比ant更丰富Modal组件功能实现示例详解
目录
- 有哪些比ant更丰富的功能
- render部分
- 渲染黑色蒙层
- 渲染弹框主体
- 设置body overflow:hiiden
有哪些比ant更丰富的功能
普通的modal组件如下:
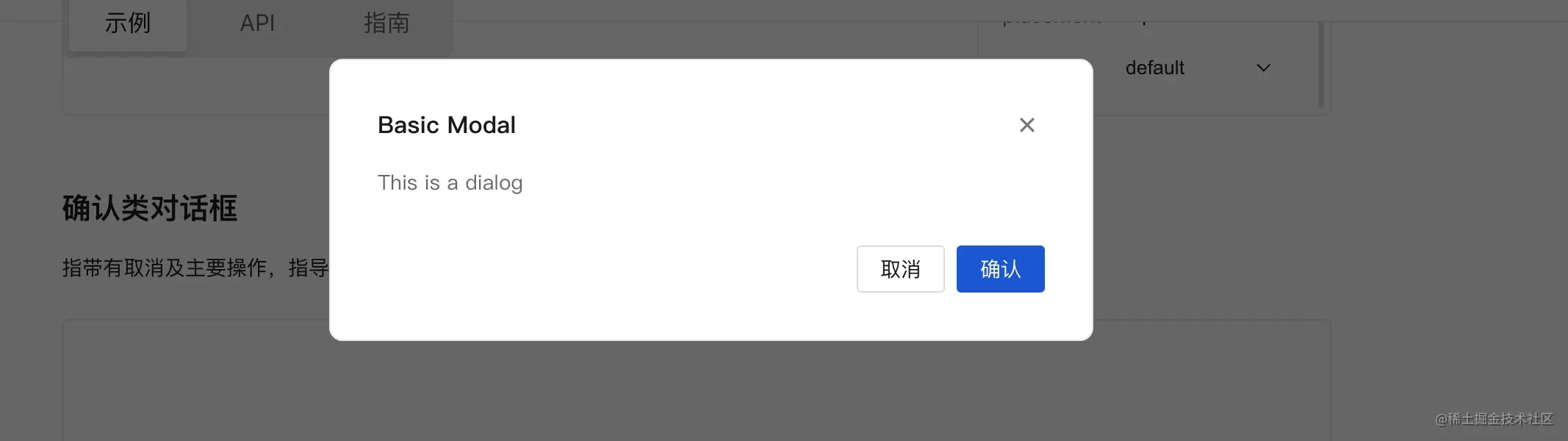
我们写的modal额外支持,后面没有蒙版,并且Modal框能够拖拽
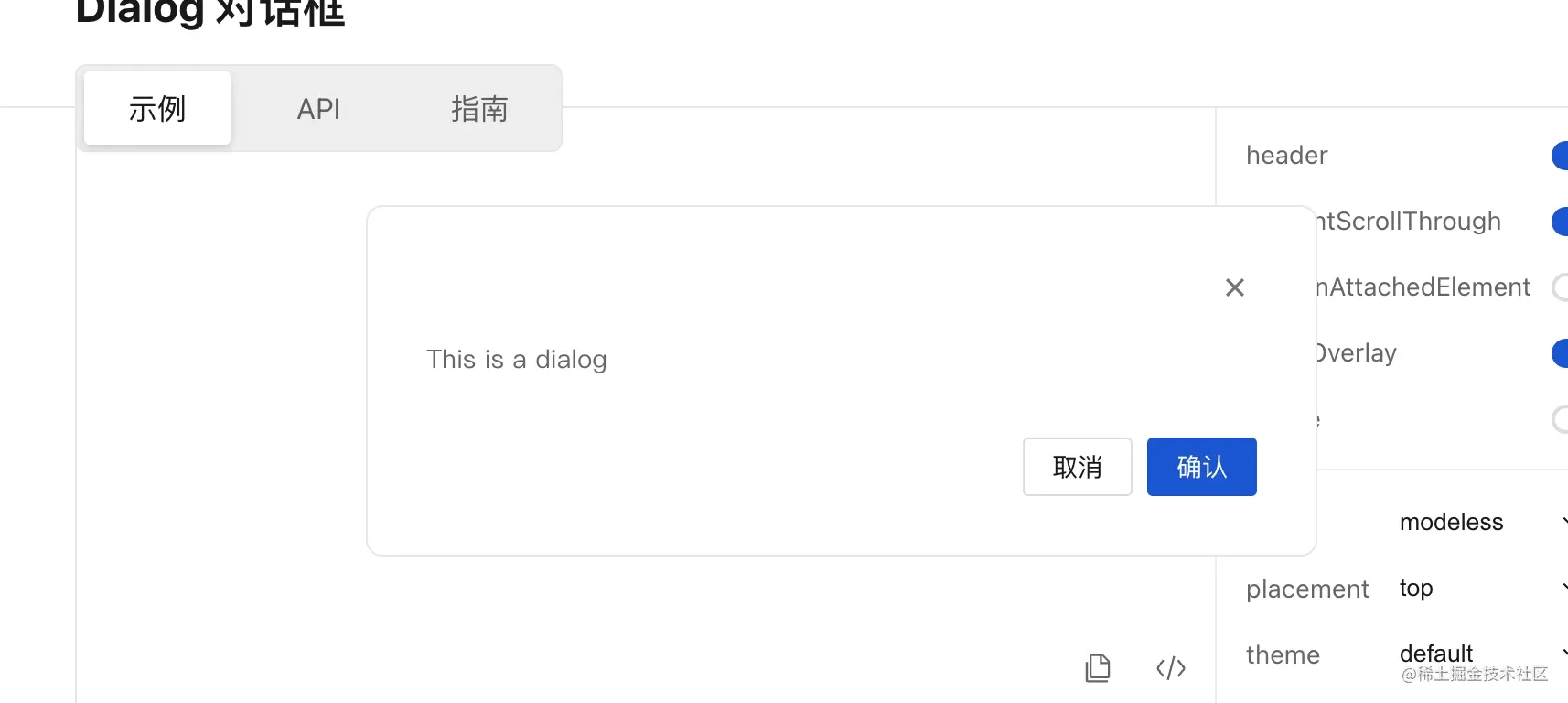
还支持渲染在文档流里,上面的都是fixed布局,我们这个正常渲染到文档下面:
render部分
<RenderDialog
{...restState}
visible={visible}
prefixCls={prefixCls}
header={renderHeader}
attach={attach}
closeBtn={renderCloseIcon()}
classPrefix={classPrefix}
onClose={onClose}
onConfirm={onConfirm}
footer={footer === true ? defaultFooter() : footer}
ref={dialogDom}
/>
大家记住这个RenderDialog,接下来都是上面传参的解释:
resetState: 是对象,一堆属性的集合,哪些属性呢,我们往下看
// 其实默认参数写到这里并不科学,因为react有个静态属性defaultProps属性支持合并props
const [state, setState] = useSetState<DialogProps>({
width: 520, // 默认宽度是520
visible: false, // 默认visible是false
zIndex: 2500, // 默认zIndex 2500
placement: 'center', // 默认渲染到屏幕中间
mode: 'modal', // 默认的模式是modal是ant那种渲染结果,其他模式我们下面谈
showOverlay: true, // 是否展示透明黑色蒙版
destroyOnClose: false, // 关闭弹窗的时候是否销毁里面的内容
draggable: false, // 是否能拖拽modal
preventScrollThrough: true, // 防止滚动穿透
...props,
});
restState在下面,除了state上某些属性。
const {
visible, // 控制对话框是否显示
attach, // 对话框挂载的节点,默认挂在组件本身的位置。数据类型为 String 时,会被当作选择器处理,进行节点查询。示例:'body' 或 () => document.body
closeBtn, // 关闭按钮,可以自定义。值为 true 显示默认关闭按钮,值为 false 不显示关闭按钮。值类型为 string 则直接显示值,// 底部操作栏,默认会有“确认”和“取消”两个按钮。值为 true 显示默认操作按钮,值为 false 不显示任何内容,值类型为 Function 表示自定义底部内容
footer = true, // 如果“取消”按钮存在,则点击“取消”按钮时触发,同时触发关闭事件
onCancel = noop, // 如果“确认”按钮存在,则点击“确认”按钮时触发,或者键盘按下回车键时触发
onConfirm = noop, // 如果“确认”按钮存在,则点击“确认”按钮时触发,或者键盘按下回车键时触发
cancelBtn = cancelText, // 取消按钮,可自定义。值为 null 则不显示取消按钮。值类型为字符串,则表示自定义按钮文本,值类型为 Object 则表示透传 Button 组件属性。
confirmBtn = confirmText, // 确认按钮。值为 null 则不显示确认按钮。值类型为字符串,则表示自定义按钮文本,值类型为 Object 则表示透传 Button 组件属性。
onClose = noop, // 关闭事件,点击取消按钮、点击关闭按钮、点击蒙层、按下 ESC 等场景下触发
...restState
} = state;
说了这么多,我们接着看RenderDialog组件上传入的属性。
prefixCls不讲了,是css属性前缀,一个字符串,接着看header属性被包装为renderHeader
const renderHeader = useMemo(() => {
if (!state.header) return null;
const iconMap = {
info: <InfoCircleFilledIcon className={`${classPrefix}-is-info`} />,
warning: <InfoCircleFilledIcon className={`${classPrefix}-is-warning`} />,
error: <InfoCircleFilledIcon className={`${classPrefix}-is-error`} />,
success: <CheckCircleFilledIcon className={`${classPrefix}-is-success`} />,
};
return (
<div className={`${prefixCls}__header-content`}>
{iconMap[state.theme]}
{state.header}
</div>
);
// eslint-disable-next-line react-hooks/exhaustive-deps
}, [state.header, state.theme, prefixCls, classPrefix]);
其实就是在header的文字前面多了一个icon,比如成功的弹窗如下:
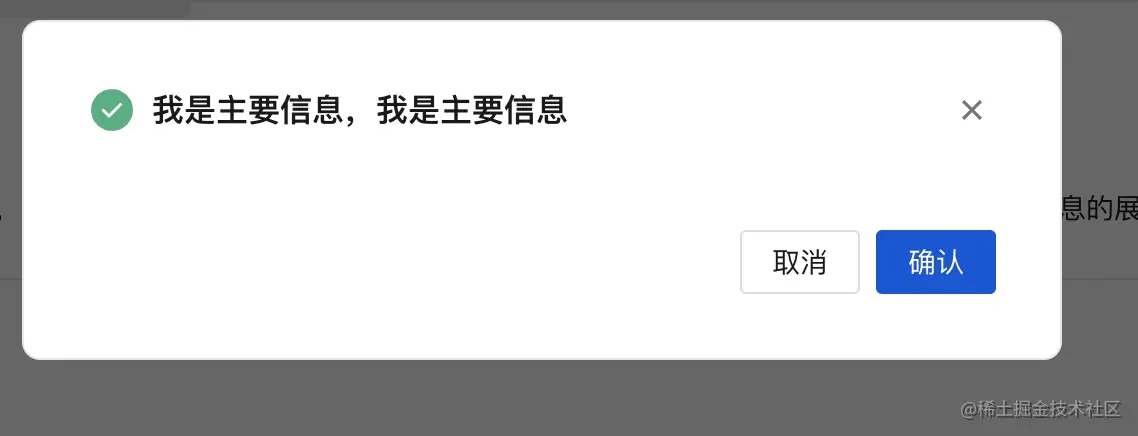
接着看closeBtn属性
const renderCloseIcon = () => {
if (closeBtn === false) return null;
if (closeBtn === true) return <CloseIcon style={{ verticalAlign: 'unset' }} />;
return closeBtn || <CloseIcon style={{ verticalAlign: 'unset' }} />;
};
这个是右上角关闭按钮的Icon,很简单,如果是false,什么都不许安然,如果是undefined或者true渲染这个icon。
好了,我们把整个代码放到下面,有代码注释,没写注释的是上面咋们已经讲过的内容,接着就要进入RenderDialog这个组件内部了。
import 的部分省略了
// 渲染 footer的button方法
const renderDialogButton = (btn: TdDialogProps['cancelBtn'], defaultProps: ButtonProps) => {
let result = null;
if (isString(btn)) {
result = <Button {...defaultProps}>{btn}</Button>;
} else if (isFunction(btn)) {
