Android简单自定义音乐波动特效图
本文实例为大家分享了Android简单自定义音乐波动特效图的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
最终效果:
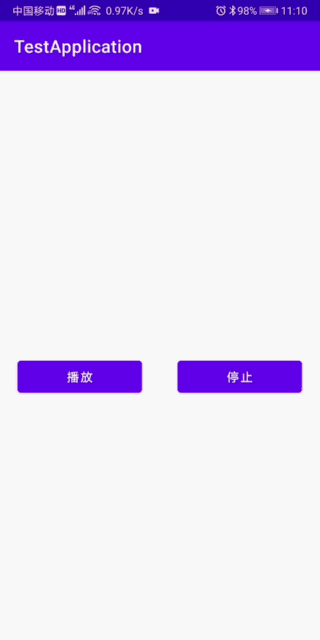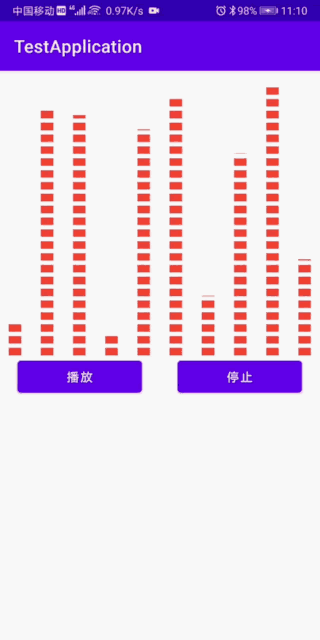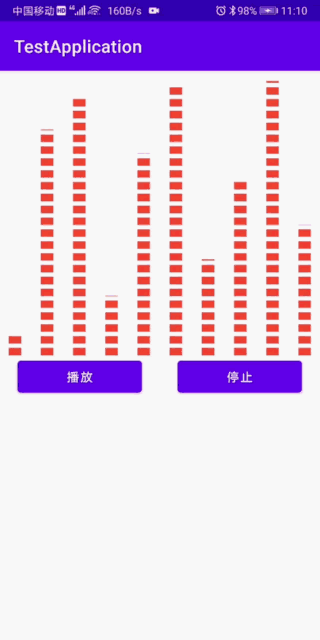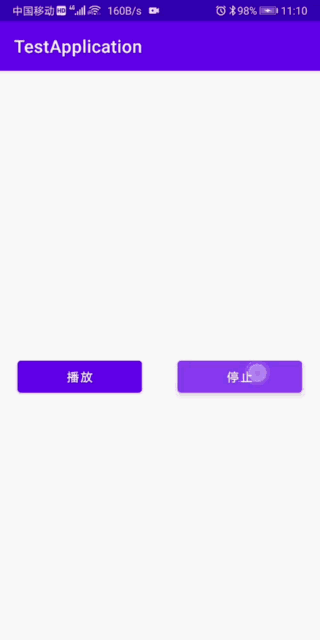
思路:就是绘制一个不断变化高度的矩形或者是宽虚线
1.自定义属性:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="musicPlayViewAttr">
<!--指针颜色-->
<attr name="point_color" format="color" />
<!--指针数量-->
<attr name="point_num" format="integer" />
<!--指针宽度-->
<attr name="point_width" format="float" />
<!--指针波动速度-->
<attr name="point_speed" format="integer" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
2.编写自定义MusicPlayview
/**
* 音乐播放波动动画
*/
public class MusicPlayView extends View {
//坐标原点x
private float mBasePointX;
//坐标原点y
private float mBasePointY;
//指针的数量 默认10
private int mPointNum;
//指针间的间隙 默认5dp
private float mPointSpace;
//每个指针的宽度 默认5dp
private float mPointWidth;
//指针的颜色
private int mPointColor = Color.RED;
//指针的集合
private List<Pointer> mPoints;
//控制开始/停止
private boolean mIsPlaying = false;
//播放线程
private Thread mPlayThread;
//指针波动速度
private int mPointSpeed;
//画笔
private Paint mPaint;
public MusicPlayView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public MusicPlayView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
//取出自定义属性
TypedArray ta = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.musicPlayViewAttr);
mPointNum = ta.getInt(R.styleable.musicPlayViewAttr_point_num, 10);
mPointWidth = dp2px(getContext(),
ta.getFloat(R.styleable.musicPlayViewAttr_point_width, 5f));
mPointColor = ta.getColor(R.styleable.musicPlayViewAttr_point_color, Color.RED);
mPointSpeed = ta.getInt(R.styleable.musicPlayViewAttr_point_speed, 40);
init();
}
public MusicPlayView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
TypedArray ta = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.musicPlayViewAttr);
mPointNum = ta.getInt(R.styleable.musicPlayViewAttr_point_num, 10);
mPointWidth = dp2px(getContext(), ta.getFloat(R.styleable.musicPlayViewAttr_point_width, 5f));
mPointColor = ta.getColor(R.styleable.musicPlayViewAttr_point_color, Color.RED);
mPointSpeed = ta.getInt(R.styleable.musicPlayViewAttr_point_speed, 40);
init();
}
/**
* 初始化画笔
*/
private void init() {
mPoints = new ArrayList<>();
//绘制虚线
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
mPaint.setColor(mPointColor);
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(mPointWidth);
mPaint.setPathEffect(new DashPathEffect(new float[]{25, 15}, 0));//虚线间隔
setLayerType(LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE, null);
}
/**
* 设置指针高度和即那个
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom);
//获取逻辑原点的Y
mBasePointY = getHeight() - getPaddingBottom();
Random random = new Random();
if (mPoints != null)
mPoints.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < mPointNum; i++) {
//随机高度
mPoints.add(new Pointer((float) (0.1 * (random.nextInt(10) + 1) * (getHeight() - getPaddingBottom() - getPaddingTop()))));
}
//计算每个指针之间的间隔 view宽度 - 左右的padding - 所有指针总共宽度 再除以多少个间隔
mPointSpace = (getWidth() - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight() - mPointWidth * mPointNum) / (mPointNum - 1);
}
/**
* 开始绘制虚线
*/
