Entity Framework加载控制Loading Entities
Entity Framework允许控制对象之间的关系,在使用EF的过程中,很多时候我们会进行查询的操作,当我们进行查询的时候,哪些数据会被加载到内存中呢?所有的数据都需要吗?在一些场合可能有意义,例如:当查询的实体仅仅拥有一个相关的子实体时可以加载所有的数据到内存中。但是,在多数情况下,你可能并不需要加载全部的数据, 而是只要加载一部分的数据即可。
默认情况下,EF仅仅加载查询中涉及到的实体,但是它支持两种特性来帮助你控制加载:
- 1、贪婪加载
- 2、延迟加载
下面以客户类型、客户和客户邮件三个实体之间的关系来讲解两种加载方式。
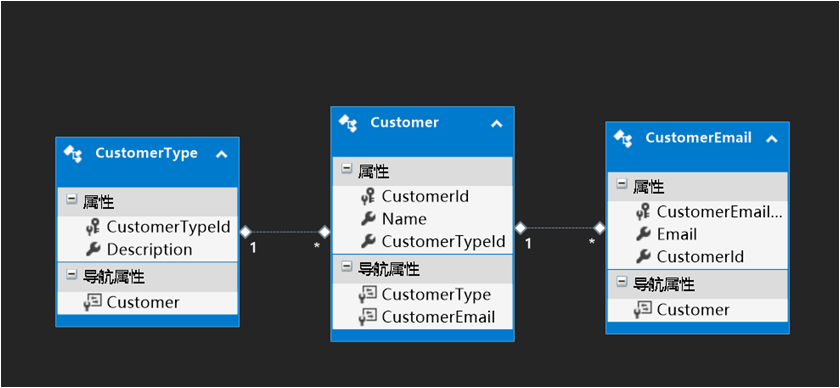
从上图可以看出三个实体类之间的关系:
客户类型和客户是一对多的关系:一个客户类型可以有多个客户。
客户和客户邮件是一对一的关系:一个客户只有一个邮箱地址。(假设只有一个邮箱地址)
一、延迟加载(Lazy Loading)
延迟加载:即在需要或者使用的时候才会加载数据。默认情况下,EF使用延迟加载的方式来加载数据。延迟加载是这样一种过程:直到LINQ查询的结果被枚举时,该查询涉及到的相关实体才会从数据库加载。如果加载的实体包含了其他实体的导航属性,那么直到用户访问该导航属性时,这些相关的实体才会被加载。
使用延迟加载必须满足两个条件:
1、实体类是由Public修饰符修饰的,不能是封闭类。
2、导航属性标记为Virtual。
1、定义实体类
CustomerType实体类定义如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace LazyLoding.Model
{
public class CustomerType
{
public int CustomerTypeId { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
// 导航属性使用virtual关键字修饰,用于延迟加载
public virtual ICollection<Customer> Customers { get; set; }
}
}
Customer实体类定义如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace LazyLoding.Model
{
public class Customer
{
public int CustomerId { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
// 导航属性使用virtual关键字修饰,用于延迟加载
public virtual CustomerType CustomerType { get; set; }
// 导航属性使用virtual关键字修饰,用于延迟加载
public virtual CustomerEmail CustomerEmail { get; set; }
}
}
CustomerEmail实体类定义如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace LazyLoding.Model
{
public class CustomerEmail
{
public int CustomerEmailId { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
// 导航属性使用virtual关键字修饰,用于延迟加载
public virtual Customer Customer { get; set; }
}
}
2、定义数据上下文类,并配置实体关系
using LazyLoding.Model;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace LazyLoding.EF
{
public class Context :DbContext
{
public Context()
: base("name=AppConnection")
{
}
#region 将领域实体添加到DbSet中
public DbSet<CustomerType> CustomerTypes { get; set; }
public DbSet<Customer> Customers { get; set; }
public DbSet<CustomerEmail> CustomerEmails { get; set; }
#endregion
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
// 设置表名和主键
modelBuilder.Entity<CustomerType>().ToTable("CustomerType").HasKey(p => p.CustomerTypeId);
modelBuilder.Entity<Customer>().ToTable("Customer").HasKey(p => p.CustomerId);
modelBuilder.Entity<CustomerEmail>().ToTable("CustomerEmail").HasKey(p => p.CustomerEmailId);
// 设置实体关系
/*
配置一对多关系
HasMany:表示一个CustomerType里面包含多个Customers
WithRequired:表示必选,CustomerType不能为空
MapKey:定义实体之间的外键
*/
modelBuilder.Entity<CustomerType>().HasMany(p => p.Customers).WithRequired(t => t.CustomerType)
.Map(m =>
{
m.MapKey("CustomerTypeId");
});
/*
配置一对一的关系
HasRequired:表示前者必选包含后者,前者可以独立存在,后者不可独立存在
WithRequiredPrincipal:指明实体的主要 这里表示指定Customer表是主表可以独立存在
MapKey:定义实体之间的外键
*/
modelBuilder.Entity<Customer>().HasRequired(p => p.CustomerEmail).WithRequiredPrincipal(t => t.Customer)
.Map(m =>
{
m.MapKey("CustomerId");
});
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
}
}
}
3、使用数据迁移生成数据库,并重写Configuration类的Seed()方法填充种子数据
Configuration类定义如下:
namespace LazyLoding.Migrations
{
using LazyLoding.Model;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Data.Entity.Migrations;
using System.Linq;
internal sealed class Configuration : DbMigrationsConfiguration<LazyLoding.EF.Context>
{
public Configuration()
{
AutomaticMigrationsEnabled = false;
}
protected override void Seed(LazyLoding.EF.Context context)
{
// This method will be called after migrating to the latest version.
