Python中的数据可视化matplotlib与绘图库模块
目录
- 一、条形图bar()
- 二、直方图
- 三、折线图
- 四、散点图+直线图
- 五、饼图
- 六、箱型图
- 七、plot函数参数
- 八、图像标注参数
- 九、Matplolib应用
matplotlib官方文档:https://matplotlib.org/stable/users/index.html
matplotlib是一个绘图库,它可以创建常用的统计图,包括条形图、箱型图、折线图、散点图、饼图和直方图。
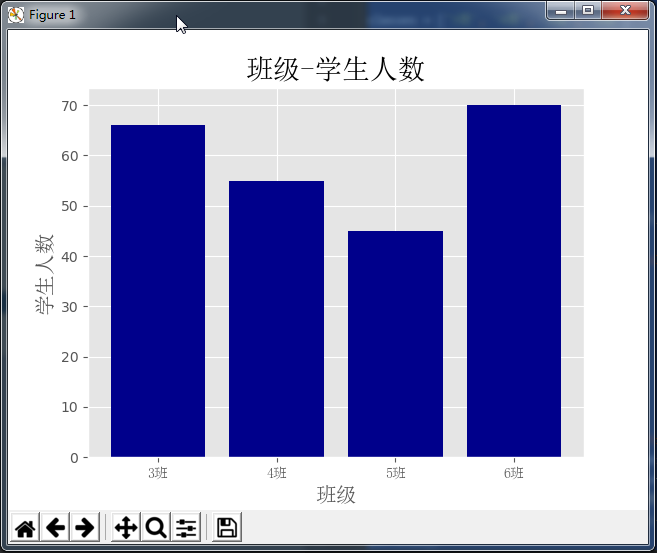
一、条形图bar()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r'c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc')
# 修改背景为条纹
plt.style.use('ggplot')
classes = ['3班', '4班', '5班', '6班']
classes_index = range(len(classes))
print(list(classes_index))
# [0, 1, 2, 3]
student_amounts = [66, 55, 45, 70]
# 画布设置
fig = plt.figure()
# 1,1,1表示一张画布切割成1行1列共一张图的第1个;2,2,1表示一张画布切割成2行2列共4张图的第一个(左上角)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax1.bar(classes_index, student_amounts, align='center', color='darkblue')
ax1.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax1.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
plt.xticks(classes_index,
classes,
rotation=0,
fontsize=13,
fontproperties=font)
plt.xlabel('班级', fontproperties=font, fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel('学生人数', fontproperties=font, fontsize=15)
plt.title('班级-学生人数', fontproperties=font, fontsize=20)
# 保存图片,bbox_inches='tight'去掉图形四周的空白
# plt.savefig('classes_students.png', dpi=400, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
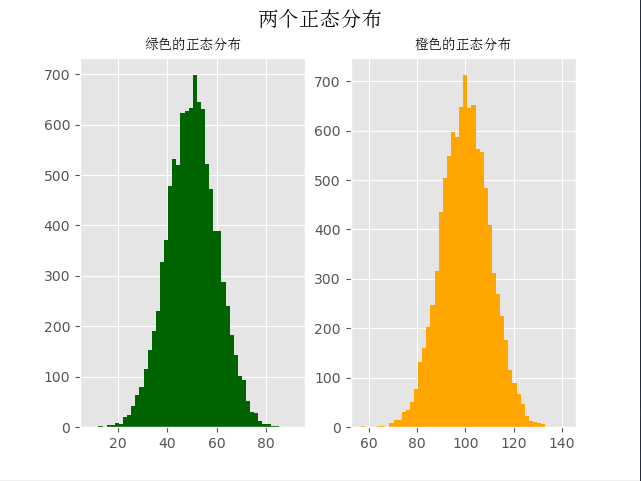
二、直方图
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r'c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc')
# 修改背景为条纹
plt.style.use('ggplot')
mu1, mu2, sigma = 50, 100, 10
# 构造均值为50的符合正态分布的数据
x1 = mu1 + sigma * np.random.randn(10000)
print(x1)
# [59.00855949 43.16272141 48.77109774 ... 57.94645859 54.70312714
# 58.94125528]
# 构造均值为100的符合正态分布的数据
x2 = mu2 + sigma * np.random.randn(10000)
print(x2)
# [115.19915511 82.09208214 110.88092454 ... 95.0872103 104.21549068
# 133.36025251]
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121)
# bins=50表示每个变量的值分成50份,即会有50根柱子
ax1.hist(x1, bins=50, color='darkgreen')
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122)
