springsecurity基于token的认证方式
目录
- 前言
- 基于token的表单登录
- 基于token的短信验证码登录
- 基于token的社交登录
- 简化的OAuth的授权改造
- 标准的OAuth授权改造
- 关于用户的绑定
- 之前的社交登录绑定用户
- 自定义providerSignUtils
- 总结
前言
上一篇博客简析了一下spring security oauth中生成AccessToken的源码,目的就是为了方便我们将原有的表单登录,短信登录以及社交登录的认证方法,都改造成基于AccessToken的认证方式
基于token的表单登录
在简析了spring security oauth的源码之后,我们发现,其实有些源码我们并不能用,至少,TokenEndPoint这个组件,我们就没法用,因为这个组件只会响应/oauth/token的请求,而且spring security oauth会根据OAuth协议中常用的4种授权模式去生成令牌,而我们这里是自定义的登录,自然用不上OAuth协议中的授权模式,因此我们改造自定义的登录,只能借鉴其令牌生成方式。
如果有印象,在前几篇博客中总结过自定义登录成功处理的方式,无论前面登录逻辑如何认证,我们只需要在认证成功之后,自定义生成AccessToken 即可,因此我们只需要重新处理我们自定义登录成功的处理方式即可。
那么如何处理,依旧是一个问题,这就回到了上一篇博客中的内容,构造AccessToken需要OAuth2Request和Authentication,其中Authentication是登录成功后的认证详情信息,在登录成功处理器中,会有相关参数传递进来。OAuth2Request由ClientDeatails和TokenRequest组成,这在上一篇博客中我们已经总结过了,ClientDetails根据传递参数中的ClientId和clientSecret等client配置信息组成,TokenRequest则由请求中其他参数实例化而成,具体如下图所示
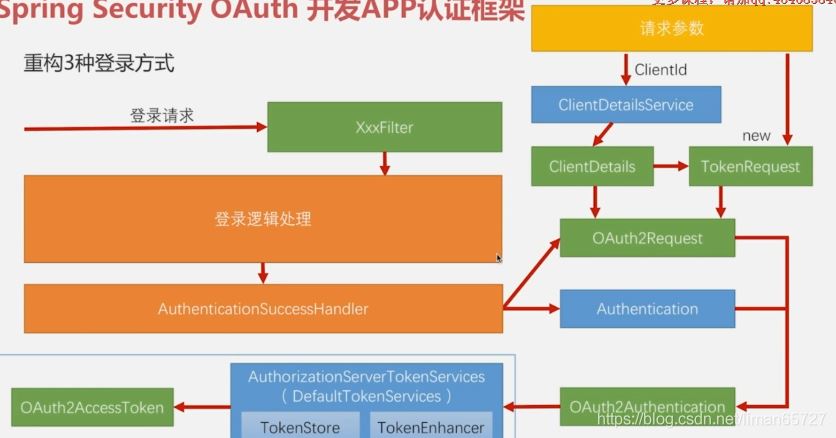
相关改造代码如下
/**
* autor:liman
* createtime:2021/7/10
* comment: 自定义登录成功处理器
*/
@Component("selfAuthenticationSuccessHandler")
@Slf4j
public class SelfAuthenticationSuccessHandler extends SimpleUrlAuthenticationSuccessHandler {
@Autowired
private SecurityProperties securityProperties;
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@Autowired
private ClientDetailsService clientDetailsService;
@Autowired
private AuthorizationServerTokenServices authenticationServerTokenServices;
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response
, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
log.info("自定义登录成功的处理器");
String header = request.getHeader("Authorization");
if (header == null || !header.startsWith("Basic ")) {
throw new UnapprovedClientAuthenticationException("请求头中没有client相关的信息");
}
String[] tokens = extractAndDecodeHeader(header, request);
assert tokens.length == 2;
String clientId = tokens[0];
String clientSecret = tokens[1];
//得到clientDeatils信息
ClientDetails clientDetails = clientDetailsService.loadClientByClientId(clientId);//得到clientDetails信息
if (null == clientDetails) {
throw new UnapprovedClientAuthenticationException("clientid对应的信息不存在" + clientId);
} else if (!StringUtils.equals(clientSecret, clientDetails.getClientSecret())) {
throw new UnapprovedClientAuthenticationException("clientSecret信息不匹配" + clientSecret);
}
//构建自己的tokenRequest,由于这里不能使用OAuth2中的四种授权模式,因此这里第四个参数设置为"customer"
//同理,第一个参数主要用于组装并生成Authentication,而这里的Authentication已经通过参数传递进来,因此可以直接赋一个空的Map
TokenRequest tokenRequest = new TokenRequest(MapUtils.EMPTY_MAP, clientId, clientDetails.getScope(), "customer");
//构建OAuth2Request
OAuth2Request oAuth2Request = tokenRequest.createOAuth2Request(clientDetails);
//构建 OAuth2Authentication
OAuth2Authentication oAuth2Authentication = new OAuth2Authentication(oAuth2Request, authentication);
//生成accessToken,这里依旧使用的是spring security oauth中默认的DefaultTokenService
OAuth2AccessToken accessToken = authenticationServerTokenServices.createAccessToken(oAuth2Authentication);
