Python3实现简单可学习的手写体识别(实例讲解)
1.前言
版本:Python3.6.1 + PyQt5 + SQL Server 2012
以前一直觉得,机器学习、手写体识别这种程序都是很高大上很难的,直到偶然看到了这个视频,听了老师讲的思路后,瞬间觉得原来这个并不是那么的难,原来我还是有可能做到的。
于是我开始顺着思路打算用Python、PyQt、SQLServer做一个出来,看看能不能行。然而中间遇到了太多的问题,数据库方面的问题有十几个,PyQt方面的问题有接近一百个,还有数十个Python基础语法的问题。但好在,通过不断的Google,终于凑出了这么一个成品来。
最终还是把都凑在一个函数里的代码重构了一下,改写成了4个模块:
main.py、Learning.py、LearningDB.py、LearningUI.py
其中LearningDB实现python与数据库的交互,LearningUI实现界面的交互,Learning继承LearningUI类添加上了与LearningDB数据库类的交互,最后通过main主函数模块运行程序。
其中涉及数据库的知识可参考之前的文章:Python3操作SQL Server数据库(实例讲解),
涉及PyQt的知识可参考:Python3使用PyQt5制作简单的画板/手写板
手写体识别的主要思路是将手写的字,用一个列表记录其所经过的点,划分为一个九宫格,然后数每个格子中点的数目,将数目转化为所占总点数的百分比。然后两两保存的九维数,求他们之间的距离,距离越近代表越接近。
2.通过pymssql与数据库的交互
因为使用程序之前先需要建表,建表我就直接使用SQL语句执行了:
create database PyLearningDB drop table table0 create table table0 (dim0 int not null, dim1 int not null, dim2 int not null, dim3 int not null, dim4 int not null, dim5 int not null, dim6 int not null, dim7 int not null, dim8 int not null) drop table table1 create table table1 (dim0 int not null, dim1 int not null, dim2 int not null, dim3 int not null, dim4 int not null, dim5 int not null, dim6 int not null, dim7 int not null, dim8 int not null) drop table table2 create table table2 (dim0 int not null, dim1 int not null, dim2 int not null, dim3 int not null, dim4 int not null, dim5 int not null, dim6 int not null, dim7 int not null, dim8 int not null) drop table table3 create table table3 (dim0 int not null, dim1 int not null, dim2 int not null, dim3 int not null, dim4 int not null, dim5 int not null, dim6 int not null, dim7 int not null, dim8 int not null) drop table table4 create table table4 (dim0 int not null, dim1 int not null, dim2 int not null, dim3 int not null, dim4 int not null, dim5 int not null, dim6 int not null, dim7 int not null, dim8 int not null) drop table table5 create table table5 (dim0 int not null, dim1 int not null, dim2 int not null, dim3 int not null, dim4 int not null, dim5 int not null, dim6 int not null, dim7 int not null, dim8 int not null) drop table table6 create table table6 (dim0 int not null, dim1 int not null, dim2 int not null, dim3 int not null, dim4 int not null, dim5 int not null, dim6 int not null, dim7 int not null, dim8 int not null) drop table table7 create table table7 (dim0 int not null, dim1 int not null, dim2 int not null, dim3 int not null, dim4 int not null, dim5 int not null, dim6 int not null, dim7 int not null, dim8 int not null) drop table table8 create table table8 (dim0 int not null, dim1 int not null, dim2 int not null, dim3 int not null, dim4 int not null, dim5 int not null, dim6 int not null, dim7 int not null, dim8 int not null) drop table table9 create table table9 (dim0 int not null, dim1 int not null, dim2 int not null, dim3 int not null, dim4 int not null, dim5 int not null, dim6 int not null, dim7 int not null, dim8 int not null)
LearningDB.py程序如下:
'''
LearningDB类
功能:定义数据库类,包含一个学习函数learn_data和一个识别函数identify_data
作者:PyLearn
博客: http://www.cnblogs.com/PyLearn/
最后修改日期: 2017/10/18
'''
import math
import pymssql
class LearningDB():
def __init__(self):
self.conn = pymssql.connect(host='127.0.0.1',
user='sa',
password='123',
database='PyLearningDB',
charset='utf8')
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor()
self.sql = ''
self.distance = 0.0
self.conn.close()
def learn_data(self, table, dim):
'''
学习数据,将数据存到对应的数据库
table指定哪个表,dim是维度数组
'''
learn_result = False
try:
if table < 0 or table > 9:
raise Exception("错误!table的值为%d!" % table)
for num in dim:
if num < 0:
raise Exception("错误!dim的值不能小于0!")