ax2.hist(x2, bins=50, color='orange')
fig.suptitle('两个正态分布', fontproperties=font, fontweight='bold', fontsize=15)
ax1.set_title('绿色的正态分布', fontproperties=font)
ax2.set_title('橙色的正态分布', fontproperties=font)
plt.show()
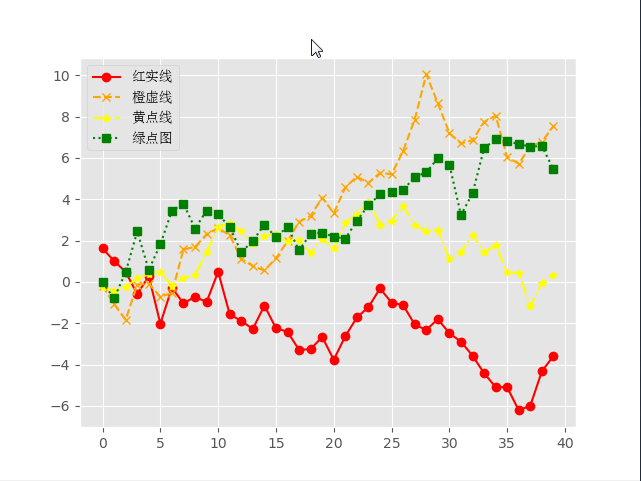
三、折线图
import numpy as np
from numpy.random import randn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r'c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc')
# 修改背景为条纹
plt.style.use('ggplot')
np.random.seed(1)
# 使用numpy的累加和,保证数据取值范围不会在(0,1)内波动
plot_data1 = randn(40).cumsum()
print(plot_data1)
# [ 1.62434536 1.01258895 0.4844172 -0.58855142 0.2768562 -2.02468249
# -0.27987073 -1.04107763 -0.72203853 -0.97140891 0.49069903 -1.56944168
# -1.89185888 -2.27591324 -1.1421438 -2.24203506 -2.41446327 -3.29232169
# -3.25010794 -2.66729273 -3.76791191 -2.6231882 -1.72159748 -1.21910314
# -0.31824719 -1.00197505 -1.12486527 -2.06063471 -2.32852279 -1.79816732
# -2.48982807 -2.8865816 -3.5737543 -4.41895994 -5.09020607 -5.10287067
# -6.22018102 -5.98576532 -4.32596314 -3.58391898]
plot_data2 = randn(40).cumsum()
plot_data3 = randn(40).cumsum()
plot_data4 = randn(40).cumsum()
plt.plot(plot_data1, marker='o', color='red', linestyle='-', label='红实线')
plt.plot(plot_data2, marker='x', color='orange', linestyle='--', label='橙虚线')
plt.plot(plot_data3, marker='*', color='yellow', linestyle='-.', label='黄点线')
plt.plot(plot_data4, marker='s', color='green', linestyle=':', label='绿点图')
# loc='best'给label自动选择最好的位置
plt.legend(loc='best', prop=font)
plt.show()
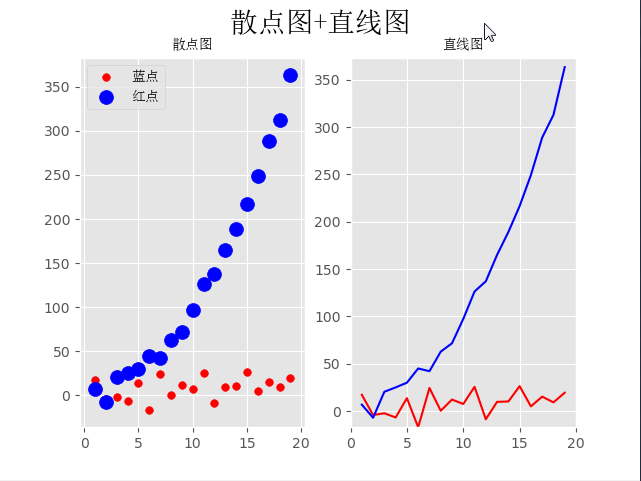
四、散点图+直线图
import numpy as np
from numpy.random import randn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r'c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc')
# 修改背景为条纹
plt.style.use('ggplot')
x = np.arange(1, 20, 1)
print(x)
# [ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19]
# 拟合一条水平散点线
np.random.seed(1)
y_linear = x + 10 * np.random.randn(19)
