Java Spring 声明式事务详解
目录
- 项目结构:
- 表结构:
- 基于xml的声明式事务配置
- 完全注解(零xml)方式配置
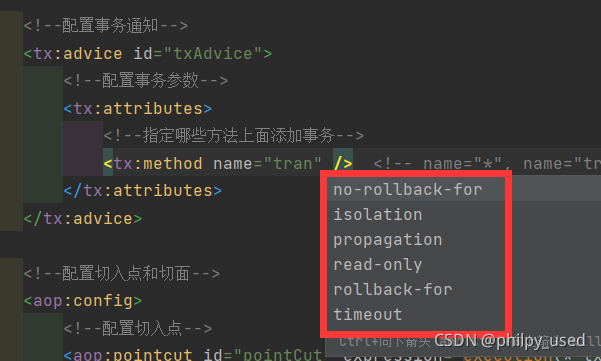
- 事务参数
- no-rollback-for
- rollback-for
- read-only
- timeout
- isolation
- propagation
- 总结
项目结构:

表结构:

基于xml的声明式事务配置
IAccountDao.java:
package tx.dao;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public interface IAccountDao {
void add(String name, BigDecimal money);
void sub(String name, BigDecimal money);
}
AccountDaoImpl.java:
package tx.service.impl;
import tx.dao.IAccountDao;
import tx.service.IAccountService;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
private IAccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(IAccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Override
public void tran(String from, String to, BigDecimal money) {
accountDao.sub(from, money);
accountDao.add(to, money);
}
}
IAccountService.java:
package tx.service;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public interface IAccountService {
void tran(String from, String to, BigDecimal money);
}
AccountDaoImpl.java:
package tx.dao.impl;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import tx.dao.IAccountDao;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
@Override
public void add(String name, BigDecimal money) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set balance = balance + ? where name = ? ", money.toString(), name);
}
@Override
public void sub(String name, BigDecimal money) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set balance = balance - ? where name = ? ", money.toString(), name);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
">
<!--配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useSSL=false"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="19834044876"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
</bean>
<!--创建事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!--注入数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--配置jdbcTemplate对象-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!--注入dataSource-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--将JdbcTemplate注入到AccountDao中-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="tx.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"/>
</bean>
<!--将AccountDao注入到AccountService中-->
<bean id="accountService" class="tx.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事务通知-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice">
<!--配置事务参数-->
<tx:attributes>
<!--指定哪些方法上面添加事务-->
<tx:method name="tran"/> <!-- name="*", name="tran*", name="*tran", ... -->
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--配置切入点和切面-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="pointCut" expression="execution(* tx.service.IAccountService.*(..))"/>
<!--配置通知-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointCut"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("tx.xml");
IAccountService accountService = context.getBean("accountService", IAccountService.class);
accountService.tran("小明", "小红", new BigDecimal(500));
完全注解(零xml)方式配置
IAccountDao.java:
package tx.dao;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public interface IAccountDao {
void add(String name, BigDecimal money);
void sub(String name, BigDecimal money);
}
AccountDaoImpl.java:
package tx.dao.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import tx.dao.IAccountDao;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
@Repository
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public void add(String name, BigDecimal money) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set balance = balance + ? where name = ? ", money.toString(), name);
}
@Override
public void sub(String name, BigDecimal money) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set balance = balance - ? where name = ? ", money.toString(), name);
}
}
IAccountService.java:
package tx.service;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public interface IAccountService {
void tran(String from, String to, BigDecimal money);
}
AccountServiceImpl.java:
package tx.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import tx.dao.IAccountDao;
import tx.service.IAccountService;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
@Service
@Transactional
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
@Autowired
private IAccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void tran(String from, String to, BigDecimal money) {
accountDao.sub(from, money);
accountDao.add(to, money);
}
}
TXConfig.java
package tx.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import tx.service.IAccountService;
import tx.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "tx")
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class TXConfig {
/**
* 配置数据源
*/
@Bean
public DataSource getDataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useSSL=false");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("19834044876");
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
return dataSource;
}
/**
* 创建事务管理器
*/
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager getTransactionManager() {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(getDataSource());
}
/**
* 配置jdbcTemplate对象
*/
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate() {
return new JdbcTemplate(getDataSource());
}
@Bean(name = "accountService")
public IAccountService getAccountService() {
return new AccountServiceImpl();
}
}
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TXConfig.class);
IAccountService accountService = context.getBean("accountService", IAccountService.class);
accountService.tran("小明", "小红", new BigDecimal(500));
事务参数

no-rollback-for
指定碰到哪些异常不需要回滚
rollback-for
指定碰到哪些异常需要回滚
read-only
设置事务为只读事务
timeout
以秒为单位,设置事务超出指定时常后自动回滚
默认为-1,即不管事务运行多久都不回滚
isolation
事务的隔离级别
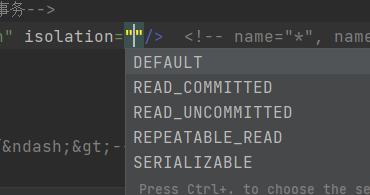

默认为DEFAULT,即使用当前数据库的隔离级别

propagation
事务的传播行为
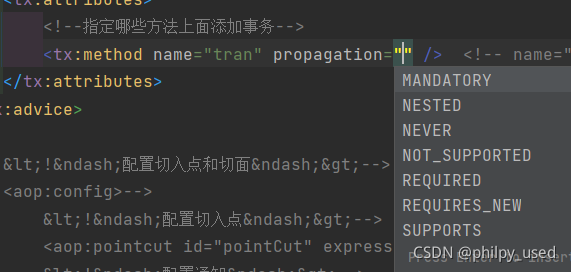
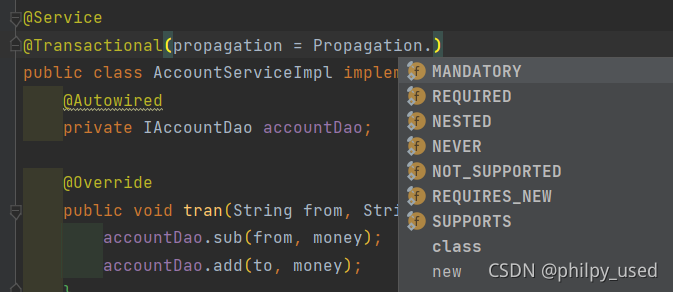
默认为REQUIRED

总结
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能够给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注我们的更多内容!
赞 (0)

