如何实现定时推送的具体方案
详细内容
详细内容大概分为4个部分,1.应用场景 2.遇到问题 3.设计 4.实现 5.运行效果
1.应用场景
需要定时推送数据,且轻量化的实现。
2.遇到问题
- 如果启动一个定时器去定时轮询
- (1)轮询效率比较低
- (2)每次扫库,已经被执行过记录,仍然会被扫描(只是不会出现在结果集中),会做重复工作
- (3)时效性不够好,如果每小时轮询一次,最差的情况下会有时间误差
- 如何利用“延时消息”,对于每个任务只触发一次,保证效率的同时保证实时性,是今天要讨论的问题。
3.设计
高效延时消息,包含两个重要的数据结构:
- 环形队列,例如可以创建一个包含3600个slot的环形队列(本质是个数组)
- 任务集合,环上每一个slot是一个Set
同时,启动一个timer,这个timer每隔1s,在上述环形队列中移动一格,有一个Current Index指针来标识正在检测的slot。
Task结构中有两个很重要的属性:
- Cycle-Num:当Current Index第几圈扫描到这个Slot时,执行任务
- Task-Function:需要执行的任务指针
假设当前Current Index指向第一格,当有延时消息到达之后,例如希望3610秒之后,触发一个延时消息任务,只需:
- 计算这个Task应该放在哪一个slot,现在指向1,3610秒之后,应该是第11格,所以这个Task应该放在第11个slot的Set中
- 计算这个Task的Cycle-Num,由于环形队列是3600格(每秒移动一格,正好1小时),这个任务是3610秒后执行,所以应该绕3610/3600=1圈之后再执行,于是Cycle-Num=1
Current Index不停的移动,每秒移动到一个新slot,这个slot中对应的Set,每个Task看Cycle-Num是不是0:
- 如果不是0,说明还需要多移动几圈,将Cycle-Num减1
- 如果是0,说明马上要执行这个Task了,取出Task-Funciton执行(可以用单独的线程来执行Task),并把这个Task从Set中删除
使用了“延时消息”方案之后,“订单48小时后关闭评价”的需求,只需将在订单关闭时,触发一个48小时之后的延时消息即可:
- 无需再轮询全部订单,效率高
- 一个订单,任务只执行一次
- 时效性好,精确到秒(控制timer移动频率可以控制精度)
4.实现
首先写一个方案要理清楚自己的项目结构,我做了如下分层。
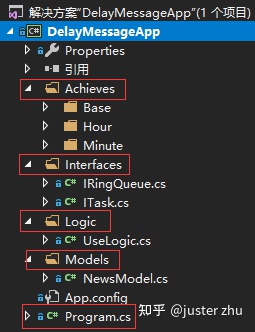
Interfaces , 这层里主要约束延迟消息队列的队列和消息任务行。
public interface IRingQueue<T>
{
/// <summary>
/// Add tasks [add tasks will automatically generate: task Id, task slot location, number of task cycles]
/// </summary>
/// <param name="delayTime">The specified task is executed after N seconds.</param>
/// <param name="action">Definitions of callback</param>
void Add(long delayTime,Action<T> action);
/// <summary>
/// Add tasks [add tasks will automatically generate: task Id, task slot location, number of task cycles]
/// </summary>
/// <param name="delayTime">The specified task is executed after N seconds.</param>
/// <param name="action">Definitions of callback.</param>
/// <param name="data">Parameters used in the callback function.</param>
void Add(long delayTime, Action<T> action, T data);
/// <summary>
/// Add tasks [add tasks will automatically generate: task Id, task slot location, number of task cycles]
/// </summary>
/// <param name="delayTime"></param>
/// <param name="action">Definitions of callback</param>
/// <param name="data">Parameters used in the callback function.</param>
/// <param name="id">Task ID, used when deleting tasks.</param>
void Add(long delayTime, Action<T> action, T data, long id);
/// <summary>
/// Remove tasks [need to know: where the task is, which specific task].
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index">Task slot location</param>
/// <param name="id">Task ID, used when deleting tasks.</param>
void Remove(long id);
/// <summary>
/// Launch queue.
/// </summary>
void Start();
}
public interface ITask
{
}
Achieves,这层里实现之前定义的接口,这里写成抽象类是为了后面方便扩展。
using System;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using DelayMessageApp.Interfaces;
namespace DelayMessageApp.Achieves.Base
{
public abstract class BaseQueue<T> : IRingQueue<T>
{
private long _pointer = 0L;
private ConcurrentBag<BaseTask<T>>[] _arraySlot;
private int ArrayMax;
/// <summary>
/// Ring queue.