# print(y_linear)
# [ 17.24345364 -4.11756414 -2.28171752 -6.72968622 13.65407629
# -17.01538697 24.44811764 0.38793099 12.19039096 7.50629625
# 25.62107937 -8.60140709 9.77582796 10.15945645 26.33769442
# 5.00108733 15.27571792 9.22141582 19.42213747]
# 拟合一条x²的散点线
y_quad = x**2 + 10 * np.random.randn(19)
print(y_quad)
# [ 6.82815214 -7.00619177 20.4472371 25.01590721 30.02494339
# 45.00855949 42.16272141 62.77109774 71.64230566 97.3211192
# 126.30355467 137.08339248 165.03246473 189.128273 216.54794359
# 249.28753869 288.87335401 312.82689651 363.34415698]
# s是散点大小
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121)
plt.scatter(x, y_linear, s=30, color='r', label='蓝点')
plt.scatter(x, y_quad, s=100, color='b', label='红点')
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122)
plt.plot(x, y_linear, color='r')
plt.plot(x, y_quad, color='b')
# 限制x轴和y轴的范围取值
plt.xlim(min(x) - 1, max(x) + 1)
plt.ylim(min(y_quad) - 10, max(y_quad) + 10)
fig.suptitle('散点图+直线图', fontproperties=font, fontsize=20)
ax1.set_title('散点图', fontproperties=font)
ax1.legend(prop=font)
ax2.set_title('直线图', fontproperties=font)
plt.show()
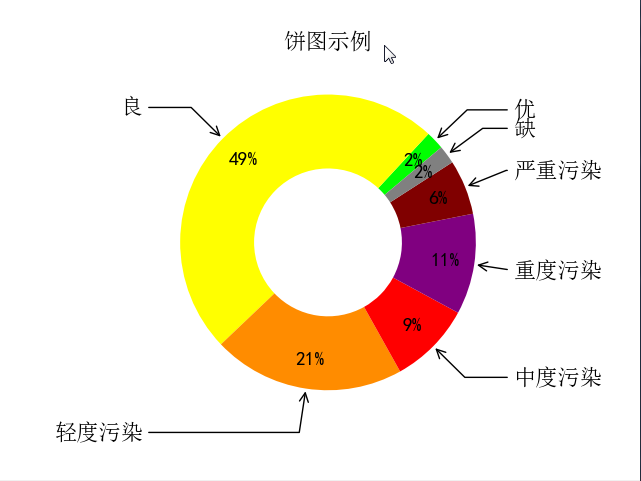
五、饼图
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pylab import mpl
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r'c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc')
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
fig, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw=dict(aspect="equal"))
recipe = ['优', '良', '轻度污染', '中度污染', '重度污染', '严重污染', '缺']
data = [2, 49, 21, 9, 11, 6, 2]
colors = ['lime', 'yellow', 'darkorange', 'red', 'purple', 'maroon', 'grey']
wedges, texts, texts2 = ax.pie(data,
wedgeprops=dict(width=0.5),
startangle=40,
colors=colors,
autopct='%1.0f%%',
pctdistance=0.8)
plt.setp(texts2, size=14, weight="bold")
bbox_props = dict(boxstyle="square,pad=0.3", fc="w", ec="k", lw=0.72)
kw = dict(xycoords='data',
textcoords='data',
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->"),
bbox=None,
zorder=0,
va="center")
for i, p in enumerate(wedges):
ang = (p.theta2 - p.theta1) / 2. + p.theta1
y = np.sin(np.deg2rad(ang))
x = np.cos(np.deg2rad(ang))