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(accessToken));//将authentication作为json写到前端
}
/**
* Decodes the header into a username and password.
*
* @throws BadCredentialsException if the Basic header is not present or is not valid
* Base64
*/
//TODO:解码请求头中的Base64编码的 appId和AppSecret
private String[] extractAndDecodeHeader(String header, HttpServletRequest request)
throws IOException {
//格式:Basic+空格+Base64加密的appid和AppSecret,所以这里substring(6)
byte[] base64Token = header.substring(6).getBytes("UTF-8");
byte[] decoded;
try {
decoded = Base64.decode(base64Token);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(
"Failed to decode basic authentication token");
}
String token = new String(decoded, "UTF-8");
int delim = token.indexOf(":");
if (delim == -1) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("Invalid basic authentication token");
}
return new String[]{token.substring(0, delim), token.substring(delim + 1)};
}
}
基于token的短信验证码登录
之前提到过,由于基于token的认证交互,其实不一定会有session会话的概念,如果我们的验证码依旧存于session中,则并不能正常校验,因此在基于token的短信验证码登录的重构中,我们唯一要做的,就是将验证码存于Redis等缓存中间件中,验证码的key值为deviceid。
方案比较简单,这里只贴出Redis操作验证码的方法
/**
* 基于redis的验证码存取器,避免由于没有session导致无法存取验证码的问题
*/
@Component
public class RedisValidateCodeRepository implements ValidateCodeRepository {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate;
/*
* (non-Javadoc)
*/
@Override
public void save(ServletWebRequest request, ValidateCode code, ValidateCodeType type) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(buildKey(request, type), code, 30, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}
/*
* (non-Javadoc)
*/
@Override
public ValidateCode get(ServletWebRequest request, ValidateCodeType type) {
Object value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(buildKey(request, type));
if (value == null) {
return null;
}
return (ValidateCode) value;
}
/*
* (non-Javadoc)
*
*/
@Override
public void remove(ServletWebRequest request, ValidateCodeType type) {
redisTemplate.delete(buildKey(request, type));
}
/**
* @param request
* @param type
* @return
*/
private String buildKey(ServletWebRequest request, ValidateCodeType type) {
String deviceId = request.getHeader("deviceId");
if (StringUtils.isBlank(deviceId)) {
throw new ValidateCodeException("请在请求头中携带deviceId参数");
}
return "code:" + type.toString().toLowerCase() + ":" + deviceId;
}
}
基于token的社交登录
在调通微信社交登录之后,再进行总结,只是需要明确的是,这里分为两种情况,一种是简化模式,一种是标准的OAuth2授权模式(这两种的区别,在QQ登录和微信登录流程中有详细的体现)。
简化的OAuth的授权改造
简化的OAuth模式,OAuth协议简化的认证模式,与标准最大的不同,其实就是在获取授权码的时候,顺带将openId(第三方用户id)和accessToken(获取用户信息的令牌),在这种前后端彻底分离的架构中,前三步前端可以通过服务提供商的SDK完成openId和AccessToken的获取。但是并不能根据openId作为我们自己登录系统凭证,因此我们需要提供一个根据openId进行登录的方式这个与之前短信登录方式大同小异
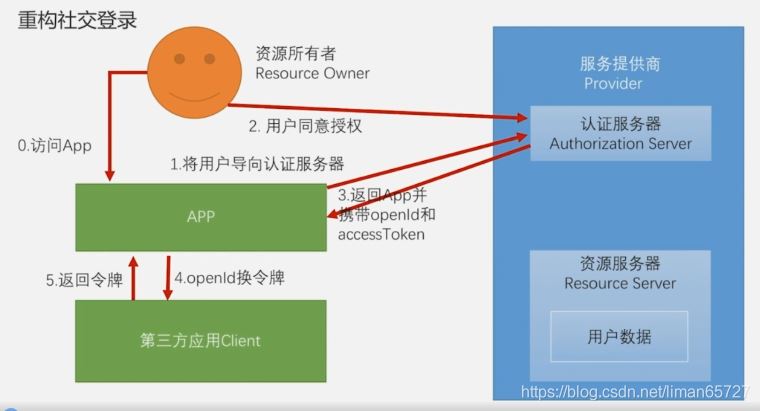
1、OpenIdAuthenticationToken
/**
* autor:liman
* createtime:2021/8/4
* comment:OpenIdAuthenticationToken
*/
public class OpenIdAuthenticationToken extends AbstractAuthenticationToken {
private static final long serialVersionUID = SpringSecurityCoreVersion.SERIAL_VERSION_UID;
private final Object principal;
