Spring中集成Groovy的四种方式(小结)
groovy是一种动态脚本语言,适用于一些可变、和规则配置性的需求,目前Spring提供ScriptSource接口,支持两种类型,一种是
ResourceScriptSource,另一种是 StaticScriptSource,但是有的场景我们需要把groovy代码放进DB中,所以我们需要扩展这个。

ResourceScriptSource:在 resources 下面写groovy类
StaticScriptSource:把groovy类代码放进XML里
DatabaseScriptSource:把groovy类代码放进数据库中
工程模块为:

ResourceScriptSource
groovy的pom
<dependency>
<artifactId>groovy-all</artifactId>
<groupId>org.codehaus.groovy</groupId>
<version>2.1.9</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
HelloService接口
package com.maple.resource.groovy;
/**
* @author: maple
* @version: HelloService.java, v 0.1 2020年09月25日 21:26 maple Exp $
*/
public interface HelloService {
String sayHello();
}
resources下面建groovy实现类

package com.maple.resource.groovy
class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
String name;
@Override
String sayHello() {
return "Hello $name. Welcome to resource in Groovy.";
}
}
在spring-groovy.xml中配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:lang="http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang
http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang/spring-lang.xsd">
<lang:groovy id="helloService" script-source="classpath:groovy/HelloServiceImpl.groovy">
<lang:property name="name" value="maple"></lang:property>
</lang:groovy>
</beans>
主类 GroovyResourceApplication
package com.maple.resource;
import com.maple.resource.groovy.HelloService;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class GroovyResourceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//SpringApplication.run(GroovyResourceApplication.class, args);
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-groovy.xml");
HelloService bean = context.getBean(HelloService.class);
String sayHello = bean.sayHello();
System.out.println(sayHello);
}
}
启动并测试
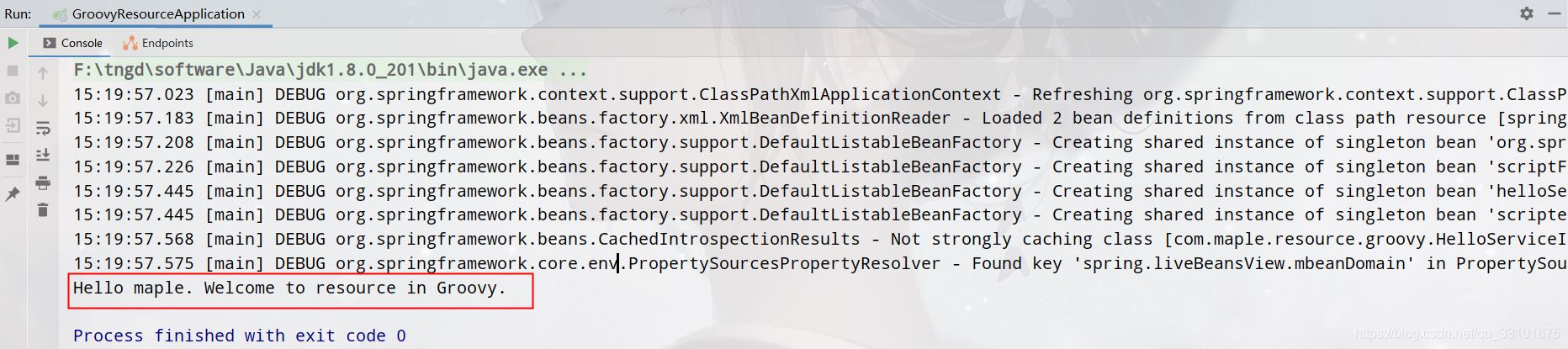
StaticScriptSource
groovy的pom
<dependency>
<artifactId>groovy-all</artifactId>
<groupId>org.codehaus.groovy</groupId>
<version>2.1.9</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
HelloService接口
package com.maple.groovy.staticscript.groovy;
/**
* @author: maple
* @version: HelloService.java, v 0.1 2020年09月25日 21:26 maple Exp $
*/
public interface HelloService {
String sayHello();
}
在spring-groovy.xml中配置具体的实现类
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:lang="http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang
http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang/spring-lang.xsd">
<lang:groovy id="helloService">
<lang:inline-script>
import com.maple.groovy.staticscript.groovy.HelloService
class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
String name;
@Override
String sayHello() {
return "Hello $name. Welcome to static script in Groovy.";
}
}
</lang:inline-script>
<lang:property name="name" value="maple"/>
</lang:groovy>
</beans>
主类 GroovyStaticscriptApplication
package com.maple.groovy.staticscript;
import com.maple.groovy.staticscript.groovy.HelloService;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class GroovyStaticscriptApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//SpringApplication.run(GroovyStaticscriptApplication.class, args);
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-groovy.xml");
HelloService bean = context.getBean(HelloService.class);
String sayHello = bean.sayHello();
System.out.println(sayHello);
}
}
启动并测试