self.conn = pymssql.connect(host='127.0.0.1',
user='sa',
password='123',
database='PyLearningDB',
charset='utf8')
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor()
self.sql = 'insert into table%d values(%d, %d, %d, %d, %d, %d, %d, %d, %d)' %(
table, dim[0], dim[1], dim[2], dim[3], dim[4], dim[5], dim[6], dim[7], dim[8])
self.cursor.execute(self.sql)
self.conn.commit()
learn_result = True
except Exception as ex_learn:
self.conn.rollback()
raise ex_learn
finally:
self.conn.close()
return learn_result
def identify_data(self, test_data):
'''
识别数据,将数据一一对比,返回最接近的近似值
'''
try:
table_data = []
for i in range(10):
table_data.append(self.__get_data(i, test_data))
#返回table_data中最小值的索引
return table_data.index(min(table_data))
except Exception as ex_identify:
raise ex_identify
def __get_data(self, table, test_data):
'''
取出table表中所有数据
并与测试数据进行比较,返回最小值
如果table表中无数据,则全部取0
'''
try:
if table < 0 or table > 9:
raise Exception("错误!table的值不能为%d!" % table)
self.conn = pymssql.connect(host='127.0.0.1',
user='sa',
password='123',
database='PyLearningDB',
charset='utf8')
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor()
self.sql = 'select * from table%d' % table
self.cursor.execute(self.sql)
receive_sql = self.cursor.fetchall()
if not receive_sql:
new_receive_sql = [(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0)]
else:
new_receive_sql = receive_sql
finally:
self.conn.close()
#计算最小值
dim_data = []
for receive_data in new_receive_sql:
dim_data.append(self.__distance_data(test_data, receive_data))
#返回dimData中最小值
return min(dim_data)
def __distance_data(self, test_data, table_data):
'''
求九维空间中两点之间的距离
'''
self.distance = 0.0
for i in range(9):
self.distance += (test_data[i] - table_data[i]) ** 2
return math.sqrt(self.distance)
3.通过pyqt与界面的交互
LearningUI.py程序如下:
'''
LearningUI类
功能:生成UI界面,以及定义事件处理方法
作者:PyLearn
博客: http://www.cnblogs.com/PyLearn/
最后修改日期: 2017/10/18
'''
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import (QWidget, QPushButton, QLabel, QComboBox, QDesktopWidget)
from PyQt5.QtGui import (QPainter, QPen, QFont)
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt
class LearningUI(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(LearningUI, self).__init__()
self.__init_ui()
#设置只有鼠标按下时才跟踪移动,否则不按的时候也在画画
self.setMouseTracking(False)
#self.pos_xy保存所有绘画的点
self.pos_xy = []
#设置pos_x、pos_y方便计算
self.pos_x = []
self.pos_y = []
#设置关联事件
self.btn_learn.clicked.connect(self.btn_learn_on_clicked)
self.btn_recognize.clicked.connect(self.btn_recognize_on_clicked)
self.btn_clear.clicked.connect(self.btn_clear_on_clicked)
def __init_ui(self):
'''
定义UI界面:
三个按钮:学习、识别、清屏
btn_learn、btn_recognize、btn_clear
一个组合框:选择0-9
combo_table
两条标签:请在屏幕空白处用鼠标输入0-9中的某一个数字进行识别!
2017/10/10 by PyLearn
一条输出识别结果的标签
label_output
'''
#添加三个按钮,分别是学习、识别、清屏
self.btn_learn = QPushButton("学习", self)
self.btn_learn.setGeometry(50, 400, 70, 40)
self.btn_recognize = QPushButton("识别", self)
self.btn_recognize.setGeometry(320, 400, 70, 40)
self.btn_clear = QPushButton("清屏", self)
self.btn_clear.setGeometry(420, 400, 70, 40)
#添加一个组合框,选择0-9
self.combo_table = QComboBox(self)
for i in range(10):
self.combo_table.addItem("%d" % i)
self.combo_table.setGeometry(150, 400, 70, 40)
#添加两条标签
self.label_head = QLabel('请在屏幕空白处用鼠标输入0-9中的某一个数字进行识别!', self)
self.label_head.move(75, 50)
self.label_end = QLabel('2017/10/10 by PyLearn', self)
self.label_end.move(375, 470)
#添加一条输出识别结果的标签
'''
setStyleSheet设置边框大小、颜色
setFont设置字体大小、形状、加粗
setAlignment设置文本居中
'''
self.label_output = QLabel('', self)
self.label_output.setGeometry(50, 100, 150, 250)
self.label_output.setStyleSheet("QLabel{border:1px solid black;}")
self.label_output.setFont(QFont("Roman times", 100, QFont.Bold))
self.label_output.setAlignment(Qt.AlignCenter)
'''
setFixedSize()固定了窗体的宽度与高度
self.center()将窗体居中显示
setWindowTitle()设置窗体的标题
'''
self.setFixedSize(550, 500)
self.center()
self.setWindowTitle('0-9手写体识别(机器学习中的"HelloWorld!")')