private String providerId;
/**
openId,和providerId作为principal
*/
public OpenIdAuthenticationToken(String openId, String providerId) {
super(null);
this.principal = openId;
this.providerId = providerId;
setAuthenticated(false);
}
/**
* This constructor should only be used by <code>AuthenticationManager</code> or
* <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> implementations that are satisfied with
* producing a trusted (i.e. {@link #isAuthenticated()} = <code>true</code>)
* authentication token.
*
* @param principal
* @param credentials
* @param authorities
*/
public OpenIdAuthenticationToken(Object principal,
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
super(authorities);
this.principal = principal;
super.setAuthenticated(true); // must use super, as we override
}
public Object getCredentials() {
return null;
}
public Object getPrincipal() {
return this.principal;
}
public String getProviderId() {
return providerId;
}
public void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (isAuthenticated) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Cannot set this token to trusted - use constructor which takes a GrantedAuthority list instead");
}
super.setAuthenticated(false);
}
@Override
public void eraseCredentials() {
super.eraseCredentials();
}
}
2、OpenIdAuthenticationFilter
/**
* autor:liman
* createtime:2021/8/4
* comment:基于openId登录的过滤器
*/
@Slf4j
public class OpenIdAuthenticationFilter extends AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {
private String openIdParameter = "openId";
private String providerIdParameter = "providerId";
private boolean postOnly = true;
public OpenIdAuthenticationFilter() {
super(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/authentication/openid", "POST"));
}
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws AuthenticationException {
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
//获取请求中的openId和providerId
String openid = obtainOpenId(request);
String providerId = obtainProviderId(request);
if (openid == null) {
openid = "";
}
if (providerId == null) {
providerId = "";
}
openid = openid.trim();
providerId = providerId.trim();
//构造OpenIdAuthenticationToken
OpenIdAuthenticationToken authRequest = new OpenIdAuthenticationToken(openid, providerId);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
//交给AuthenticationManager进行认证
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
/**
* 获取openId
*/
protected String obtainOpenId(HttpServletRequest request) {
return request.getParameter(openIdParameter);
}
/**
* 获取提供商id
*/
protected String obtainProviderId(HttpServletRequest request) {
return request.getParameter(providerIdParameter);
}
protected void setDetails(HttpServletRequest request, OpenIdAuthenticationToken authRequest) {
authRequest.setDetails(authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request));
}
public void setOpenIdParameter(String openIdParameter) {
Assert.hasText(openIdParameter, "Username parameter must not be empty or null");