result = btn();
}
return result;
};
const Dialog = forwardRef((props: DialogProps, ref: React.Ref<DialogInstance>) => {
// 这部分忽略就好,用来获取全局配置的css前缀字符串
const { classPrefix } = useConfig();
// 这个也忽略,获取icon组件的
const { CloseIcon, InfoCircleFilledIcon, CheckCircleFilledIcon } = useGlobalIcon({
CloseIcon: TdCloseIcon,
InfoCircleFilledIcon: TdInfoCircleFilledIcon,
CheckCircleFilledIcon: TdCheckCircleFilledIcon,
});
// 用来引用dialog弹框的dom
const dialogDom = useRef<HTMLDivElement>();
const [state, setState] = useSetState<DialogProps>({
width: 520,
visible: false,
zIndex: 2500,
placement: 'center',
mode: 'modal',
showOverlay: true,
destroyOnClose: false,
draggable: false,
preventScrollThrough: true,
...props,
});
// 国际化有关的
const [local, t] = useLocaleReceiver('dialog');
const confirmText = t(local.confirm);
const cancelText = t(local.cancel);
const {
visible,
attach,
closeBtn,
footer = true,
onCancel = noop,
onConfirm = noop,
cancelBtn = cancelText,
confirmBtn = confirmText,
onClose = noop,
...restState
} = state;
useEffect(() => {
setState((prevState) => ({
...prevState,
...props,
}));
}, [props, setState, isPlugin]);
const prefixCls = `${classPrefix}-dialog`;
const renderCloseIcon = () => {
if (closeBtn === false) return null;
if (closeBtn === true) return <CloseIcon style={{ verticalAlign: 'unset' }} />;
return closeBtn || <CloseIcon style={{ verticalAlign: 'unset' }} />;
};
// 这里把一些外部方法暴露给调用者,只需要传入ref就可以获取
React.useImperativeHandle(ref, () => ({
show() {
setState({ visible: true });
},
hide() {
setState({ visible: false });
},
destroy() {
setState({ visible: false, destroyOnClose: true });
},
update(newOptions) {
setState((prevState) => ({
...prevState,
...(newOptions as DialogProps),
}));
},
}));
const renderHeader = useMemo(() => {
if (!state.header) return null;
const iconMap = {
info: <InfoCircleFilledIcon className={`${classPrefix}-is-info`} />,
warning: <InfoCircleFilledIcon className={`${classPrefix}-is-warning`} />,
error: <InfoCircleFilledIcon className={`${classPrefix}-is-error`} />,
success: <CheckCircleFilledIcon className={`${classPrefix}-is-success`} />,
};
return (
<div className={`${prefixCls}__header-content`}>
{iconMap[state.theme]}
{state.header}
</div>
);
// eslint-disable-next-line react-hooks/exhaustive-deps
}, [state.header, state.theme, prefixCls, classPrefix]);
// 渲染footer的时候,点击取消按钮会用到
const handleCancel = (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>) => {
onCancel({ e });
onClose({ e, trigger: 'cancel' });
};
// 渲染footer的时候,点击确认按钮会用到
const handleConfirm = (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>) => {
onConfirm({ e });
};
const defaultFooter = () => {
const renderCancelBtn = renderDialogButton(cancelBtn, { variant: 'outline' });
const renderConfirmBtn = renderDialogButton(confirmBtn, { theme: 'primary' });
return (
<>
{renderCancelBtn &&
React.cloneElement(renderCancelBtn, {
onClick: handleCancel,
...renderCancelBtn.props,
})}
{renderConfirmBtn &&
React.cloneElement(renderConfirmBtn, {
onClick: handleConfirm,
...renderConfirmBtn.props,
})}
</>
);
};
return (
<RenderDialog
{...restState}
visible={visible}
prefixCls={prefixCls}
header={renderHeader}
attach={attach}
closeBtn={renderCloseIcon()}
