基于Properties类操作.properties配置文件方法总结
目录
- 一、properties文件
- 二、Properties类
- Properties类使用详解
- 概述
- 常见方法
- 写入
- 读取
- 遍历
一、properties文件
Properties文件是java中很常用的一种配置文件,文件后缀为“.properties”,属文本文件,文件的内容格式是“键=值”的格式,可以用“#”作为注释,java编程中用到的地方很多,运用配置文件,可以便于java深层次的解耦。
例如java应用通过JDBC连接数据库时,可以把数据库的配置写在配置文件 jdbc.properties:
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/user user=root password=123456
这样我们就可以通过加载properties配置文件来连接数据库,达到深层次的解耦目的,如果想要换成oracle或是DB2,我们只需要修改配置文件即可,不用修改任何代码就可以更换数据库。
二、Properties类
java中提供了配置文件的操作类Properties类(java.util.Properties):
读取properties文件的通用方法:根据键得到value
/**
* 读取config.properties文件中的内容,放到Properties类中
* @param filePath 文件路径
* @param key 配置文件中的key
* @return 返回key对应的value
*/
public static String readConfigFiles(String filePath,String key) {
Properties prop = new Properties();
try{
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
prop.load(inputStream);
inputStream.close();
return prop.getProperty(key);
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("未找到相关配置文件");
return null;
}
}
把配置文件以键值对的形式存放到Map中:
/**
* 把.properties文件中的键值对存放在Map中
* @param inputStream 配置文件(inputstream形式传入)
* @return 返回Map
*/
public Map<String, String> convertPropertityFileToMap(InputStream inputStream) {
try {
Properties prop = new Properties();
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
if (inputStream != null) {
prop.load(inputStream);
Enumeration keyNames = prop.propertyNames();
while (keyNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = (String) keyNames.nextElement();
String value = prop.getProperty(key);
map.put(key, value);
}
return map;
} else {
return null;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
Properties类使用详解
概述
Properties 继承于 Hashtable。表示一个持久的属性集,属性列表以key-value的形式存在,key和value都是字符串。
Properties 类被许多Java类使用。例如,在获取环境变量时它就作为System.getProperties()方法的返回值。
我们在很多需要避免硬编码的应用场景下需要使用properties文件来加载程序需要的配置信息,比如JDBC、MyBatis框架等。Properties类则是properties文件和程序的中间桥梁,不论是从properties文件读取信息还是写入信息到properties文件都要经由Properties类。
常见方法
除了从Hashtable中所定义的方法,Properties定义了以下方法:
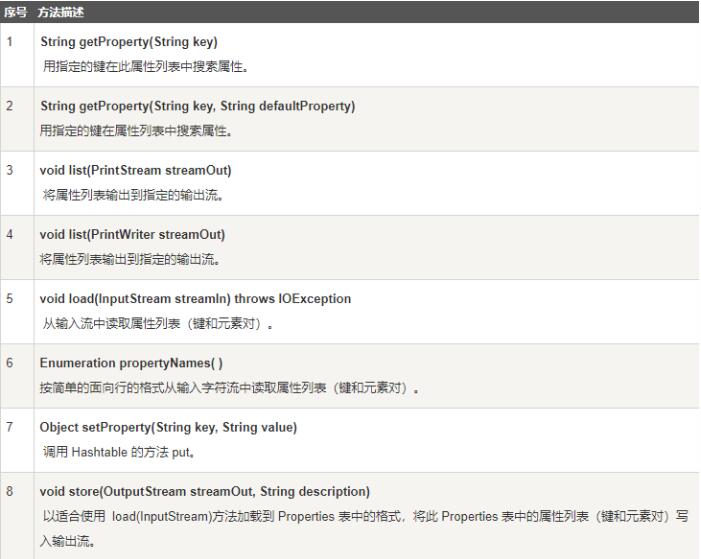
Properties类
下面我们从写入、读取、遍历等角度来解析Properties类的常见用法:
写入
Properties类调用setProperty方法将键值对保存到内存中,此时可以通过getProperty方法读取,propertyNames方法进行遍历,但是并没有将键值对持久化到属性文件中,故需要调用store方法持久化键值对到属性文件中。
package cn.habitdiary;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Properties;
import junit.framework.TestCase;
public class PropertiesTester extends TestCase {
public void writeProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
OutputStream output = null;
try {
output = new FileOutputStream("config.properties");
properties.setProperty("url", "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/");
properties.setProperty("username", "root");
properties.setProperty("password", "root");
properties.setProperty("database", "users");//保存键值对到内存
properties.store(output, "Steven1997 modify" + new Date().toString());
// 保存键值对到文件中
} catch (IOException io) {
io.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (output != null) {
try {
output.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
读取
下面给出常见的六种读取properties文件的方式:
package cn.habitdiary;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.PropertyResourceBundle;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
/**
* 读取properties文件的方式
*
*/
public class LoadPropertiesFileUtil {
private static String basePath = "src/main/java/cn/habitdiary/prop.properties";
private static String path = "";
/**
* 一、 使用java.util.Properties类的load(InputStream in)方法加载properties文件
*
* @return
*/
public static String getPath1() {
try {
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(
new File(basePath)));
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(in);