DatabaseScriptSource
下面我们先建表,把基本工作做完,这里我使用mybatisplus,dao、service等代码省略
CREATE TABLE `groovy_script` ( `id` BIGINT ( 20 ) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `script_name` VARCHAR ( 64 ) NOT NULL COMMENT 'script name', `script_content` text NOT NULL COMMENT 'script content', `status` VARCHAR ( 16 ) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'ENABLE' COMMENT 'ENABLE/DISENABLE', `extend_info` VARCHAR ( 4096 ) DEFAULT NULL, `created_time` TIMESTAMP ( 6 ) NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ( 6 ), `modified_time` TIMESTAMP ( 6 ) NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ( 6 ) ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ( 6 ), PRIMARY KEY ( `id` ) ) ENGINE = INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT = 1 DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8mb4 COMMENT = 'groovy script';
INSERT INTO `gane-platform`.`groovy_script`(`id`, `script_name`, `script_content`, `status`, `extend_info`, `created_time`, `modified_time`) VALUES (1, 'helloService', 'package com.maple.resource.groovy\r\n\r\nimport com.maple.database.groovy.HelloService\r\n\r\npublic class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {\r\n\r\n @Override\r\n String sayHello(String name) {\r\n return \"Hello \"+name+\". Welcome to database in Groovy.\";\r\n }\r\n}', 'ENABLE', NULL, '2020-09-26 17:16:36.477818', '2020-09-27 08:23:10.790553');
方法一:
1、实时读取DB里的groovy脚本文件
2、利用GroovyClassLoader去编译脚本文件
3、把class对象注入成Spring bean
4、反射调用脚本的方法
package com.maple.database.controller;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper;
import com.maple.database.entity.GroovyScript;
import com.maple.database.groovy.SpringContextUtils;
import com.maple.database.service.GroovyScriptService;
import groovy.lang.GroovyClassLoader;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author: maple
* @version: GroovyController.java, v 0.1 2020年09月26日 17:18 maple Exp $
*/
@RestController
public class GroovyController {
@Resource
private GroovyScriptService groovyScriptService;
@GetMapping("/groovyTest")
private String groovyTest() throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException {
GroovyScript groovyScript = groovyScriptService.getOne(new QueryWrapper<GroovyScript>()
.eq("script_name", "helloService").eq("status", "ENABLE"));
System.out.println(groovyScript.getScriptContent());
Class clazz = new GroovyClassLoader().parseClass(groovyScript.getScriptContent());
Object o = clazz.newInstance();
SpringContextUtils.autowireBean(o);
Method method = clazz.getMethod("sayHello", String.class);
return (String) method.invoke(o, "maple");
}
}
package com.maple.database.groovy;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author: maple
* @version: SpringContextUtils.java, v 0.1 2020年09月26日 17:29 maple Exp $
*/
@Component
public class SpringContextUtils implements ApplicationContextAware {
static ApplicationContext context;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
SpringContextUtils.context = applicationContext;
}
public static void autowireBean(Object bean) {
context.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory().autowireBean(bean);
}
public static ApplicationContext getContext() {
return context;
}
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz) {
return context.getBean(clazz);
}
public static <T> T getBean(String name) {
return (T) context.getBean(name);
}
}
启动测试结果为:
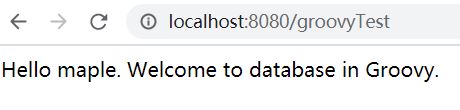
总结:
优点:实时读取DB里的脚本,当脚本更改时,可以直接修改DB,对代码无侵入
缺点:每次都要查询DB,反射调用代码写死了
方法二:
1、我们模仿groovy-resource的思路,resource的XML配置是下面这样的
<lang:groovy id="helloService" script-source="classpath:groovy/HelloServiceImpl.groovy" />
所以,我们可以把DatabaseScriptSource的XML保存成这种格式
<lang:groovy id="helloService" script-source="database:helloService"/>
2、然后模仿Spring保存成XML格式的document的思路,我们也把groovy保存成XML格式的document,放进内存里
3、groovy的关键处理类是ScriptFactoryPostProcessor,当 Spring 装载应用程序上下文时,它首先创建工厂 bean(例如 GroovyScriptFactory bean)。然后,执行ScriptFactoryPostProcessor bean,用实际的脚本对象替换所有的工厂 bean。例如,我们本次测试的配置产生一个名为 helloService 的 bean,它的类型是groovierspring.GroovyHelloService。(如果启用 Spring 中的 debug 级日志记录,并观察应用程序上下文的启动,将会看到 Spring 首先创建一个名为 scriptFactory.helloService 的工厂 bean,然后 ScriptFactoryPostProcessor 从该工厂 bean 创建 helloService bean)。
我们发现ScriptFactoryPostProcessor这个类中,有getScriptSource这个方法,该方法里有convertToScriptSource方法


