RabbitListener 注解,指定需要监听的队列名称即可。
@Component
public class Consumer {
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.QUEUE_NAME)
public void consumeMessage(String message) {
Console.log("consume message {}", message);
}
}
运行项目
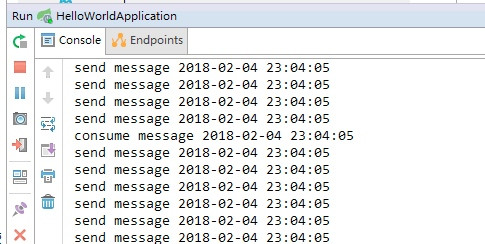
运行项目,然后打开浏览器,输入 http://localhost:9999/sendMessage 。在控制台就可以看到生产者在不停的的发送消息,消费者不断的在消费消息。
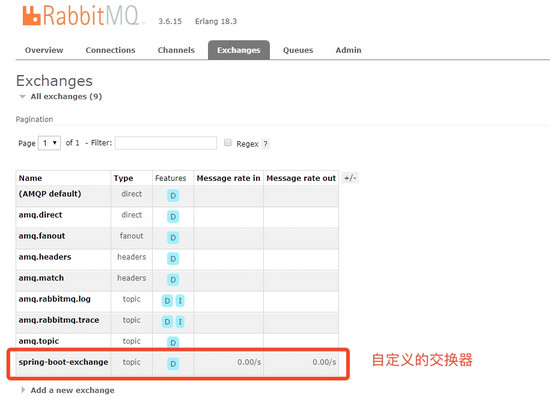
打开 RabbitMQ web 控制台,也可以看到刚才我们在代码里面配置的交换器和队列,以及绑定信息。
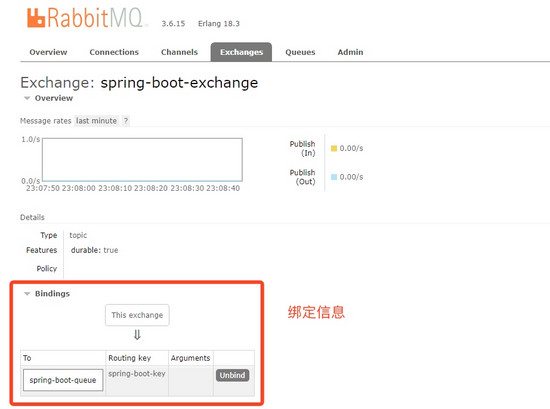
点击进入交换器的详情
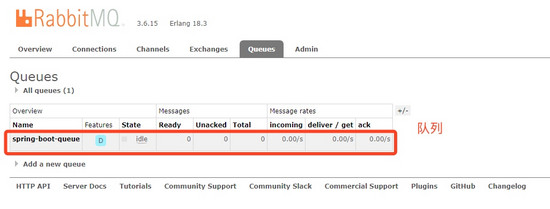
结语
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。
您可能感兴趣的文章:
- SpringBoot与rabbitmq的结合的示例
- springboot整合rabbitmq的示例代码
- spring boot集成rabbitmq的实例教程
- 详解Spring Boot 配置多个RabbitMQ
- spring boot整合RabbitMQ实例详解(Fanout模式)
- Spring Boot整合RabbitMQ实例(Topic模式)
- spring boot整合RabbitMQ(Direct模式)
- 详解spring boot集成RabbitMQ
- Spring Boot中使用RabbitMQ的示例代码