/// </summary>
public ConcurrentBag<BaseTask<T>>[] ArraySlot
{
get { return _arraySlot ?? (_arraySlot = new ConcurrentBag<BaseTask<T>>[ArrayMax]); }
}
public BaseQueue(int arrayMax)
{
if (arrayMax < 60 && arrayMax % 60 == 0)
throw new Exception("Ring queue length cannot be less than 60 and is a multiple of 60 .");
ArrayMax = arrayMax;
}
public void Add(long delayTime, Action<T> action)
{
Add(delayTime, action, default(T));
}
public void Add(long delayTime,Action<T> action,T data)
{
Add(delayTime, action, data,0);
}
public void Add(long delayTime, Action<T> action, T data,long id)
{
NextSlot(delayTime, out long cycle, out long pointer);
ArraySlot[pointer] = ArraySlot[pointer] ?? (ArraySlot[pointer] = new ConcurrentBag<BaseTask<T>>());
var baseTask = new BaseTask<T>(cycle, action, data,id);
ArraySlot[pointer].Add(baseTask);
}
/// <summary>
/// Remove tasks based on ID.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="id"></param>
public void Remove(long id)
{
try
{
Parallel.ForEach(ArraySlot, (ConcurrentBag<BaseTask<T>> collection, ParallelLoopState state) =>
{
var resulTask = collection.FirstOrDefault(p => p.Id == id);
if (resulTask != null)
{
collection.TryTake(out resulTask);
state.Break();
}
});
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
}
public void Start()
{
while (true)
{
RightMovePointer();
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now.ToString());
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Calculate the information of the next slot.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="delayTime">Delayed execution time.</param>
/// <param name="cycle">Number of turns.</param>
/// <param name="index">Task location.</param>
private void NextSlot(long delayTime, out long cycle,out long index)
{
try
{
var circle = delayTime / ArrayMax;
var second = delayTime % ArrayMax;
var current_pointer = GetPointer();
var queue_index = 0L;
if (delayTime - ArrayMax > ArrayMax)
{
circle = 1;
}
else if (second > ArrayMax)
{
circle += 1;
}
if (delayTime - circle * ArrayMax < ArrayMax)
{
second = delayTime - circle * ArrayMax;
}
if (current_pointer + delayTime >= ArrayMax)
{
cycle = (int)((current_pointer + delayTime) / ArrayMax);
if (current_pointer + second - ArrayMax < 0)
{
queue_index = current_pointer + second;
}
else if (current_pointer + second - ArrayMax > 0)
{
queue_index = current_pointer + second - ArrayMax;
}
}
else
{
cycle = 0;
queue_index = current_pointer + second;
}
index = queue_index;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
throw;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Get the current location of the pointer.
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
private long GetPointer()
{
return Interlocked.Read(ref _pointer);
}
/// <summary>
/// Reset pointer position.
/// </summary>
private void ReSetPointer()
{
Interlocked.Exchange(ref _pointer, 0);
}
/// <summary>
/// Pointer moves clockwise.
/// </summary>
private void RightMovePointer()
{
try
{
if (GetPointer() >= ArrayMax - 1)
{
ReSetPointer();
}
else
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref _pointer);
}
var pointer = GetPointer();
var taskCollection = ArraySlot[pointer];
if (taskCollection == null || taskCollection.Count == 0) return;
Parallel.ForEach(taskCollection, (BaseTask<T> task) =>
{
if (task.Cycle > 0)
{
task.SubCycleNumber();
}
if (task.Cycle <= 0)
{
taskCollection.TryTake(out task);
task.TaskAction(task.Data);
}
});
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
throw;
}
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Threading;
using DelayMessageApp.Interfaces;
namespace DelayMessageApp.Achieves.Base
{
public class BaseTask<T> : ITask
{
private long _cycle;
private long _id;
private T _data;
public Action<T> TaskAction { get; set; }
public long Cycle
{
get { return Interlocked.Read(ref _cycle); }
set { Interlocked.Exchange(ref _cycle, value); }
}
public long Id
{
get { return _id; }
set { _id = value; }
}
public T Data
{
get { return _data; }
set { _data = value; }
}
public BaseTask(long cycle, Action<T> action, T data,long id)
{
Cycle = cycle;
TaskAction = action;
Data = data;
Id = id;
}
public BaseTask(long cycle, Action<T> action,T data)
{
Cycle = cycle;
TaskAction = action;
Data = data;
}
public BaseTask(long cycle, Action<T> action)
{
Cycle = cycle;
TaskAction = action;
}
public void SubCycleNumber()
{
Interlocked.Decrement(ref _cycle);
}
}
}
Logic,这层主要实现调用逻辑,调用者最终只需要关心把任务放进队列并指定什么时候执行就行了,根本不需要关心其它的任何信息。
public static void Start()
{
//1.Initialize queues of different granularity.
IRingQueue<NewsModel> minuteRingQueue = new MinuteQueue<NewsModel>();
//2.Open thread.
var lstTasks = new List<Task>
{
Task.Factory.StartNew(minuteRingQueue.Start)
};
//3.Add tasks performed in different periods.
minuteRingQueue.Add(5, new Action<NewsModel>((NewsModel newsObj) =>
{
Console.WriteLine(newsObj.News);
}), new NewsModel() { News = "Trump's visit to China!" });
minuteRingQueue.Add(10, new Action<NewsModel>((NewsModel newsObj) =>
{
Console.WriteLine(newsObj.News);
}), new NewsModel() { News = "Putin Pu's visit to China!" });
minuteRingQueue.Add(60, new Action<NewsModel>((NewsModel newsObj) =>
{
Console.WriteLine(newsObj.News);
}), new NewsModel() { News = "Eisenhower's visit to China!" });
minuteRingQueue.Add(120, new Action<NewsModel>((NewsModel newsObj) =>
{
Console.WriteLine(newsObj.News);
}), new NewsModel() { News = "Xi Jinping's visit to the US!" });
//3.Waiting for all tasks to complete is usually not completed. Because there is an infinite loop.
//F5 Run the program and see the effect.
Task.WaitAll(lstTasks.ToArray());
Console.Read();
}
Models,这层就是用来在延迟任务中带入的数据模型类而已了。自己用的时候换成任意自定义类型都可以。
5.运行效果

到此这篇关于如何实现定时推送的具体方案的文章就介绍到这了,希望对大家有所帮助,更多相关C#内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持我们!
赞 (0)