// You can use the DbSet<T>.AddOrUpdate() helper extension method
// to avoid creating duplicate seed data.
// 初始化种子数据
context.CustomerTypes.AddOrUpdate(
new CustomerType()
{
Description = "零售",
Customers = new List<Customer>()
{
new Customer(){Name="小乔", CustomerEmail=new CustomerEmail(){ Email="qiao@qq.com"}},
new Customer(){Name="周瑜",CustomerEmail=new CustomerEmail(){Email="yu@126.com"}}
}
},
new CustomerType()
{
Description = "电商",
Customers = new List<Customer>()
{
new Customer(){Name="张飞", CustomerEmail=new CustomerEmail(){Email="zf@qq.com"}},
new Customer(){Name="刘备",CustomerEmail=new CustomerEmail(){Email="lb@163.com"}}
}
}
);
}
}
}
4、查看生成的数据库

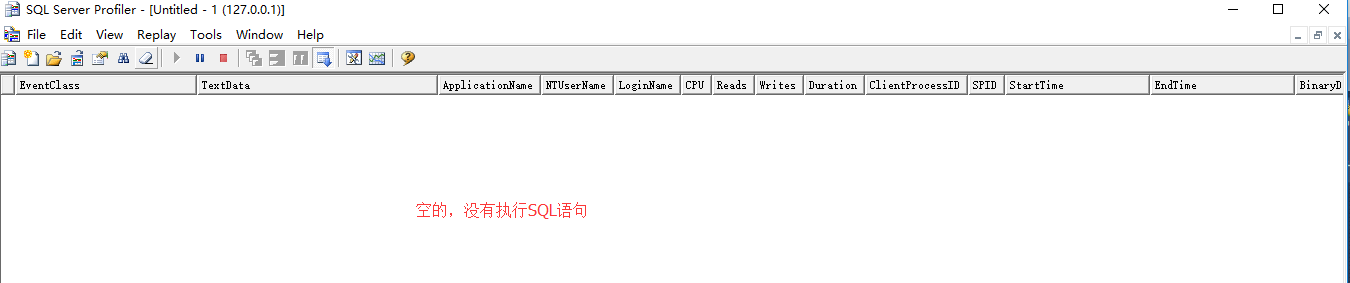
5、查看Main方法,并打开SQL Server Profiler监视器监视数据库
// 还没有查询数据库 var customerType = dbContext.CustomerTypes;
继续执行
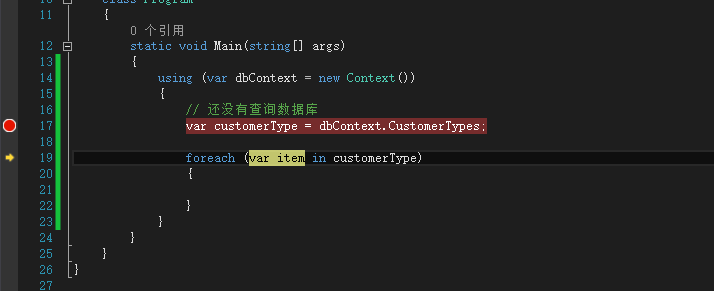
查看监视器:

发现这时候产生了查询的SQL语句。
这就是EF的延迟加载技术,只有在数据真正用到的时候才会去数据库中查询。
使用Code First时,延迟加载依赖于导航属性的本质。如果导航属性是virtual修饰的,那么延迟加载就开启了,如果要关闭延迟加载,不要给导航属性加virtual关键字就可以了。
注意:如果想要为所有的实体关闭延迟加载,那么可以在Context的构造函数中配置关闭属性即可,代码如下:
public Context() : base("name=AppConnection")
{
// 配置关闭延迟加载
this.Configuration.LazyLoadingEnabled = false;
}
二、贪婪加载(Eager Load)
贪婪加载:顾名思义就是一次性把所有数据都加载出来。贪婪加载是这样一种过程:当我们要加载查询中的主要实体时,同时也加载与之相关的所有实体。要实现贪婪加载,我们要使用Include()方法。
下面我们看一下如何在加载Customer数据的时候,同时也加载所有的CustomerType数据(操作此功能时暂时先关闭延迟加载以免影响)。
//贪婪加载,以下两种方式都可以
// 在使用Lambda表达式指明要加载的导航实体时,要引用命名空间:System.Data.Entity
var customers = dbContext.Customers.Include(p => p.CustomerType).Include(p => p.CustomerEmail).ToList();
//方式2
var query = dbContext.Customers.Include("CustomerType").Include("CustomerEmails");
总结:
贪婪加载:
- 1、减少数据访问的延迟,在一次数据库的访问中返回所有的数据。
- 2、一次性加载所有的数据到内存中,可能导致部分数据实际用不到,从而导致读取数据的速度变慢,效率变低。
延迟加载:
- 1、只在需要读取关联数据的时候才进行加载。每一条数据都会访问一次数据库,导致数据库的压力加大。
- 2、可能因为数据访问的延迟而降低性能,因为循环中,每一条数据都会访问一次数据库,导致数据库的压力增大。
如何选择使用哪种查询机制:
- 1、如果是在foreach循环中加载数据,那么使用延迟加载会比较好,因为不需要一次性将所有数据都读取出来,这样虽然可能会造成多次查询数据库,但基本上在可以接受的范围之内。
- 2、如果在开发时就可以预见需要一次性加载所有的数据,包含关联表的所有数据,那么使用贪婪加载是比较好的选择,但是此种方式会导致效率问题,尤其是在数据量大的情况下。
代码下载地址:点此下载
到此这篇关于Entity Framework加载控制Loading Entities的文章就介绍到这了。希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。