this.openIdParameter = openIdParameter;
}
public void setPostOnly(boolean postOnly) {
this.postOnly = postOnly;
}
public final String getOpenIdParameter() {
return openIdParameter;
}
public String getProviderIdParameter() {
return providerIdParameter;
}
public void setProviderIdParameter(String providerIdParameter) {
this.providerIdParameter = providerIdParameter;
}
}
3、OpenIdAuthenticationProvider
/**
*
*/
package com.learn.springsecurity.app.social.openid;
/**
* @author zhailiang
*
*/
public class OpenIdAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
private SocialUserDetailsService userDetailsService;
private UsersConnectionRepository usersConnectionRepository;
/*
* (non-Javadoc)
*
* @see org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationProvider#
* authenticate(org.springframework.security.core.Authentication)
*/
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
OpenIdAuthenticationToken authenticationToken = (OpenIdAuthenticationToken) authentication;
Set<String> providerUserIds = new HashSet<>();
providerUserIds.add((String) authenticationToken.getPrincipal());
//之前社交登录中介绍的usersConnectionRepository,从user_connection表中根据providerId和openId查询用户id
Set<String> userIds = usersConnectionRepository.findUserIdsConnectedTo(authenticationToken.getProviderId(), providerUserIds);
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(userIds) || userIds.size() != 1) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException("无法获取用户信息");
}
//获取到userId了
String userId = userIds.iterator().next();
//利用UserDetailsService根据userId查询用户信息
UserDetails user = userDetailsService.loadUserByUserId(userId);
if (user == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException("无法获取用户信息");
}
OpenIdAuthenticationToken authenticationResult = new OpenIdAuthenticationToken(user, user.getAuthorities());
authenticationResult.setDetails(authenticationToken.getDetails());
return authenticationResult;
}
/*
* (non-Javadoc)
*
* @see org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationProvider#
* supports(java.lang.Class)
*/
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return OpenIdAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication);
}
public SocialUserDetailsService getUserDetailsService() {
return userDetailsService;
}
public void setUserDetailsService(SocialUserDetailsService userDetailsService) {
this.userDetailsService = userDetailsService;
}
public UsersConnectionRepository getUsersConnectionRepository() {
return usersConnectionRepository;
}
public void setUsersConnectionRepository(UsersConnectionRepository usersConnectionRepository) {
this.usersConnectionRepository = usersConnectionRepository;
}
}
4、配置类
/**
* @author zhailiang
*
*/
@Component
public class OpenIdAuthenticationSecurityConfig extends SecurityConfigurerAdapter<DefaultSecurityFilterChain, HttpSecurity> {
@Autowired
private AuthenticationSuccessHandler selfAuthenticationSuccessHandler;
@Autowired