def center(self):
'''
窗口居中显示
'''
qt_center = self.frameGeometry()
desktop_center = QDesktopWidget().availableGeometry().center()
qt_center.moveCenter(desktop_center)
self.move(qt_center.topLeft())
def paintEvent(self, event):
'''
首先判断pos_xy列表中是不是至少有两个点了
然后将pos_xy中第一个点赋值给point_start
利用中间变量pos_tmp遍历整个pos_xy列表
point_end = pos_tmp
判断point_end是否是断点,如果是
point_start赋值为断点
continue
判断point_start是否是断点,如果是
point_start赋值为point_end
continue
画point_start到point_end之间的线
point_start = point_end
这样,不断地将相邻两个点之间画线,就能留下鼠标移动轨迹了
'''
painter = QPainter()
painter.begin(self)
pen = QPen(Qt.black, 2, Qt.SolidLine)
painter.setPen(pen)
if len(self.pos_xy) > 1:
point_start = self.pos_xy[0]
for pos_tmp in self.pos_xy:
point_end = pos_tmp
if point_end == (-1, -1):
point_start = point_end
continue
if point_start == (-1, -1):
point_start = point_end
continue
painter.drawLine(point_start[0], point_start[1], point_end[0], point_end[1])
point_start = point_end
painter.end()
def mouseReleaseEvent(self, event):
'''
重写鼠标按住后松开的事件
在每次松开后向pos_xy列表中添加一个断点(-1, -1)
然后在绘画时判断一下是不是断点就行了
是断点的话就跳过去,不与之前的连续
'''
pos_test = (-1, -1)
self.pos_xy.append(pos_test)
self.update()
def mouseMoveEvent(self, event):
'''
按住鼠标移动:将移动的点加入self.pos_xy列表
'''
#self.pos_x和self.pos_y总是比self.pos_xy少一到两个点,还不知道原因在哪
self.pos_x.append(event.pos().x())
self.pos_y.append(event.pos().y())
#中间变量pos_tmp提取当前点
pos_tmp = (event.pos().x(), event.pos().y())
#pos_tmp添加到self.pos_xy中
self.pos_xy.append(pos_tmp)
self.update()
def btn_learn_on_clicked(self):
'''
需要用到数据库,因此在在子类中实现
'''
pass
def btn_recognize_on_clicked(self):
'''
需要用到数据库,因此在在子类中实现
'''
pass
def btn_clear_on_clicked(self):
'''
按下清屏按钮:
将列表赋值为空
将输出识别结果的标签赋值为空
然后刷新界面,重新绘画即可清屏
'''
self.pos_xy = []
self.pos_x = []
self.pos_y = []
self.label_output.setText('')
self.update()
def get_pos_xy(self):
'''
将手写体在平面上分为9个格子
计算每个格子里点的数量
然后点的数量转化为占总点数的百分比
接着返回一个数组dim[9]
横轴依次是min_x、min2_x、max2_x、max_x
纵轴依次是min_y、min2_y、max2_y、max_y
'''
if not self.pos_xy:
return None
pos_count = len(self.pos_x)
max_x = max(self.pos_x)
max_y = max(self.pos_y)
min_x = min(self.pos_x)
min_y = min(self.pos_y)
dim = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
dis_x = (max_x - min_x) // 3
dis_y = (max_y - min_y) // 3
min2_x = min_x + dis_x
min2_y = min_y + dis_y
max2_x = max_x - dis_x
max2_y = max_y - dis_y
for i in range(len(self.pos_x)):
if self.pos_y[i] >= min_y and self.pos_y[i] < min2_y:
if self.pos_x[i] >= min_x and self.pos_x[i] < min2_x:
dim[0] += 1
continue
if self.pos_x[i] >= min2_x and self.pos_x[i] < max2_x:
dim[1] += 1
continue
if self.pos_x[i] >= max2_x and self.pos_x[i] <= max_x:
dim[2] += 1
continue
elif self.pos_y[i] >= min2_y and self.pos_y[i] < max2_y:
if self.pos_x[i] >= min_x and self.pos_x[i] < min2_x:
dim[3] += 1
continue
if self.pos_x[i] >= min2_x and self.pos_x[i] < max2_x:
dim[4] += 1
continue
if self.pos_x[i] >= max2_x and self.pos_x[i] <= max_x:
dim[5] += 1
continue
elif self.pos_y[i] >= max2_y and self.pos_y[i] <= max_y:
if self.pos_x[i] >= min_x and self.pos_x[i] < min2_x:
dim[6] += 1
continue
if self.pos_x[i] >= min2_x and self.pos_x[i] < max2_x:
dim[7] += 1
continue
if self.pos_x[i] >= max2_x and self.pos_x[i] <= max_x:
dim[8] += 1
continue
else:
pos_count -= 1
continue
#将数量转化为所占百分比
for num in dim:
num = num * 100 // pos_count
return dim
4.UI与数据库的交互
Learning.py程序如下:
'''
Learning类
功能:重写LearningUI类中的两个用到了数据库的方法:
类中添加一个LearningDB类对象的数据成员self.learn_db
作者:PyLearn
博客: http://www.cnblogs.com/PyLearn/
最后修改日期: 2017/10/18
'''
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMessageBox
from LearningUI import LearningUI
from LearningDB import LearningDB
class Learning(LearningUI):
'''
Learning实现btn_learn_on_clicked和btn_recognize_on_clicked两个方法
'''
def __init__(self):
super(Learning, self).__init__()
#学习函数learn_data(table, dim)和一个识别函数identify_data(test_data)
self.learn_db = LearningDB()
def btn_learn_on_clicked(self):
if not self.pos_xy:
QMessageBox.critical(self, "注意", "请先写入您要学习的数字!")
return None
#获取要学习的数字learn_num
learn_num = self.combo_table.currentIndex()
#弹出确认对话框
qbox = QMessageBox()
qbox.setIcon(QMessageBox.Information)
qbox.setWindowTitle("请确认")
qbox.setText("学习数字 %d ?" % learn_num)
qbox.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Yes | QMessageBox.No)
qbox.setDefaultButton(QMessageBox.No)
qbox.button(QMessageBox.Yes).setText("是")
qbox.button(QMessageBox.No).setText("否")
reply = qbox.exec()
#判断对话框结果,执行程序
if reply == QMessageBox.Yes:
learn_result = False
learn_dim = self.get_pos_xy()
if learn_dim:
learn_result = self.learn_db.learn_data(learn_num, learn_dim)
else:
print('get_pos_xy()函数返回空值')
return None
if learn_result:
QMessageBox.about(self, "提示", "学习成功!")
else:
QMessageBox.about(self, "提示", "学习失败!")
else:
return None
def btn_recognize_on_clicked(self):
#如果没有进行绘画,警告后退出
if not self.pos_xy:
QMessageBox.critical(self, "注意", "请先写入您要识别的数字!")
return None
else:
recognize_num = 0
recognize_dim = self.get_pos_xy()
if recognize_dim:
recognize_num = self.learn_db.identify_data(recognize_dim)
else:
print('recognize_dim为空')
return None
self.label_output.setText('%d' % recognize_num)
5.最后的main主函数
''' 主函数main 功能:生成Learning对象,进入主循环 作者:PyLearn 最后修改日期: 2017/10/18 ''' import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication from Learning import Learning if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) py_learning = Learning() py_learning.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())
将以上4个程序放在同一个目录下,直接执行main.py就行了。
运行界面如下:
学习数字4:
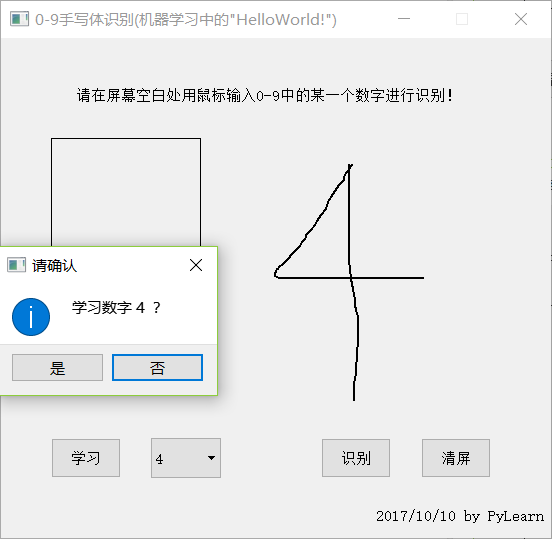
第一次运行需要全部学习至少一次才能有一点正确率。
识别3:

以上这篇Python3实现简单可学习的手写体识别(实例讲解)就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

