详解SpringMVC注解版前台向后台传值的两种方式
一、概述。
在很多企业的开法中常常用到SpringMVC+Spring+Hibernate(mybatis)这样的架构,SpringMVC相当于Struts是页面到Contorller直接的交互的框架也是界面把信息传输到Contorller层的一种架构,通过这个架构可以让我们把页面和Contorller层解耦,使得开发人员的分工更加明确。
二、代码演示。
1、首先配置SpringMVC环境。
1.1导入jar。

值得注意的是红色标记的commons-logging这个jar包一定得引入进去不然会报错。
1.2、xml配置文件。
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.1">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springMVC</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springMVC</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.spring</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
</web-app>
springMVC-servlet.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.gaowei.controller" />
</beans>
2、前台界面代码。
login.jsp
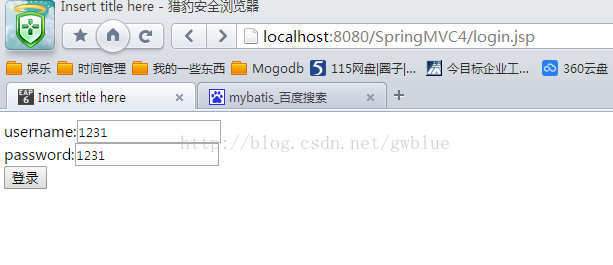
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <form action="login.spring" method="post"> username:<input type="text" name="username"> <br/> password:<input type="text" name="password"> <br/> <input type="submit" value="登录"> </form> </body> </html>
No.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> No! </body> </html>
Ok.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
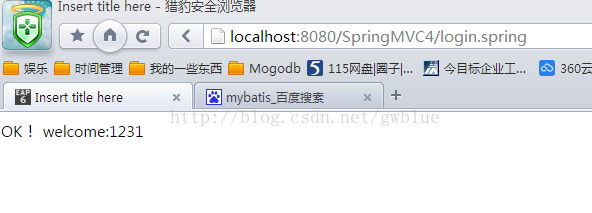
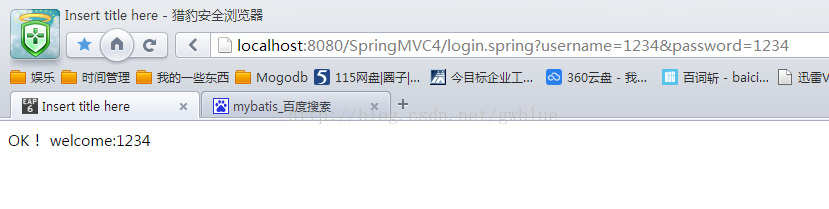
OK! welcome:${username}
</body>
</html>
3、Contorller层接收前台的两种方式。
方式一:
利用@RequestParam这个注解
package com.gaowei.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
@Controller
public class Login {
//方式一
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username,
@RequestParam("password") String password,Model model){
if (username.equals(password))
{
model.addAttribute("username", username);
return "ok.jsp";
} else {
return "no.jsp";
}
}
}
方式二:
package com.gaowei.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
@Controller
public class Login {
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(String username,String password,Model model){
if (username.equals(password))
{
model.addAttribute("username", username);
return "ok.jsp";
} else {
return "no.jsp";
}
}
}
4、界面结果。
第一种传值方式:
第二种传值方式:
三、总结。
这里体现出了SpringMVC传值方式的多样性满足了开发人员的不同需求。第一种用来表单的提交。第二种用来界面间相互传值,也为了方便开发人员利用AJAX。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。
赞 (0)