在convertToScriptSource这个方法中,他默认支持我们前面说过的static script和resource两种类型,但是现在我们新增了一种database类型,所以我们需要重写该方法,其他的工作都一样,交给ScriptFactoryPostProcessor帮我们去处理。
package com.maple.database.manage;
import com.maple.database.groovy.DatabaseScriptSource;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
import org.springframework.scripting.ScriptSource;
import org.springframework.scripting.support.ResourceScriptSource;
import org.springframework.scripting.support.ScriptFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.scripting.support.StaticScriptSource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author: maple
* @version: CustomerScriptFactoryPostProcessor.java, v 0.1 2020年09月26日 20:36 maple Exp $
*/
@Component
public class CustomerScriptFactoryPostProcessor extends ScriptFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
protected ScriptSource convertToScriptSource(String beanName, String scriptSourceLocator, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
if (scriptSourceLocator.startsWith(INLINE_SCRIPT_PREFIX)) {
return new StaticScriptSource(scriptSourceLocator.substring(INLINE_SCRIPT_PREFIX.length()), beanName);
}
if (scriptSourceLocator.startsWith(GroovyConstant.SCRIPT_SOURCE_PREFIX)) {
return new DatabaseScriptSource(StringUtils.substringAfter(scriptSourceLocator, GroovyConstant.SCRIPT_SOURCE_PREFIX));
}
return new ResourceScriptSource(resourceLoader.getResource(scriptSourceLocator));
}
}
但是我们也要看看ScriptFactoryPostProcessor帮我们处理的其他工作都是什么:
(1)predictBeanType:是 Spring 中从 BeanDefinition 中提取 Bean 类型的底层 API