classPrefix={classPrefix}
onClose={onClose}
onConfirm={onConfirm}
footer={footer === true ? defaultFooter() : footer}
ref={dialogDom}
/>
);
});
Dialog.displayName = 'Dialog';
Dialog.defaultProps = dialogDefaultProps;
export default Dialog;
接着,我们要渲染的部分其实很简单,包括
- 背后的黑色蒙层
- 弹框
- 弹框的标题
- 弹框的内容区域
- 弹框的footer
- 还需要弹框动画,比如zoom或者fade
渲染黑色蒙层
代码如下,很简单
const renderMask = () => {
let maskElement;
if (showOverlay) {
maskElement = (
<CSSTransition
in={visible}
appear
timeout={transitionTime}
classNames={`${prefixCls}-fade`}
mountOnEnter
unmountOnExit
nodeRef={maskRef}
>
<div ref={maskRef} className={`${prefixCls}__mask`} />
</CSSTransition>
);
}
return maskElement;
};
首先介绍一下CSSTransition,这是react-transition-group动画库的一个组件,用来帮助我们实现css动画的。 其中一些属性说明如下:
- in: ture就是开始动画,false就是停止动画
- appear:boolean,为
false时当CSSTransition控件加载完毕后不执行动画,为true时控件加载完毕则立即执行动画。如果要组件初次渲染就有动画,则需要设成true。 - timeout 动画时间
- classNames:动画的类名,比如classNames:'demo',会自动在进入动画的时候帮你把类名改为 demo-enter-active, demo-enter-done, 在退出动画同样会有类名的改变。
- mountOnEnter:一进来的时候不显示dom元素
- unmountOnExit:boolean,为
true时组件将移除处于隐藏状态的元素,为false时组件保持动画结束时的状态而不移除元素。一般要设成true。 - nodeRef,获取蒙层的ref
蒙层主要靠css实现,我们看下css
position: fixed; top: 0; left: 0; width: 100%; height: 100%; z-index: 1; background: var(--td-mask-active); pointer-events: auto;
渲染弹框主体
也非常简单啊,我们把注释写在下面的代码里了,其中有一个需要小小注意的功能就是拖拽功能
// 渲染Dialog主体
const renderDialog = () => {
const dest: any = {};
// 把width变为有px结尾的字符串
if (props.width !== undefined) {
dest.width = GetCSSValue(props.width);
}
// normal 场景下,需要设置 zindex 为auto 避免出现多个 dialog,normal 出现在最上层
if (props.mode === 'normal') {
dest.zIndex = 'auto';
}
// 获取footer
const footer = props.footer ? <div className={`${prefixCls}__footer`}>{props.footer}</div> : null;
// 获取header
const { header } = props;
// 获取Dialog body
const body = <div className={`${prefixCls}__body`}>{props.body || props.children}</div>;
// 关闭按钮,可以自定义。值为 true 显示默认关闭按钮,值为 false 不显示关闭按钮。值类型为 string 则直接显示值,如:“关闭”。
const closer = closeBtn && (
<span onClick={handleCloseBtnClick} className={`${prefixCls}__close`}>
{closeBtn}
</span>
);
const validWindow = typeof window === 'object';
// 获取屏幕高度
const screenHeight = validWindow ? window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight : undefined;
// 获取屏幕宽度
const screenWidth = validWindow ? window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth : undefined;
// 设置style
const style = { ...dest, ...props.style };
let dialogOffset = { x: 0, y: 0 };
// 拖拽代码实现部分
const onDialogMove = (e: MouseEvent) => {
// offsetWidth是指元素的宽 + padding + border的总和
const { style, offsetWidth, offsetHeight } = dialog.current;
// diffX是指弹框部分距离body左边部分
let diffX = e.clientX - dialogOffset.x;
let diffY = e.clientY - dialogOffset.y;
// 拖拽上左边界限制
if (diffX < 0) diffX = 0;
if (diffY < 0) diffY = 0;
// 右边的限制
if (screenWidth - offsetWidth - diffX < 0) diffX = screenWidth - offsetWidth;
// 下边的限制
if (screenHeight - offsetHeight - diffY < 0) diffY = screenHeight - offsetHeight;
style.position = 'absolute';
style.left = `${diffX}px`;
style.top = `${diffY}px`;
};
const onDialogMoveEnd = () => {
// 恢复指针样式为默认,并且注销mousemove, mouseup事件
dialog.current.style.cursor = 'default';
document.removeEventListener('mousemove', onDialogMove);
document.removeEventListener('mouseup', onDialogMoveEnd);
