Mybatis之association和collection用法
目录
- association和collection用法
- 1.单个关联查询association
- 2.多个关联查询 collection
- 3.鉴别器discriminator
- association和collection关联查询用法
- 一对多 collection
- 一对一 & 多对一
association和collection用法
1.单个关联查询association
1.1实体之间的关联表示
package com.worldly.config.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @Description
* @Author xiaoqx <worldly_xuan@163.com>
* @Version V1.0.0
* @Since 2017/11/26
*/
public class Employee implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String email;
private String tel;
//关联的部门实体,查询某个人的时候可以把所在部门信息查询出来
private Department dep;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getTel() {
return tel;
}
public void setTel(String tel) {
this.tel = tel;
}
public Department getDep() {
return dep;
}
public void setDep(Department dep) {
this.dep = dep;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{\"Employee\":{"
+ "\"id\":\"" + id + "\""
+ ", \"name\":\"" + name + "\""
+ ", \"email\":\"" + email + "\""
+ ", \"tel\":\"" + tel + "\""
+ ", \"dep\":" + dep
+ "}}";
}
}
1.2 两种关联查询方式
//第一中方式:直接进行关联查询把关联实体的属性在xml中配置
//然后关联查出来
<resultMap id="emp2ResultMap" type="com.worldly.config.entity.Employee">
<id column="emp_id" property="id"></id>
<result column="emp_name" property="name"/>
<result column="emp_email" property="email"/>
<result column="emp_tel" property="tel"/>
<association property="dep" column="emp_dep" javaType="com.worldly.config.entity.Department">
<id column="dep_id" property="id"/>
<result column="dep_name" property="name"/>
<result column="dep_addr" property="addr"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectEmployAll" resultMap="emp2ResultMap">
SELECT
*
FROM
t_emp e
INNER JOIN t_dep d ON e.emp_dep = d.dep_id
</select>
//第二中查询方式,采用 association中的select来查询
<resultMap id="empResultMap" type="com.worldly.config.entity.Employee">
<id column="emp_id" property="id"></id>
<result column="emp_name" property="name"/>
<result column="emp_email" property="email"/>
<result column="emp_tel" property="tel"/>
<association column="emp_dep" property="dep" javaType="com.worldly.config.entity.Department" select="selectDepByCondition"></association>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectEmployeeList" resultMap="empResultMap" databaseId="mysql">
select * from t_emp
</select>
<resultMap id="depResultMap" type="com.worldly.config.entity.Department">
<id column="dep_id" property="id"></id>
<result column="dep_name" property="name"/>