(2)我们再来看prepareScriptBeans准备了什么

(3)scriptBeanFactory.registerBeanDefinition,向beanDefinitionMap里put键值对
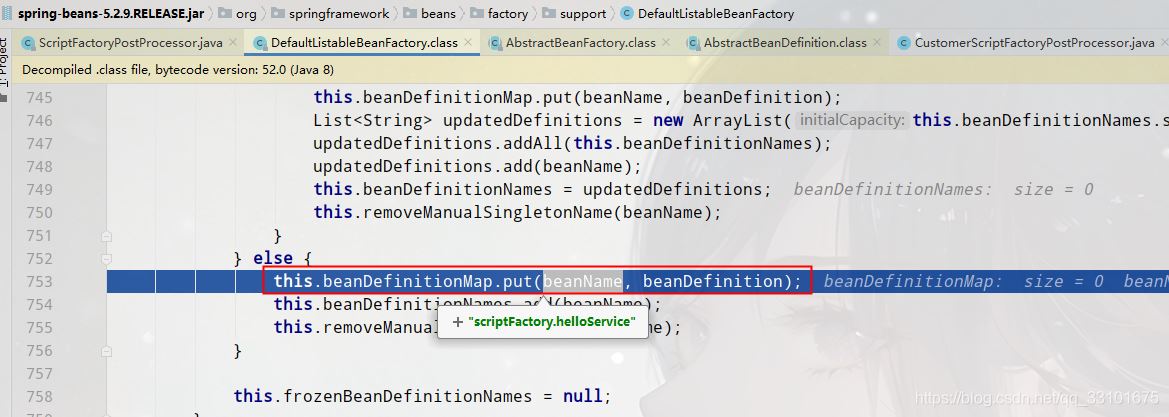