private AuthenticationFailureHandler selfAuthenticationFailureHandler;
@Autowired
private SocialUserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Autowired
private UsersConnectionRepository usersConnectionRepository;
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
OpenIdAuthenticationFilter OpenIdAuthenticationFilter = new OpenIdAuthenticationFilter();
OpenIdAuthenticationFilter.setAuthenticationManager(http.getSharedObject(AuthenticationManager.class));
OpenIdAuthenticationFilter.setAuthenticationSuccessHandler(selfAuthenticationSuccessHandler);
OpenIdAuthenticationFilter.setAuthenticationFailureHandler(selfAuthenticationFailureHandler);
OpenIdAuthenticationProvider OpenIdAuthenticationProvider = new OpenIdAuthenticationProvider();
OpenIdAuthenticationProvider.setUserDetailsService(userDetailsService);
OpenIdAuthenticationProvider.setUsersConnectionRepository(usersConnectionRepository);
http.authenticationProvider(OpenIdAuthenticationProvider)
.addFilterAfter(OpenIdAuthenticationFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
}
测试结果
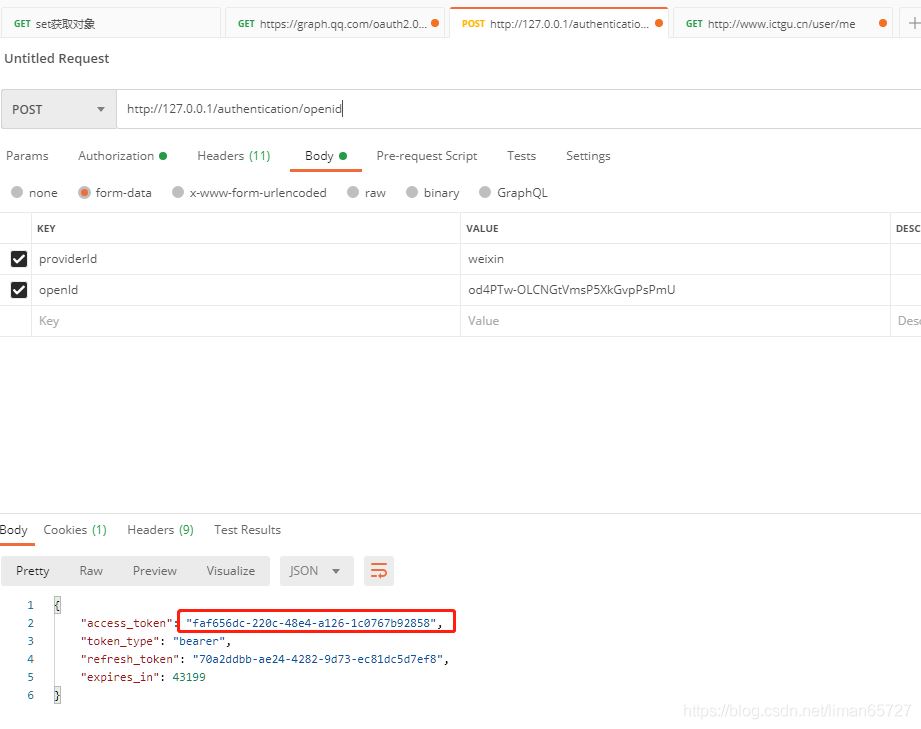
标准的OAuth授权改造
标准的OAuth模式
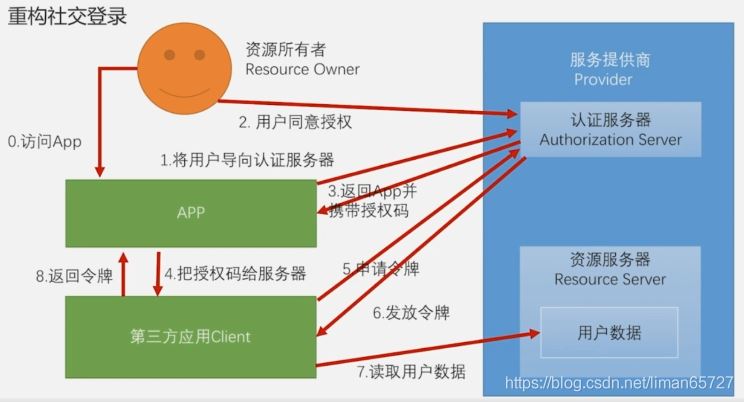
针对标准的授权模式,我们并不需要做多少改动,因为在社交登录那一节中我们已经做了相关开发,只是需要说明的是,只是在spring-social的过滤器——SocialAuthenticationFilter中,在正常社交登录流程完成之后会默认跳转到某个页面,而这个并不适用于前后端分离的项目,因此要针对这个问题定制化解决。这需要回到之前SocialAuthenticationFilter加入到认证过滤器链上的代码。之前我们说过社交登录的过滤器链不需要我们手动配置,只需要初始化SpringSocialConfiguer的时候,会自动加入到社交登录的认证过滤器链上
@Configuration
@EnableSocial
public class SocialConfig extends SocialConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public SpringSocialConfigurer selfSocialSecurityConfig(){
SpringSocialConfigurer selfSpringSocialConfig = new SpringSocialConfigurer();
return selfSpringSocialConfig;
}
}
我们只需要改变SocialAuthenticationFilter的默认处理即可,因此我们给他加一个后置处理器,但是这个后置处理器是在SpringSocialConfigurer的postProcess函数中进行处理
/**
* autor:liman
* createtime:2021/7/15
* comment:自定义的springsocial配置类
*/
public class SelfSpringSocialConfig extends SpringSocialConfigurer {
private String processFilterUrl;
@Autowired(required = false)
private ConnectionSignUp connectionSignUp;
@Autowired(required = false)
private SocialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor socialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor;
public SelfSpringSocialConfig(String processFilterUrl) {
this.processFilterUrl = processFilterUrl;
}
@Override
protected <T> T postProcess(T object) {
SocialAuthenticationFilter socialAuthenticationFilter = (SocialAuthenticationFilter) super.postProcess(object);
socialAuthenticationFilter.setFilterProcessesUrl(processFilterUrl);
if(null!=socialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor){
socialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor.process(socialAuthenticationFilter);
}
return (T) socialAuthenticationFilter;
}
public ConnectionSignUp getConnectionSignUp() {
return connectionSignUp;
}
public void setConnectionSignUp(ConnectionSignUp connectionSignUp) {
this.connectionSignUp = connectionSignUp;