horizontalalignment = {-1: "right", 1: "left"}[int(np.sign(x))]
connectionstyle = "angle,angleA=0,angleB={}".format(ang)
kw["arrowprops"].update({"connectionstyle": connectionstyle})
ax.annotate(recipe[i],
xy=(x, y),
xytext=(1.25 * np.sign(x), 1.3 * y),
size=16,
horizontalalignment=horizontalalignment,
fontproperties=font,
**kw)
ax.set_title("饼图示例", fontproperties=font)
plt.show()
# plt.savefig('jiaopie2.png')
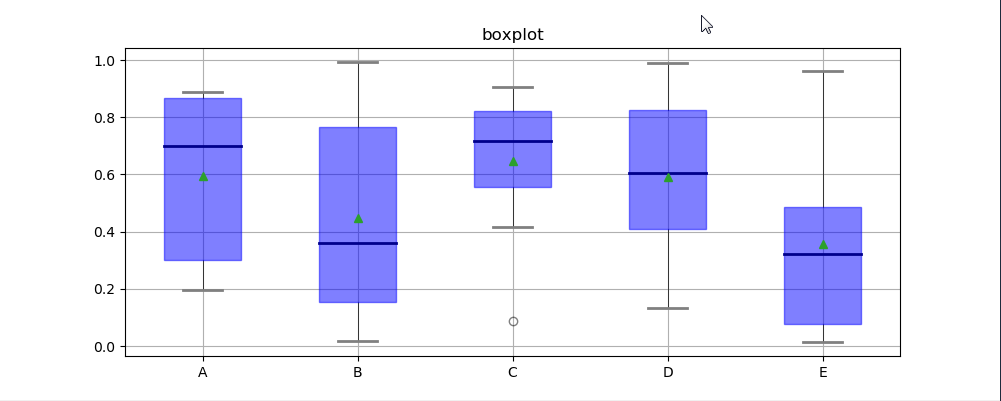
六、箱型图
箱型图:又称为盒须图、盒式图、盒状图或箱线图,是一种用作显示一组数据分散情况资料的统计图(在数据分析中常用在异常值检测)
包含一组数据的:最大值、最小值、中位数、上四分位数(Q3)、下四分位数(Q1)、异常值
- 中位数 →一组数据平均分成两份,中间的数
- 上四分位数Q1 →是将序列平均分成四份,计算(n+1)/4与(n-1)/4两种,一般使用(n+1)/4
- 下四分位数Q3 →是将序列平均分成四份,计算(1+n)/4*3=6.75
- 内限 →T形的盒须就是内限,最大值区间Q3+1.5IQR,最小值区间Q1-1.5IQR (IQR=Q3-Q1)
- 外限 →T形的盒须就是内限,最大值区间Q3+3IQR,最小值区间Q1-3IQR (IQR=Q3-Q1)
- 异常值 →内限之外 - 中度异常,外限之外 - 极度异常
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r'c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc')
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(10, 5), columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'])
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 4))
# 创建图表、数据
f = df.boxplot(
sym='o', # 异常点形状,参考marker
vert=True, # 是否垂直
whis=1.5, # IQR,默认1.5,也可以设置区间比如[5,95],代表强制上下边缘为数据95%和5%位置
patch_artist=True, # 上下四分位框内是否填充,True为填充
meanline=False,
showmeans=True, # 是否有均值线及其形状
showbox=True, # 是否显示箱线
showcaps=True, # 是否显示边缘线
showfliers=True, # 是否显示异常值
notch=False, # 中间箱体是否缺口
return_type='dict' # 返回类型为字典
)
plt.title('boxplot')
for box in f['boxes']:
box.set(color='b', linewidth=1) # 箱体边框颜色
box.set(facecolor='b', alpha=0.5) # 箱体内部填充颜色
for whisker in f['whiskers']:
whisker.set(color='k', linewidth=0.5, linestyle='-')
for cap in f['caps']:
cap.set(color='gray', linewidth=2)
for median in f['medians']:
median.set(color='DarkBlue', linewidth=2)
for flier in f['fliers']:
flier.set(marker='o', color='y', alpha=0.5)
# boxes, 箱线
# medians, 中位值的横线,
# whiskers, 从box到error bar之间的竖线.
# fliers, 异常值
# caps, error bar横线
# means, 均值的横线
plt.show()
七、plot函数参数
- 线型linestyle(-,-.,--,..)