};
// 拖拽开始,对应mouseDown事件
const onDialogMoveStart = (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLDivElement>) => {
contentClickRef.current = true;
// 阻止事件冒泡, mode === 'modeless才能拖拽
if (canDraggable && e.currentTarget === e.target) {
const { offsetLeft, offsetTop, offsetHeight, offsetWidth } = dialog.current;
// 如果弹出框超出屏幕范围 不能进行拖拽
if (offsetWidth > screenWidth || offsetHeight > screenHeight) return;
// 拖拽样式设置为move
dialog.current.style.cursor = 'move';
// 计算鼠标 e.clientX是鼠标在屏幕的坐标,offsetLeft是Dialog主体跟body的距离
// 所以e.clientX - offsetLeft就是鼠标在是Dialog主体上的横坐标
const diffX = e.clientX - offsetLeft;
const diffY = e.clientY - offsetTop;
dialogOffset = {
x: diffX,
y: diffY,
};
// 此时把mousemove和mouseup事件也绑定一下,其实不建议绑定在这里直接操作dom
document.addEventListener('mousemove', onDialogMove);
document.addEventListener('mouseup', onDialogMoveEnd);
}
};
// 顶部定位实现
const positionStyle: any = {};
if (props.top) {
const topValue = GetCSSValue(props.top);
positionStyle.paddingTop = topValue;
}
// 此处获取定位方式 top 优先级较高 存在时 默认使用 top 定位
const positionClass = classnames(
`${prefixCls}__position`,
{ [`${prefixCls}--top`]: !!props.top },
`${props.placement && !props.top ? `${prefixCls}--${props.placement}` : ''}`,
);
// 然后就是用css去渲染header body和footer
const dialogElement = (
<div className={isNormal ? '' : `${prefixCls}__wrap`}>
<div className={isNormal ? '' : positionClass} style={positionStyle} onClick={onMaskClick} ref={dialogPosition}>
<div
ref={dialog}
style={style}
className={classnames(`${prefixCls}`, `${prefixCls}--default`)}
onMouseDown={onDialogMoveStart}
>
<div className={classnames(`${prefixCls}__header`)}>
{header}
{closer}
</div>
{body}
{footer}
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
return (
<CSSTransition
in={props.visible}
appear
mountOnEnter
unmountOnExit={destroyOnClose}
timeout={transitionTime}
classNames={`${prefixCls}-zoom`}
onEntered={props.onOpened}
onExited={onAnimateLeave}
nodeRef={dialog}
>
{dialogElement}
</CSSTransition>
);
};
我们这里贴一下css部分:
header:
.t-dialog__header {
color: var(--td-text-color-primary);
font: var(--td-font-title-medium);
font-weight: 600;
display: flex;
align-items: flex-start;
word-break: break-word;
}
这里注意下:word-wrap:break-word
它会把整个单词看成一个整体,如果该行末端宽度不够显示整个单词,它会自动把整个单词放到下一行,而不会把单词截断掉的。
body
.t-dialog__body {
padding: 16px 0;
color: var(--td-text-color-secondary);
font: var(--td-font-body-medium);
overflow: auto;
word-break: break-word;
}
footer
width: 100%; text-align: right; padding: 16px 0 0 0;
好了,我们结合一下弹框和蒙层,看下render函数
const render = () => {
// 。。。省略css部分
// 如果不是 modal 模式 默认没有 mask 也就没有相关点击 mask 事件
const dialog = (
<div ref={wrap} className={wrapClass} style={wrapStyle} onKeyDown={handleKeyDown} tabIndex={0}>
{mode === 'modal' && renderMask()}
{dialogBody} // 这里就是我们上面讲的renderDialog
</div>
);
return dialog;
};
设置body overflow:hiiden
为啥要设置body overflow:hiiden这个属性呢,你打开modal弹窗的时候,如果此时body还有滚动条,那么你滚动鼠标滚轮还可以向下滑动,但是一般情况下,我们打开弹框,是希望用户目标锁定在当前交互,此时最好不要允许用户滚动界面。
当然你也可以允许用户滚动,我们用一个preventScrollThrough参数控制。
先记住当前body的css样式,以及body的overflow的值,代码如下
useLayoutEffect(() => {
bodyOverflow.current = document.body.style.overflow;
bodyCssTextRef.current = document.body.style.cssText;
}, []);
const isModal = mode === 'modal';