}
public SocialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor getSocialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor() {
return socialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor;
}
public void setSocialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor(SocialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor socialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor) {
this.socialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor = socialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor;
}
}
//将我们自定义的 SpringSocialConfigurer交给spring托管
@Configuration
@EnableSocial
public class SocialConfig extends SocialConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public SpringSocialConfigurer selfSocialSecurityConfig(){
String processFilterUrl = securityProperties.getSocial().getProcessFilterUrl();
SelfSpringSocialConfig selfSpringSocialConfig = new SelfSpringSocialConfig(processFilterUrl);
//指定第三方用户信息认证不存在的注册页
selfSpringSocialConfig.signupUrl(securityProperties.getBrowser().getSiguUpPage());
selfSpringSocialConfig.setConnectionSignUp(connectionSignUp);
selfSpringSocialConfig.setSocialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor(socialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor);
return selfSpringSocialConfig;
}
}
我们自定义的过滤器后置处理器如下
/**
* autor:liman
* createtime:2021/8/7
* comment:APP社交登录认证后置处理器
*/
@Component
public class AppSocialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor implements SocialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor {
@Autowired
private AuthenticationSuccessHandler selfAuthenticationSuccessHandler;
@Override
public void process(SocialAuthenticationFilter socialAuthenticationFilter) {
socialAuthenticationFilter.setAuthenticationSuccessHandler(selfAuthenticationSuccessHandler);
}
}
关于用户的绑定
这里需要总结一下之前的社交登录中用户注册绑定的操作。
之前的社交登录绑定用户
在之前的社交登录中,如果spring social发现用户是第一次登录,则会跳转到相关的页面,这个页面我们其实也可以自己定义并配置
@Configuration
@EnableSocial
public class SocialConfig extends SocialConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public SpringSocialConfigurer selfSocialSecurityConfig(){
String processFilterUrl = securityProperties.getSocial().getProcessFilterUrl();
SelfSpringSocialConfig selfSpringSocialConfig = new SelfSpringSocialConfig(processFilterUrl);
//指定第三方用户信息认证不存在的注册页
selfSpringSocialConfig.signupUrl(securityProperties.getBrowser().getSiguUpPage());
selfSpringSocialConfig.setConnectionSignUp(connectionSignUp);
selfSpringSocialConfig.setSocialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor(socialAuthenticationFilterPostProcessor);
return selfSpringSocialConfig;
}
@Bean
public ProviderSignInUtils providerSignInUtils(ConnectionFactoryLocator connectionFactoryLocator){
return new ProviderSignInUtils(connectionFactoryLocator,
getUsersConnectionRepository(connectionFactoryLocator));
}
}