<result column="dep_addr" property="addr"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectDepByCondition" resultMap="depResultMap">
SELECT
*
FROM
t_dep d
WHERE
d.dep_id = #{emp_dep}
</select>
1.3 两种方式的优劣
a.查询条件相同,所用的时间:从测试结果显示,关联查询要比嵌套查询快一点(结果不一定准确,可能关联表多的时候,结果会有所变化)
a.查询条件相同,所用的时间:从测试结果显示,关联查询要比嵌套查询快一点(结果不一定准确,可能关联表多的时候,结果会有所变化)
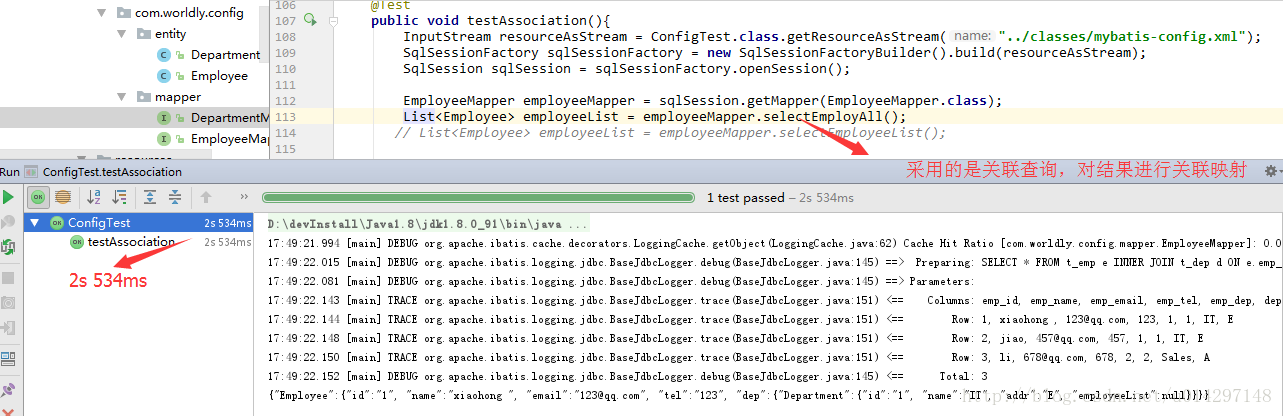
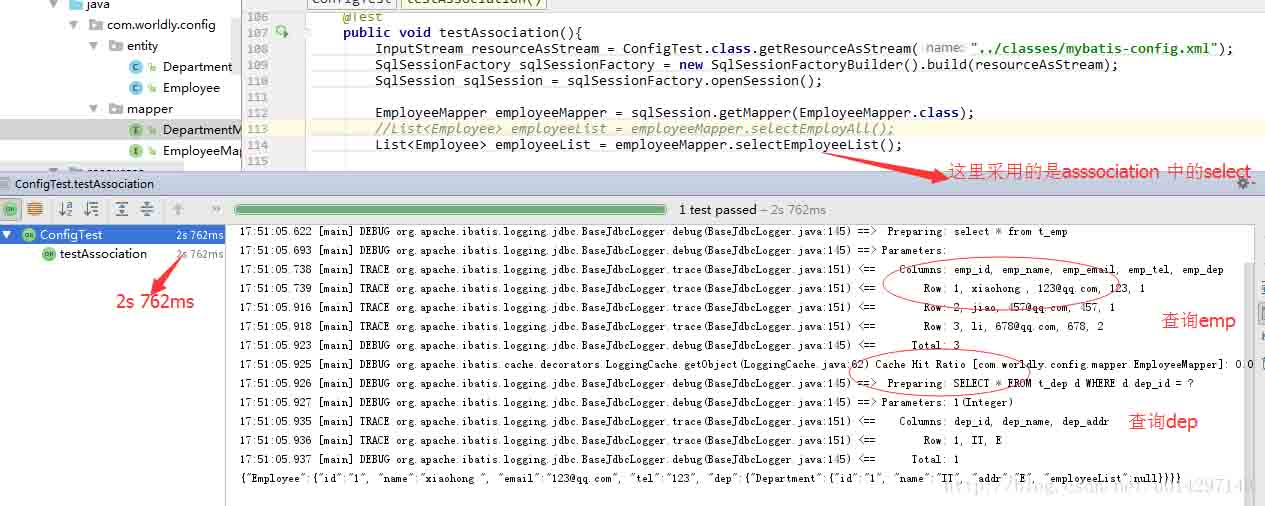
b.适用的情况
2.多个关联查询 collection
2.1实体之间的关联表示
package com.worldly.config.entity;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Description
* @Author xiaoqx <worldly_xuan@163.com>
* @Version V1.0.0
* @Since 1.0
* @Date 2017/12/16
*/
public class Department {
private int id;
private String name;
private String addr;
List<Employee> employeeList;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getNamel() {
return name;
}
public void setNamel(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddr() {
return addr;
}
public void setAddr(String addr) {
this.addr = addr;
}
public List<Employee> getEmployeeList() {
return employeeList;
}
public void setEmployeeList(List<Employee> employeeList) {
this.employeeList = employeeList;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{\"Department\":{"
+ "\"id\":\"" + id + "\""
+ ", \"name\":\"" + name + "\""
+ ", \"addr\":\"" + addr + "\""
+ ", \"employeeList\":" + employeeList
+ "}}";
}
}
2.2 两种关联查询方式
//第一种方式嵌套查询
<resultMap id="depResultMap2" type="com.worldly.config.entity.Department">
<id column="dep_id" property="id"></id>
<result column="dep_name" property="name"/>
<result column="dep_addr" property="addr"/>
<collection column="dep_id" property="employeeList" javaType="java.util.List" ofType="com.worldly.config.entity.Employee"
select="selectEmpBydepId"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectDepByCondition" resultMap="depResultMap2">
SELECT
*
FROM
t_dep d
WHERE
d.dep_id = #{param}
</select>
<resultMap id="empResultMap" type="com.worldly.config.entity.Employee">
<id column="emp_id" property="id"></id>
<result column="emp_name" property="name"/>
<result column="emp_email" property="email"/>
<result column="emp_tel" property="tel"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectEmpBydepId" resultMap="empResultMap">
SELECT
*
FROM
t_emp e
WHERE
e.emp_dep = #{dep_id}
</select>
//第二中方式关联查询
<resultMap id="dep2ResultMap" type="com.worldly.config.entity.Department">
<id column="dep_id" property="id"></id>