- 点型marker(v,^,s,*,H,+,x,D,o,…)
- 颜色color(b,g,r,y,k,w,…)
八、图像标注参数
- 设置图像标题:plt.title()
- 设置x轴名称:plt.xlabel()
- 设置y轴名称:plt.ylabel()
- 设置X轴范围:plt.xlim()
- 设置Y轴范围:plt.ylim()
- 设置X轴刻度:plt.xticks()
- 设置Y轴刻度:plt.yticks()
- 设置曲线图例:plt.legend()
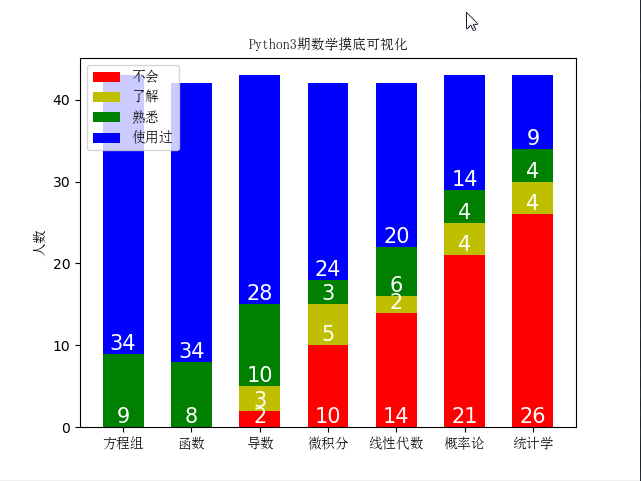
九、Matplolib应用
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r'c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc')
header_list = ['方程组', '函数', '导数', '微积分', '线性代数', '概率论', '统计学']
py3_df = pd.read_excel('py3.xlsx', header=None, skiprows=[0, 1], names=header_list)
# 处理带有NaN的行
py3_df = py3_df.dropna(axis=0) #
print(py3_df)
# 自定义映射
map_dict = {
'不会': 0,
'了解': 1,
'熟悉': 2,
'使用过': 3,
}
for header in header_list:
py3_df[header] = py3_df[header].map(map_dict)
unable_series = (py3_df == 0).sum(axis=0)
know_series = (py3_df == 1).sum(axis=0)
familiar_series = (py3_df == 2).sum(axis=0)
use_series = (py3_df == 3).sum(axis=0)
unable_label = '不会'
know_label = '了解'
familiar_label = '熟悉'
use_label = '使用过'
for i in range(len(header_list)):
bottom = 0
# 描绘不会的条形图
plt.bar(x=header_list[i], height=unable_series[i], width=0.60, color='r', label=unable_label)
if unable_series[i] != 0:
plt.text(header_list[i], bottom, s=unable_series[i], ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=15, color='white')
bottom += unable_series[i]
# 描绘了解的条形图
plt.bar(x=header_list[i], height=know_series[i], width=0.60, color='y', bottom=bottom, label=know_label)
if know_series[i] != 0:
plt.text(header_list[i], bottom, s=know_series[i], ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=15, color='white')
bottom += know_series[i]
# 描绘熟悉的条形图
plt.bar(x=header_list[i], height=familiar_series[i], width=0.60, color='g', bottom=bottom, label=familiar_label)
if familiar_series[i] != 0:
plt.text(header_list[i], bottom, s=familiar_series[i], ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=15, color='white')
bottom += familiar_series[i]
# 描绘使用过的条形图
plt.bar(x=header_list[i], height=use_series[i], width=0.60, color='b', bottom=bottom, label=use_label)
if use_series[i] != 0:
plt.text(header_list[i], bottom, s=use_series[i], ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=15, color='white')
unable_label = know_label = familiar_label = use_label = ''
plt.xticks(header_list, fontproperties=font)
plt.ylabel('人数', fontproperties=font)
plt.title('Python3期数学摸底可视化', fontproperties=font)
plt.legend(prop=font, loc='upper left')
plt.show()
方程组 函数 导数 微积分 线性代数 概率论 统计学 0 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 不会 不会 不会 1 使用过 使用过 了解 不会 不会 不会 不会 2 使用过 使用过 熟悉 不会 不会 不会 不会 3 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 了解 了解 了解 了解 4 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 5 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 不会 了解 6 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 不会 7 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 8 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 使用过 使用过 9 熟悉 熟悉 使用过 不会 使用过 使用过 不会 10 使用过 使用过 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 11 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 12 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 13 使用过 使用过 了解 不会 不会 不会 不会 14 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 15 使用过 使用过 熟悉 不会 不会 不会 不会 16 熟悉 熟悉 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 17 使用过 使用过 使用过 了解 不会 不会 不会 18 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 19 使用过 使用过 使用过 了解 不会 不会 不会 20 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 21 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 22 使用过 很了解 熟悉 了解一点,不会运用 了解一点,不会运用 了解 不会 23 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 熟悉 使用过 熟悉 24 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 使用过 不会 不会 不会 25 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 26 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 27 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 不会 不会 不会 28 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 了解 29 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 了解 不会 30 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 31 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 使用过 使用过 32 熟悉 熟悉 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 33 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 熟悉 使用过 熟悉 34 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 使用过 使用过 熟悉 不会 35 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 36 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 了解 37 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 38 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 不会 不会 39 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 不会 不会 不会 40 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 41 使用过 使用过 熟悉 了解 了解 了解 不会 42 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 不会 不会 43 熟悉 使用过 了解 了解 不会 不会 不会
到此这篇关于Python中数据可视化matplotlib与绘图库模块的文章就介绍到这了。希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。
赞 (0)