我们配置的代码中,可以自定义页面路径,我们自定义页面如下(一个简单的登录绑定页面)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>登录</title> </head> <body> <h2>Demo注册页</h2> <form action="user/regist" method="post"> <table> <tr> <td>用户名:</td> <td><input type="text" name="username"></td> </tr> <tr> <td>密码:</td> <td><input type="password" name="password"></td> </tr> <tr> <td colspan="2"> <button type="submit" name="type" value="regist">注册</button> <button type="submit" name="type" value="binding">绑定</button> </td> </tr> </table> </form> </body> </html>
在用户第一次跳转到这个页面的用户选择注册,或者绑定,都会请求/user/register接口,这个接口借助providerSignInUtils完成会话中的用户数据更新
@Autowired
private ProviderSignInUtils providerSignInUtils;
@PostMapping("/register")
public void userRegister(@RequestBody User user, HttpServletRequest request) {
//利用providerSignInUtils,将注册之后的用户信息,关联到会话中
providerSignInUtils.doPostSignUp(user.getId(),new ServletWebRequest(request));
}
在跳转之前,spring social已经帮我们将用户信息存入会话(在SocialAuthenticationFilter中可以看到相关代码)
//以下代码位于:org.springframework.social.security.SocialAuthenticationFilter#doAuthentication
private Authentication doAuthentication(SocialAuthenticationService<?> authService, HttpServletRequest request, SocialAuthenticationToken token) {
try {
if (!authService.getConnectionCardinality().isAuthenticatePossible()) return null;
token.setDetails(authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request));
Authentication success = getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(token);
Assert.isInstanceOf(SocialUserDetails.class, success.getPrincipal(), "unexpected principle type");
updateConnections(authService, token, success);
return success;
} catch (BadCredentialsException e) {
// connection unknown, register new user?
if (signupUrl != null) {
//这里就是将社交用户信息存入会话
// store ConnectionData in session and redirect to register page
sessionStrategy.setAttribute(new ServletWebRequest(request), ProviderSignInAttempt.SESSION_ATTRIBUTE, new ProviderSignInAttempt(token.getConnection()));
throw new SocialAuthenticationRedirectException(buildSignupUrl(request));
}
throw e;
}
}
但是基于前后端分离,且并没有会话对象交互的系统,这种方式并不适用,因为并不存在会话,如何处理,需要用其他方案,其实我们可以在验证码登录的改造中受到启发,将用户数据存入会话即可,我们自定义实现一个providerSignInUtils将用户信息存入Redis即可。
自定义providerSignUtils
1、将第三方用户数据存入Redis的工具类
/**
* autor:liman
* createtime:2021/8/7
* comment:app端用户信息存入Redis的工具类
*/
@Component
public class AppSignUpUtils {
public static final String SOCIAL_REDIS_USER_PREFIX = "self:security:social:connectionData";
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private UsersConnectionRepository usersConnectionRepository;
@Autowired
private ConnectionFactoryLocator connectionFactoryLocator;
public void saveConnectionData(WebRequest webRequest, ConnectionData connectionData) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(getKey(webRequest), connectionData, 10, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}
/**
* 将用户与数据库中的信息进行绑定
* @param request
* @param userId
*/
public void doPostSignUp(WebRequest request,String userId){
String key = getKey(request);
if(!redisTemplate.hasKey(key)){
throw new RuntimeException("无法找到缓存的用户社交账号信息");
}
