Java 数据结构之堆的概念与应用
目录
- 什么是堆
- 堆的类型
- 小根堆
- 大根堆
- 堆的基本操作:创建堆
- 堆的时间复杂度和空间复杂度
- 堆的应用-优先级队列
- 概念
- 优先级队列基本操作
- 入优先级队列
- 出优先级队列首元素
- java的优先级队列
- 堆的常见面试题
- 最后一块石头的重量
- 找到K个最接近的元素
- 查找和最小的K对数字
java数据结构的堆
什么是堆
堆指的是使用数组保存完全二叉树结构,以层次遍历的方式放入数组中。
如图:

注意:堆方式适合于完全二叉树,对于非完全二叉树若使用堆则会造成空间的浪费
对于根节点与其左右孩子在数组中的下标关系可表示为:left=2parent+1,right=2parent+2,parent=(child-1)/2
堆的类型
对于堆来说一共有两种类型:一为大根堆,还有一个为小根堆
小根堆
小根堆指的是:所有的根结点的值小于左右孩子结点的值
如图:

大根堆
大根堆指的是:所有根结点的值大于左右孩子结点的值。
如图:

当使用堆进行从小到大进行排序时应该使用大堆进行排序
堆的基本操作:创建堆
以创建大堆为例:我们先给定一个数组,该数组在逻辑上可以视为一颗完全二叉树,但目前并不是堆,但我们可以通过一定的算法将其变化为堆,通常我们从倒数第一个结点进行调整,一直调整到根结点的数,这样就调整为堆了;
如示例:
//建堆前
int array[]={1,5,3,8,7,6};
//建堆后
int array[]={ 8,7,6,5,1,3 };
调整方式:
第一步:先将数组还原成一个完全二叉树
如图:
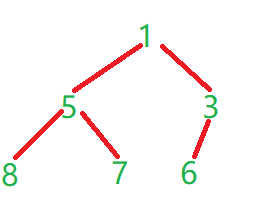
第二步:如果倒数第一个叶子结点有兄弟结点则先与兄弟结点比较大小然后再取大的结点与父结点比较大小,如果没有兄弟结点则直接与父结点比较大小,如果值比父结点值大则交换值,一直这样调整到根节点的树,就可以调整成堆。
操作如图:





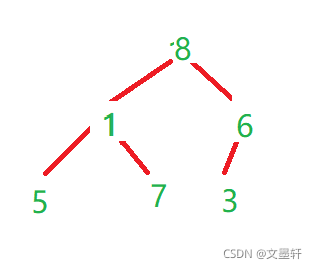


其核心代码如下:
public static void shiftDown(int[] array,int parent){
int child=2*parent+1;
while (child<array.length){
if(child+1<array.length){
if (array[child]<array[child+1]){
child++;
}
}
if(array[child]>array[parent]){
int tmp=array[child];
array[child]=array[parent];
array[parent]=tmp;
parent=child;
child=parent*2+1;
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
public static void createHeap(int[] array){
for (int i = (array.length-1-1)/2; i >=0; i--) {
shiftDown(array,i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int array[]={1,5,3,8,7,6};
createHeap(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}

堆的时间复杂度和空间复杂度
建堆时没有使用额外的空间因此其空间复杂度为O(1);
注意:该函数shiftDown(int[] array,int parent)时间复杂度为O(logn),建堆的时间复杂度为O(n*logn),但是建堆的时间复杂度为O(n)其推导如下:

堆的应用-优先级队列
概念
我们通常需要按照优先级情况对待处理对象进行处理,比如首先处理优先级最高的对象,然后处理次高的对象.一个简单的例子:一天晚上,你正在看电视,这时你的父母叫你去厨房帮忙,那么这时你应该处理最重要的事情:去厨房帮妈妈的忙在这种情况下,我们的数据结构应该提供两个最基本的操作,一个是返回最高优先级对象,一个是添加新的对象。这种数据结构就是优先级队列(Priority Queue)。
注意:实现优先级队列的方式有很多种,一般来说我们一般使用堆来构建优先级队列
优先级队列基本操作
入优先级队列
以大堆为例:
- 首先按尾插方式放入数组
- 比较其和其双亲的值的大小,如果双亲的值大,则满足堆的性质,插入结束
- 否则,交换其和双亲位置的值,重新进行 2、3 步骤
- 直到根结点
如图:



核心代码如下:
public class TestHeap {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public TestHeap() {
this.elem = new int[10];//先创建长度为10的数组
}
public boolean isFull() {
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
}
public void push(int val) {
//先判断队列是否已经满,如果以满则扩容
if (isFull()){
Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,this.elem.length*2);
}
this.elem[this.usedSize++]=val;
shiftUp(this.usedSize-1);
}
public void shiftUp(int child) {
int parent=(child-1)/2;
while (parent>=0){
if(this.elem[child]>this.elem[parent]){
int tmp=this.elem[child];
this.elem[child]=this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent]=tmp;
child=parent;
parent=(child-1)/2;
}
else{
break;
}
}
}
}
出优先级队列首元素
注意:为了防止破坏堆的结构,删除时并不是直接将堆顶元素删除,而是用数组的最后一个元素替换堆顶元素,然后通过向
下调整方式重新调整成堆
核心代码如下:
public class TestHeap {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public TestHeap() {
this.elem = new int[10];//10个0
}
public boolean isFull() {
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.usedSize == 0;
}
public int poll() {
//先判断队列是否为空,如果为空则抛出异常
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("优先级队列为空");
}
int tmp=this.elem[0];
this.elem[0]=this.elem[this.usedSize-1];
this.usedSize--;
shiftDown(0);
return tmp;
}
public void shiftDown(int parent) {
int child = 2*parent+1;
//进入这个循环 说明最起码你有左孩子
while (child < this.usedSize) {
//该条件进入是判断其是否有右兄弟
if(child+1 < this.usedSize &&
this.elem[child] < this.elem[child+1]) {
child++;
}
//child所保存的下标,就是左右孩子的最大值
if(this.elem[child] > this.elem[parent]) {
int tmp = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = 2*parent+1;
}else {
break;//如果孩子节点比父亲节点小 直接结束了
}
}
}
}
java的优先级队列
在java中,我们不必单独创建一个堆用于实现优先级对列
可以使用PriorityQueue
例如:
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue=new PriorityQueue<>();
java中的优先级对列其实是小堆若想使用大堆方法则需要从写比较方法
方法如下(方法不唯一)
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue=new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator(Integer)){
public int compare(Integer o1,Integer o2){return o2-o1}
};
优先级的使用方法:
| 错误处理 | 抛出异常 | 返回特殊值 |
|---|---|---|
| 入队列 | add(e) | offer(e) |
| 出队列 | remove() | poll() |
| 队首元素 | element() | peek() |
堆的常见面试题
最后一块石头的重量

解题思路:该题可以使用变化过的优先级队列进行解答,即将默认小堆的优先级队列改为大堆模式的优先级队列,则将每块石块的重量使用循环放入优先级队列中其自动会把最重的石块放入队首,而后,将队列的头两个元素依次取出记为max1,max2,并将sum=max1-max2;如果sum大于0则又放入队列中不是则继续重复上诉操作
class Solution {
public int lastStoneWeight(int[] stones) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((i1, i2) -> i2 - i1);//改为大堆
for(int i=0;i<stones.length;i++){
queue.offer(stones[i]);
}
while(queue.size()>=2){
int max1=queue.poll();
int max2=queue.poll();
int sum=max1-max2;
if(sum>0){
queue.offer(sum);
}
}
if(queue.size()>0){
return queue.poll();
}
return 0;
}
}

找到K个最接近的元素

题解主要思路:使用优先级队列,先判别k是否大于数组长度,大于则直接将数组存放到List,相反则先依次存放k个数,之后将想要存放到优先级队列中的数-x的绝对值记为sum1,队列中第一个元素-x的绝对值记为sum2,如果sum1小于sum2则将队列中第一个元素删除,将其他数放入队列中,最后将队列中元素存放到list中
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findClosestElements(int[] arr, int k, int x) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue=new PriorityQueue<>();
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
if(k>arr.length){
for (int num:arr) {
list.add(num);
}
}
else {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(i<k){
queue.offer(arr[i]);
}
else {
int sum1=Math.abs(arr[i]-x);
int sum2=Math.abs(queue.peek()-x);
if(sum1<sum2){
queue.poll();
queue.offer(arr[i]);
}
}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
list.add(queue.poll());
}
}
return list;
}
}

查找和最小的K对数字

主体解题思路:使用优先级队列将其先改变为大堆模式,使用循环先存放k个元素,之后想要存入队列的元素与队头元素比较,如果比队头元素小则删除队头元素,存放该元素,相反则继续上诉操作最后放入数组中
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> kSmallestPairs(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k) {
PriorityQueue<List<Integer>> queue=new PriorityQueue<>(k,(o1,o2)->{
return o2.get(0)+o2.get(1)-o1.get(0)-o1.get(1);
});
for (int i=0;i<Math.min(nums1.length,k);i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Math.min(nums2.length, k); j++) {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
if (queue.size()<k){
list.add(nums1[i]);
list.add(nums2[j]);
queue.offer(list);
}
else {
int tmp=queue.peek().get(0)+queue.peek().get(1);
if(nums1[i]+nums2[j]<tmp){
queue.poll();
list.add(nums1[i]);
list.add(nums2[j]);
queue.offer(list);
}
}
}
}
List<List<Integer>> list=new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < k&&!queue.isEmpty(); i++) {
list.add(queue.poll());
}
return list;
}
}

到此这篇关于Java 数据结构之堆的概念与应用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java 数据结构内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