useLayoutEffect(() => {
// 只有modal数量小于1的时候才重置样式,因为可能出现多个弹框,那么关闭一个弹框就出现滚动条明显不对
if (isModal) {
const openDialogDom = document.querySelectorAll(`${prefixCls}__mode`);
if (openDialogDom.length < 1) {
document.body.style.cssText = bodyCssTextRef.current;
}
// 组件销毁后重置 body 样式
return () => {
if (isModal) {
// 此处只能查询 mode 模式的 dialog 个数 因为 modeless 会点击透传 normal 是正常文档流
const openDialogDom = document.querySelectorAll(`${prefixCls}__mode`);
if (openDialogDom.length < 1) {
document.body.style.cssText = bodyCssTextRef.current;
document.body.style.overflow = bodyOverflow.current;
}
}
};
}, [preventScrollThrough, attach, visible, mode, isModal, showInAttachedElement, prefixCls]);
上面的代码还有一个问题,就是我们需要preventScrollThrough这个参数去控制是否可以body滚动页面,这个也是算比ant更丰富的功能。
const isModal = mode === 'modal';
useLayoutEffect(() => {
// 处于显示态
if (visible) {
// isModal表示是否是普通弹框,就是带黑色蒙层的
// bodyOverflow.current 引用的是body的overflow属性
// preventScrollThrough是代表是否可以滚动body
// !showInAttachedElement表示不挂载到其他dom上
if (isModal && bodyOverflow.current !== 'hidden' && preventScrollThrough && !showInAttachedElement) {
// 求出滚动条的宽度
const scrollWidth = window.innerWidth - document.body.offsetWidth;
// 减少回流
if (bodyCssTextRef.current === '') {
let bodyCssText = 'overflow: hidden;';
if (scrollWidth > 0) {
bodyCssText += `position: relative;width: calc(100% - ${scrollWidth}px);`;
}
document.body.style.cssText = bodyCssText;
} else {
if (scrollWidth > 0) {
document.body.style.width = `calc(100% - ${scrollWidth}px)`;
document.body.style.position = 'relative';
}
document.body.style.overflow = 'hidden';
}
}
// 刚进页面就focus到弹框组件上
if (wrap.current) {
wrap.current.focus();
}
} else if (isModal) {
const openDialogDom = document.querySelectorAll(`${prefixCls}__mode`);
if (openDialogDom.length < 1) {
document.body.style.cssText = bodyCssTextRef.current;
}
}
// 组件销毁后重置 body 样式
return () => {
if (isModal) {
// 此处只能查询 mode 模式的 dialog 个数 因为 modeless 会点击透传 normal 是正常文档流
const openDialogDom = document.querySelectorAll(`${prefixCls}__mode`);
if (openDialogDom.length < 1) {
document.body.style.cssText = bodyCssTextRef.current;
document.body.style.overflow = bodyOverflow.current;
}
} else {
document.body.style.cssText = bodyCssTextRef.current;
document.body.style.overflow = bodyOverflow.current;
}
};
}, [preventScrollThrough, attach, visible, mode, isModal, showInAttachedElement, prefixCls]);
其实还有一个逻辑,是把弹窗渲染到任意dom里,需要一个Portal组件,我们这里就不说了,后续将Popup或者叫trigger组件的时候我们讲吧。一篇文档内容太多不好消化。
好了,主逻辑已经写完了,很简单吧!
接下来看下完整代码,没有注释的部分是上面已经讲过的
//省去了import
// 把css的数字转为有px结尾的字符串,,这里其实应该写到一个utils文件夹里,不应该跟主代码混在一起
function GetCSSValue(v: string | number) {
return Number.isNaN(Number(v)) ? v : `${Number(v)}px`;
}
// 动画执行时间,这里其实应该写到一个constants文件里,不应该跟主代码混在一起
const transitionTime = 300;
const RenderDialog = forwardRef((props: RenderDialogProps, ref: React.Ref<HTMLDivElement>) => {
// 这里不用看,跟国际化有关
const [local] = useLocaleReceiver('dialog');
const {
prefixCls,
attach, // 对话框挂载的节点,默认挂在组件本身的位置。数据类型为 String 时,会被当作选择器处理,进行节点查询。示例:'body' 或 () => document.body
visible, // 控制对话框是否显示
mode, // 对话框类型,有三种:模态对话框、非模态对话框和普通对话框。弹出「模态对话框」时,只能操作对话框里面的内容,不能操作其他内容。弹出「非模态对话框」时,则可以操作页面内所有内容。「普通对话框」是指没有脱离文档流的对话框,可以在这个基础上开发更多的插件
zIndex, // 对话框层级,Web 侧样式默认为 2500,移动端和小程序样式默认为 1500