ConnectionData connectionData = (ConnectionData) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
//根据ConnectionData实例化创建一个Connection
Connection<?> connection = connectionFactoryLocator.getConnectionFactory(connectionData.getProviderId())
.createConnection(connectionData);
//将数据库中的用户与Redis中的用户信息关联
usersConnectionRepository.createConnectionRepository(userId).addConnection(connection);
}
/**
* 获取设备id作为key
*
* @param webRequest
* @return
*/
public String getKey(WebRequest webRequest) {
String deviceId = webRequest.getHeader("deviceId");
if (StringUtils.isBlank(deviceId)) {
throw new RuntimeException("设备id不能为空");
}
return SOCIAL_REDIS_USER_PREFIX + deviceId;
}
}
2、复写掉原来的配置类
为了避免对原有代码的侵入性处理,这里我们需要自定义一个实现BeanPostProcessor接口的类
/**
* autor:liman
* createtime:2021/8/7
* comment:由于app端的社交用户绑定,不能采用跳转,也不能操作会话,需要用自定义的providerSignUpUtils工具类
* 因此需要定义一个后置处理器,针对SpringSocialConfigurer进行一些后置处理
*/
@Component
public class AppSpringSocialConfigurerPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(StringUtils.equals(beanName,"selfSocialSecurityConfig")){
SelfSpringSocialConfig configurer = (SelfSpringSocialConfig) bean;
//复写掉原有的SelfSpringSocialConfig的signupUrl
configurer.signupUrl("/app/social/signup");
return configurer;
}
return bean;
}
}
针对上述的请求路径,我们也要写一个对应路径的controller处理方法
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class AppSecurityController {
@Autowired
private ProviderSignInUtils providerSignInUtils;
@Autowired
private AppSignUpUtils appSignUpUtils;
@GetMapping("/app/social/signup")
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED)
public BaseResponse getSocialUserInfo(HttpServletRequest request){
BaseResponse result = new BaseResponse(StatusCode.Success);
log.info("【app模式】开始获取会话中的第三方用户信息");
//先从其中拿出数据,毕竟这个时候还没有完全跳转,下一个会话,就没有该数据了
Connection<?> connectionFromSession = providerSignInUtils.getConnectionFromSession(new ServletWebRequest(request));
SocialUserInfo socialUserInfo = new SocialUserInfo();
socialUserInfo.setProviderId(connectionFromSession.getKey().getProviderId());
socialUserInfo.setProviderUserId(connectionFromSession.getKey().getProviderUserId());
socialUserInfo.setNickName(connectionFromSession.getDisplayName());
socialUserInfo.setHeadImg(connectionFromSession.getImageUrl());
//转存到自己的工具类中
appSignUpUtils.saveConnectionData(new ServletWebRequest(request),connectionFromSession.createData());
result.setData(socialUserInfo);
return result;
}
}
对于用户注册的接口也需要做调整
@PostMapping("/register")
public void userRegister(@RequestBody User user, HttpServletRequest request) {
//如果是浏览器的应用利用providerSignInUtils,将注册之后的用户信息,关联到会话中
providerSignInUtils.doPostSignUp(user.getId(),new ServletWebRequest(request));
//如果是app的应用,则利用appSignUpUtils 将注册之后的用户信息,关联到会话中
appSignUpUtils.doPostSignUp(new ServletWebRequest(request),user.getId());
}
总结
总结了基于token认证的三种登录方式,最为复杂的为社交登录方式
到此这篇关于springsecurity基于token的认证方式的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springsecurity token认证内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