<result column="dep_name" property="name"/>
<result column="dep_addr" property="addr"/>
<collection property="employeeList" ofType="com.worldly.config.entity.Employee">
<id column="emp_id" property="id"></id>
<result column="emp_name" property="name"/>
<result column="emp_email" property="email"/>
<result column="emp_tel" property="tel"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectDepWithEmp" resultMap="dep2ResultMap">
SELECT
*
FROM
t_dep d
INNER JOIN t_emp e ON d.dep_id = e.emp_dep
WHERE
d.dep_id = #{param}
</select>
2.3 多条件查询
<resultMap id="depResultMap2" type="com.worldly.config.entity.Department">
<id column="dep_id" property="id"></id>
<result column="dep_name" property="name"/>
<result column="dep_addr" property="addr"/>
<result column="dep_status" property="status"/>
<collection column="{depId=dep_id,status=dep_status}" property="employeeList" javaType="java.util.List" ofType="com.worldly.config.entity.Employee"
select="selectEmpBydepId"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectDepByCondition" resultMap="depResultMap2">
SELECT
*
FROM
t_dep d
WHERE
d.dep_id = #{param}
</select>
<resultMap id="empResultMap" type="com.worldly.config.entity.Employee">
<id column="emp_id" property="id"></id>
<result column="emp_name" property="name"/>
<result column="emp_email" property="email"/>
<result column="emp_tel" property="tel"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectEmpBydepId" resultMap="empResultMap">
SELECT
*
FROM
t_emp e
WHERE
e.emp_dep = #{depId} AND e.emp_status=#{status}
</select>
多条件查询,用{}来包装方法
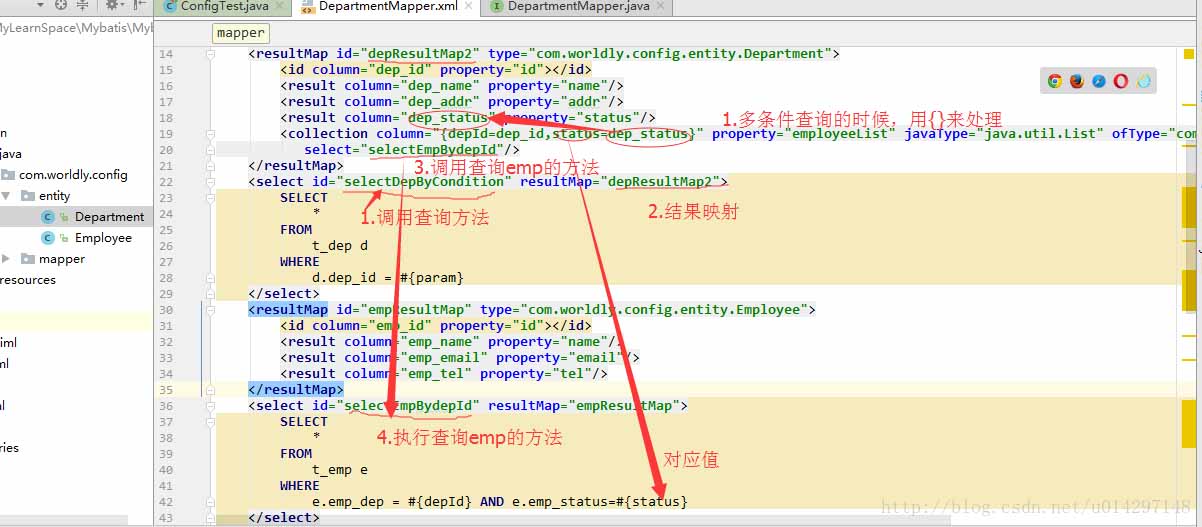
3.鉴别器discriminator
3.1 鉴别器适用的场景
3.2 鉴别器的实现
association和collection关联查询用法
这里只做最简单的用法,其它方法请自行查询;
一对多 collection
<collection property="要查询的实体集合" javaType="java.util.List" ofType="要查询的实体所在包路径" select="要查询的mapper方法" column="关联的实体中的字段=关联的数据库中的字段"/>
举例
<collection property="stsManageStudentList" javaType="java.util.List" ofType="com.crm.project.domain.StsManageStudent" select="com.crm.project.mapper.StsManageStudentMapper.selectStsManageStudentList" column="manageId=manage_id"/>
一对一 & 多对一
<association property="要查询的实体" column="数据库中的关联字段" javaType="要查询的实体所在包路径" select="要查询的mapper方法"/>
举例
<association property="stsStudent" column="student_id" javaType="com.crm.project.domain.StsStudent" select="com.crm.project.mapper.StsStudentMapper.selectStsStudentById"/>
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。
赞 (0)