showOverlay, // 是否显示遮罩层
onEscKeydown = noop,// 按下 ESC 时触发事件
onClosed = noop, // 对话框消失动画效果结束后触发
onClose = noop, // 关闭事件,点击取消按钮、点击关闭按钮、点击蒙层、按下 ESC 等场景下触发
onCloseBtnClick = noop, // 点击右上角关闭按钮时触发
onOverlayClick = noop, // 如果蒙层存在,点击蒙层时触发
onConfirm = noop, // 如果“确认”按钮存在,则点击“确认”按钮时触发,或者键盘按下回车键时触发
preventScrollThrough, // 防止滚动穿透
closeBtn, // 关闭按钮,可以自定义。值为 true 显示默认关闭按钮,值为 false 不显示关闭按钮。值类型为 string 则直接显示值,如:“关闭”。值类型为 TNode,则表示呈现自定义按钮示例
closeOnEscKeydown, // 按下 ESC 时是否触发对话框关闭事件
confirmOnEnter, // 是否在按下回车键时,触发确认事件
closeOnOverlayClick, // 点击蒙层时是否触发关闭事件
destroyOnClose, // 是否在关闭弹框的时候销毁子元素
showInAttachedElement, // 仅在挂载元素中显示抽屉,默认在浏览器可视区域显示。父元素需要有定位属性,如:position: relative
} = props;
const wrap = useRef<HTMLDivElement>(); // 挂载到包裹弹框的dom上,包裹了好几层。。。
const dialog = useRef<HTMLDivElement>(); // 引用弹窗dom
const dialogPosition = useRef<HTMLDivElement>(); // 包裹弹窗,用于定位的dom引用
const maskRef = useRef<HTMLDivElement>(); // 蒙层的dom引用
const bodyOverflow = useRef<string>();
const bodyCssTextRef = useRef<string>();
const contentClickRef = useRef(false);
const isModal = mode === 'modal';
const isNormal = mode === 'normal';
const canDraggable = props.draggable && mode === 'modeless';
const dialogOpenClass = `${prefixCls}__${mode}`;
useLayoutEffect(() => {
bodyOverflow.current = document.body.style.overflow;
bodyCssTextRef.current = document.body.style.cssText;
}, []);
useLayoutEffect(() => {
if (visible) {
if (isModal && bodyOverflow.current !== 'hidden' && preventScrollThrough && !showInAttachedElement) {
const scrollWidth = window.innerWidth - document.body.offsetWidth;
// 减少回流
if (bodyCssTextRef.current === '') {
let bodyCssText = 'overflow: hidden;';
if (scrollWidth > 0) {
bodyCssText += `position: relative;width: calc(100% - ${scrollWidth}px);`;
}
document.body.style.cssText = bodyCssText;
} else {
if (scrollWidth > 0) {
document.body.style.width = `calc(100% - ${scrollWidth}px)`;
document.body.style.position = 'relative';
}
document.body.style.overflow = 'hidden';
}
}
if (wrap.current) {
wrap.current.focus();
}
} else if (isModal) {
const openDialogDom = document.querySelectorAll(`${prefixCls}__mode`);
if (openDialogDom.length < 1) {
document.body.style.cssText = bodyCssTextRef.current;
}
}
// 组件销毁后重置 body 样式
return () => {
if (isModal) {
// 此处只能查询 mode 模式的 dialog 个数 因为 modeless 会点击透传 normal 是正常文档流
const openDialogDom = document.querySelectorAll(`${prefixCls}__mode`);
if (openDialogDom.length < 1) {
document.body.style.cssText = bodyCssTextRef.current;
document.body.style.overflow = bodyOverflow.current;
}
} else {
document.body.style.cssText = bodyCssTextRef.current;
document.body.style.overflow = bodyOverflow.current;
}
};
}, [preventScrollThrough, attach, visible, mode, isModal, showInAttachedElement, prefixCls]);
const onAnimateLeave = () => {
if (wrap.current) {
wrap.current.style.display = 'none';
}
if (isModal && preventScrollThrough) {
// 还原 body 的滚动条
const openDialogDom = document.querySelectorAll(`${prefixCls}__mode`);
if (isModal && openDialogDom.length < 1) {
document.body.style.overflow = bodyOverflow.current;
}
}
if (!isModal) {
// 关闭弹窗 清空拖拽设置的相关 css
const { style } = dialog.current;
style.position = 'relative';
style.left = 'unset';
style.top = 'unset';
}
onClosed && onClosed();
