教你使用springboot配置多数据源
一、建库建表
1.1 创建数据库db1和数据库db2

1.2 在数据库db1中创建表db1

CREATE TABLE `db1` ( `id` int unsigned zerofill NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, `age` int unsigned zerofill DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
1.3 在数据库db2中创建表db2

CREATE TABLE `db2` ( `id` int unsigned zerofill NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, `age` int unsigned zerofill DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
二、创建springboot项目
2.1 pom.xml导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
2.2 创建application.yml文件(与 2.3 二选一进行配置,推荐此方法)
server:
port: 8080 # 启动端口
spring:
datasource:
db1: # 数据源1
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
db2: # 数据源2
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db2?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
2.3 创建application.properties文件(与 2.2 二选一进行配置)
server.port=8080
spring.datasource.db1.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
spring.datasource.db1.username=root
spring.datasource.db1.password=root
spring.datasource.db1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.db2.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db2?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
spring.datasource.db2.username=root
spring.datasource.db2.password=root
spring.datasource.db2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
2.4 创建mapper文件
我个人是放在mapper包下,文件随便命名的
代码随便写的,测试而已

import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
/**
* @Author if
* @Description: What is it
* @Date 2021-05-20 下午 09:52
*/
@Mapper
public interface Db1Mapper {
@Insert("insert into db1(name,age) values('if',18)")
int add();
}
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
/**
* @Author if
* @Description: What is it
* @Date 2021-05-20 下午 09:52
*/
@Mapper
public interface Db2Mapper {
@Insert("insert into db2(name,age) values('fi',81)")
int add();
}
2.5 创建config配置文件
我个人是放在config包下,文件随便命名的

import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
* @Author if
* @Description: 注意以下有些文件路径需要更改
* @Date 2021-05-20 下午 09:56
*/
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.ifyyf.study.mapper.db1", sqlSessionFactoryRef = "db1SqlSessionFactory")
public class Db1DataSourceConfig {
@Bean("db1DataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.db1") //读取application.yml中的配置参数映射成为一个对象
public DataSource getDb1DataSource(){
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean("db1SqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory db1SqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("db1DataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
// mapper的xml形式文件位置必须要配置,不然将报错:no statement (这种错误也可能是mapper的xml中,namespace与项目的路径不一致导致)
bean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:mapping/db1/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean("db1SqlSessionTemplate")
public SqlSessionTemplate db1SqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("db1SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory){
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
* @Author if
* @Description: 注意以下有些文件路径需要更改
* @Date 2021-05-20 下午 09:56
*/
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.ifyyf.study.mapper.db2", sqlSessionFactoryRef = "db2SqlSessionFactory")
public class Db2DataSourceConfig {
@Bean("db2DataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.db2") //读取application.yml中的配置参数映射成为一个对象
public DataSource getDb2DataSource(){
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean("db2SqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory db2SqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("db2DataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
// mapper的xml形式文件位置必须要配置,不然将报错:no statement (这种错误也可能是mapper的xml中,namespace与项目的路径不一致导致)
bean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:mapping/db2/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean("db2SqlSessionTemplate")
public SqlSessionTemplate db2SqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("db2SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory){
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
三、测试代码运行
3.1 测试类中测试代码
springboot项目中测试类进行测试
import com.ifyyf.study.mapper.db1.Db1Mapper;
import com.ifyyf.study.mapper.db2.Db2Mapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@SpringBootTest
class StudyApplicationTests {
@Resource
private Db1Mapper db1Mapper;
@Resource
private Db2Mapper db2Mapper;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(db1Mapper.add());
System.out.println(db2Mapper.add());
}
}
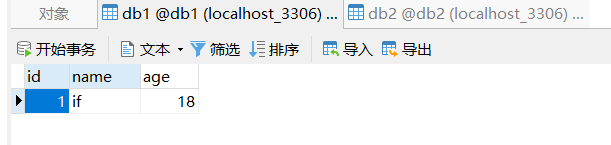
3.2 运行结果


到此这篇关于教你使用springboot配置多数据源的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot配置多数据源内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!
赞 (0)