path = prop.getProperty("path");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("properties文件路径书写有误,请检查!");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return path;
}
/**
* 二、 使用java.util.ResourceBundle类的getBundle()方法
* 注意:这个getBundle()方法的参数只能写成包路径+properties文件名,否则将抛异常
*
* @return
*/
public static String getPath2() {
ResourceBundle rb = ResourceBundle
.getBundle("cn/habitdiary/prop");
path = rb.getString("path");
return path;
}
/**
* 三、 使用java.util.PropertyResourceBundle类的构造函数
*
* @return
*/
public static String getPath3() {
InputStream in;
try {
in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(basePath));
ResourceBundle rb = new PropertyResourceBundle(in);
path = rb.getString("path");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return path;
}
/**
* 四、 使用class变量的getResourceAsStream()方法
* 注意:getResourceAsStream()方法的参数按格式写到包路径+properties文件名+.后缀
*
* @return
*/
public static String getPath4() {
InputStream in = LoadPropertiesFileUtil.class
.getResourceAsStream("cn/habitdiary/prop.properties");
Properties p = new Properties();
try {
p.load(in);
path = p.getProperty("path");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return path;
}
/**
* 五、
* 使用class.getClassLoader()所得到的java.lang.ClassLoader的
* getResourceAsStream()方法
* getResourceAsStream(name)方法的参数必须是包路径+文件名+.后缀
* 否则会报空指针异常
* @return
*/
public static String getPath5() {
InputStream in = LoadPropertiesFileUtil.class.getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("cn/habitdiary/prop.properties");
Properties p = new Properties();
try {
p.load(in);
path = p.getProperty("path");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return path;
}
/**
* 六、 使用java.lang.ClassLoader类的getSystemResourceAsStream()静态方法
* getSystemResourceAsStream()方法的参数格式也是有固定要求的
*
* @return
*/
public static String getPath6() {
InputStream in = ClassLoader
.getSystemResourceAsStream("cn/habitdiary/prop.properties");
Properties p = new Properties();
try {
p.load(in);
path = p.getProperty("path");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return path;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(LoadPropertiesFileUtil.getPath1());
System.out.println(LoadPropertiesFileUtil.getPath2());
System.out.println(LoadPropertiesFileUtil.getPath3());
System.out.println(LoadPropertiesFileUtil.getPath4());
System.out.println(LoadPropertiesFileUtil.getPath5());
System.out.println(LoadPropertiesFileUtil.getPath6());
}
}
其中第一、四、五、六种方式都是先获得文件的输入流,然后通过Properties类的load(InputStream inStream)方法加载到Properties对象中,最后通过Properties对象来操作文件内容。
第二、三中方式是通过ResourceBundle类来加载Properties文件,然后ResourceBundle对象来操做properties文件内容。
其中最重要的就是每种方式加载文件时,文件的路径需要按照方法的定义的格式来加载,否则会抛出各种异常,比如空指针异常。
遍历
下面给出四种遍历Properties中的所有键值对的方法:
/**
* 输出properties的key和value
*/
public static void printProp(Properties properties) {
System.out.println("---------(方式一)------------");
for (String key : properties.stringPropertyNames()) {
System.out.println(key + "=" + properties.getProperty(key));
}
System.out.println("---------(方式二)------------");
Set<Object> keys = properties.keySet();//返回属性key的集合
for (Object key : keys) {
System.out.println(key.toString() + "=" + properties.get(key));
}
System.out.println("---------(方式三)------------");
Set<Map.Entry<Object, Object>> entrySet = properties.entrySet();
//返回的属性键值对实体
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : entrySet) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "=" + entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println("---------(方式四)------------");
Enumeration<?> e = properties.propertyNames();
while (e.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = (String) e.nextElement();
String value = properties.getProperty(key);
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
}
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