};
const onMaskClick = (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLDivElement>) => {
if (showOverlay && (closeOnOverlayClick ?? local.closeOnOverlayClick)) {
// 判断点击事件初次点击是否为内容区域
if (contentClickRef.current) {
contentClickRef.current = false;
} else if (e.target === dialogPosition.current) {
onOverlayClick({ e });
onClose({ e, trigger: 'overlay' });
}
}
};
const handleCloseBtnClick = (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLDivElement>) => {
onCloseBtnClick({ e });
onClose({ e, trigger: 'close-btn' });
};
const handleKeyDown = (e: React.KeyboardEvent<HTMLDivElement>) => {
// https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/KeyboardEvent/keyCode
if (e.key === 'Escape') {
e.stopPropagation();
onEscKeydown({ e });
if (closeOnEscKeydown ?? local.closeOnEscKeydown) {
onClose({ e, trigger: 'esc' });
}
} else if (e.key === 'Enter' || e.key === 'NumpadEnter') {
// 回车键触发点击确认事件
e.stopPropagation();
if (confirmOnEnter) {
onConfirm({ e });
}
}
};
// 渲染Dialog主体
const renderDialog = () => {
const dest: any = {};
// 把width变为有px结尾的字符串
if (props.width !== undefined) {
dest.width = GetCSSValue(props.width);
}
// normal 场景下,需要设置 zindex 为auto 避免出现多个 dialog,normal 出现在最上层
if (props.mode === 'normal') {
dest.zIndex = 'auto';
}
// 获取footer
const footer = props.footer ? <div className={`${prefixCls}__footer`}>{props.footer}</div> : null;
// 获取header
const { header } = props;
// 获取Dialog body
const body = <div className={`${prefixCls}__body`}>{props.body || props.children}</div>;
// 关闭按钮,可以自定义。值为 true 显示默认关闭按钮,值为 false 不显示关闭按钮。值类型为 string 则直接显示值,如:“关闭”。
const closer = closeBtn && (
<span onClick={handleCloseBtnClick} className={`${prefixCls}__close`}>
{closeBtn}
</span>
);
const validWindow = typeof window === 'object';
// 获取屏幕高度
const screenHeight = validWindow ? window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight : undefined;
// 获取屏幕宽度
const screenWidth = validWindow ? window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth : undefined;
// 设置style
const style = { ...dest, ...props.style };
let dialogOffset = { x: 0, y: 0 };
// 拖拽代码实现部分
const onDialogMove = (e: MouseEvent) => {
// offsetWidth是指元素的宽 + padding + border的总和
const { style, offsetWidth, offsetHeight } = dialog.current;
// diffX是指弹框部分距离body左边部分
let diffX = e.clientX - dialogOffset.x;
let diffY = e.clientY - dialogOffset.y;
// 拖拽上左边界限制
if (diffX < 0) diffX = 0;
if (diffY < 0) diffY = 0;
// 右边的限制
if (screenWidth - offsetWidth - diffX < 0) diffX = screenWidth - offsetWidth;
// 下边的限制
if (screenHeight - offsetHeight - diffY < 0) diffY = screenHeight - offsetHeight;
style.position = 'absolute';
style.left = `${diffX}px`;
style.top = `${diffY}px`;
};
const onDialogMoveEnd = () => {
// 恢复指针样式为默认,并且注销mousemove, mouseup事件
dialog.current.style.cursor = 'default';
document.removeEventListener('mousemove', onDialogMove);
document.removeEventListener('mouseup', onDialogMoveEnd);
};
// 拖拽开始,对应mouseDown事件
const onDialogMoveStart = (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLDivElement>) => {
contentClickRef.current = true;
// 阻止事件冒泡, mode === 'modeless才能拖拽
if (canDraggable && e.currentTarget === e.target) {
const { offsetLeft, offsetTop, offsetHeight, offsetWidth } = dialog.current;