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
//指针x位置
mBasePointX = 0f + getPaddingLeft() + mPointWidth / 2;
//绘制每一个指针。
for (int i = 0; i < mPoints.size(); i++) {
//绘制虚线
float[] pts = {mBasePointX, getHeight(), mBasePointX, (mBasePointY - mPoints.get(i).getHeight())};//重下往上动画
canvas.drawLines(pts, mPaint);
//更新指针x位置
mBasePointX += (mPointSpace + mPointWidth);
}
}
/**
* 开始线程 播放
*/
public void start() {
setVisibility(VISIBLE);
if (!mIsPlaying) {
if (mPlayThread == null) {
mPlayThread = new Thread(new PlayRunnable());
mPlayThread.start();
}
mIsPlaying = true;//控制子线程中的循环
}
}
/**
* 停止线程 停止播放
*/
public void stop() {
setVisibility(INVISIBLE);
mIsPlaying = false;
invalidate();
}
/**
* 更新UI
*/
private Handler myHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
invalidate();
}
};
/**
* 子线程,循环改变每个指针的高度
*/
public class PlayRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (float i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE; ) {
try {
for (int j = 0; j < mPoints.size(); j++) {
float rate = (float) Math.abs(Math.sin(i + j));//随机数
mPoints.get(j).setHeight((mBasePointY - getPaddingTop()) * rate); //每个指针的高度
}
Thread.sleep(mPointSpeed);//控制动画速度
//开始/暂停
if (mIsPlaying) {
myHandler.sendEmptyMessage(0);
i += 0.1;
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 指针对象
*/
public class Pointer {
private float height;
public Pointer(float height) {
this.height = height;
}
public float getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(float height) {
this.height = height;
}
}
/**
* dp转px
*/
public static int dp2px(Context context, float dpVal) {
return (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP, dpVal, context.getResources()
.getDisplayMetrics());
}
}
3.在activity_main2布局中使用MusicPlayView
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<com.hk.testapplication.MusicPlayView
android:id="@+id/music_play"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:visibility="invisible"
android:padding="10dp"
app:point_color="#F44336"
app:point_num="10"
app:point_width="14" />
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1">
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_play"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp"
android:layout_marginRight="20dp"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="播放"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_stop"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp"
android:layout_marginRight="20dp"
android:text="停止"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
4.MainActivity中使用
public class MainActivity2 extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private Button mBtPlay,mBtStop;
private MusicPlayView mMusicPlayView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main2);
mMusicPlayView = findViewById(R.id.music_play);
mBtPlay = findViewById(R.id.bt_play);
mBtStop = findViewById(R.id.bt_stop);
mBtPlay.setOnClickListener(this);
mBtStop.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()){
case R.id.bt_play:
//开始播放
mMusicPlayView.start();
break;
case R.id.bt_stop:
//停止播放
mMusicPlayView.stop();
break;
}
}
}
因为注释都挺详细的,就没有做太多的介绍,我这里也只是提供一个思路,里面有很多可以优化的地方比方说线程使用和循环的时候,如果有不懂的地方可以留言。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。
赞 (0)