// 如果弹出框超出屏幕范围 不能进行拖拽
if (offsetWidth > screenWidth || offsetHeight > screenHeight) return;
// 拖拽样式设置为move
dialog.current.style.cursor = 'move';
// 计算鼠标 e.clientX是鼠标在屏幕的坐标,offsetLeft是Dialog主体跟body的距离
// 所以e.clientX - offsetLeft就是鼠标在是Dialog主体上的横坐标
const diffX = e.clientX - offsetLeft;
const diffY = e.clientY - offsetTop;
dialogOffset = {
x: diffX,
y: diffY,
};
// 此时把mousemove和mouseup事件也绑定一下,其实不建议绑定在这里直接操作dom
document.addEventListener('mousemove', onDialogMove);
document.addEventListener('mouseup', onDialogMoveEnd);
}
};
// 顶部定位实现
const positionStyle: any = {};
if (props.top) {
const topValue = GetCSSValue(props.top);
positionStyle.paddingTop = topValue;
}
// 此处获取定位方式 top 优先级较高 存在时 默认使用 top 定位
const positionClass = classnames(
`${prefixCls}__position`,
{ [`${prefixCls}--top`]: !!props.top },
`${props.placement && !props.top ? `${prefixCls}--${props.placement}` : ''}`,
);
const dialogElement = (
<div className={isNormal ? '' : `${prefixCls}__wrap`}>
<div className={isNormal ? '' : positionClass} style={positionStyle} onClick={onMaskClick} ref={dialogPosition}>
<div
ref={dialog}
style={style}
className={classnames(`${prefixCls}`, `${prefixCls}--default`)}
onMouseDown={onDialogMoveStart}
>
<div className={classnames(`${prefixCls}__header`)}>
{header}
{closer}
</div>
{body}
{footer}
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
return (
<CSSTransition
in={props.visible}
appear
mountOnEnter
unmountOnExit={destroyOnClose}
timeout={transitionTime}
classNames={`${prefixCls}-zoom`}
onEntered={props.onOpened}
onExited={onAnimateLeave}
nodeRef={dialog}
>
{dialogElement}
</CSSTransition>
);
};
const renderMask = () => {
let maskElement;
if (showOverlay) {
maskElement = (
<CSSTransition
in={visible}
appear
timeout={transitionTime}
classNames={`${prefixCls}-fade`}
mountOnEnter
unmountOnExit
nodeRef={maskRef}
>
<div ref={maskRef} className={`${prefixCls}__mask`} />
</CSSTransition>
);
}
return maskElement;
};
const render = () => {
const style: CSSProperties = {};
if (visible) {
style.display = 'block';
}
const wrapStyle = {
...style,
zIndex,
};
const dialogBody = renderDialog();
const wrapClass = classnames(
props.className,
`${prefixCls}__ctx`,
!isNormal ? `${prefixCls}__ctx--fixed` : '',
visible ? dialogOpenClass : '',
isModal && showInAttachedElement ? `${prefixCls}__ctx--absolute` : '',
props.mode === 'modeless' ? `${prefixCls}__ctx--modeless` : '',
);
// 如果不是 modal 模式 默认没有 mask 也就没有相关点击 mask 事件
const dialog = (
<div ref={wrap} className={wrapClass} style={wrapStyle} onKeyDown={handleKeyDown} tabIndex={0}>
{mode === 'modal' && renderMask()}
{dialogBody}
</div>
);
let dom = null;
if (visible || wrap.current) {
// normal 模式 attach 无效
if (attach === '' || isNormal) {
dom = dialog;
} else {
dom = (
<CSSTransition
in={visible}
appear
timeout={transitionTime}
mountOnEnter
unmountOnExit={destroyOnClose}
nodeRef={portalRef}
>
<Portal attach={attach} ref={portalRef}>
{dialog}
</Portal>
</CSSTransition>
);
}
}
return dom;
};
return render();
});
RenderDialog.defaultProps = dialogDefaultProps;
export default RenderDialog;
结束,react组件库继续搞起!
以上就是比ant更丰富Modal组件功能实现示例详解的详细内容,更多关于ant Modal组件功能的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!