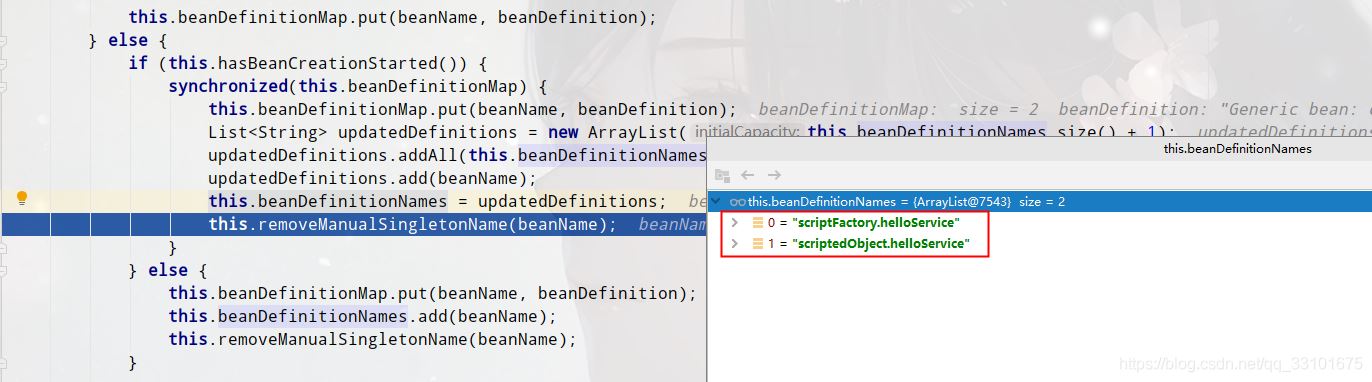
(4)createScriptedObjectBeanDefinition
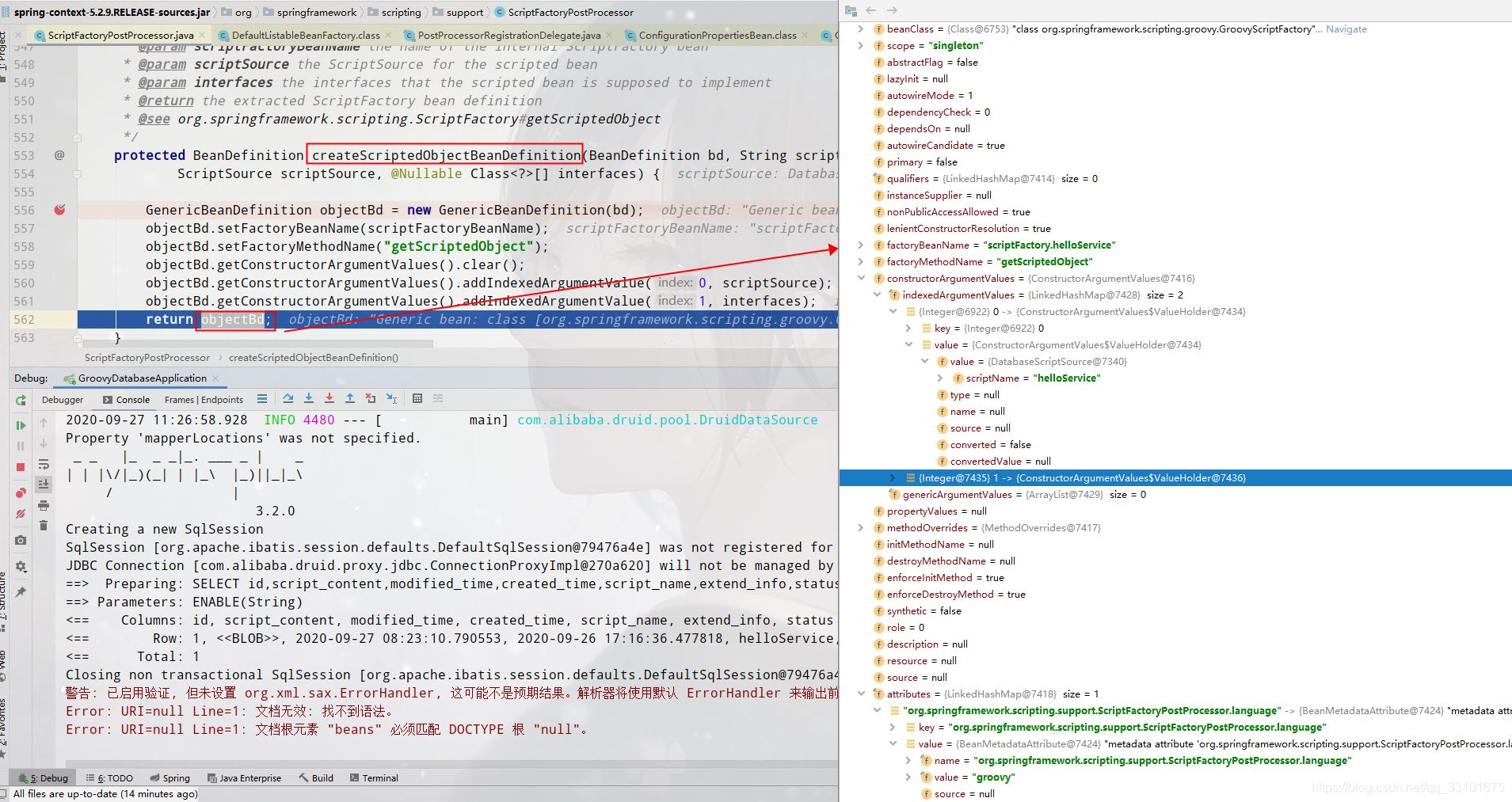
(5)Class<?> scriptedType = scriptFactory.getScriptedObjectType(scriptSource);
这句是为了拿到我们具体的实现类,也是我们的基础,它里面就是用GroovyClassLoader去编译我们的groovy脚本内容,并返回了Class<?> scriptClass我们的HelloServiceImpl

(6)ScriptSource scriptSource = getScriptSource(scriptFactoryBeanName, scriptFactory.getScriptSourceLocator());
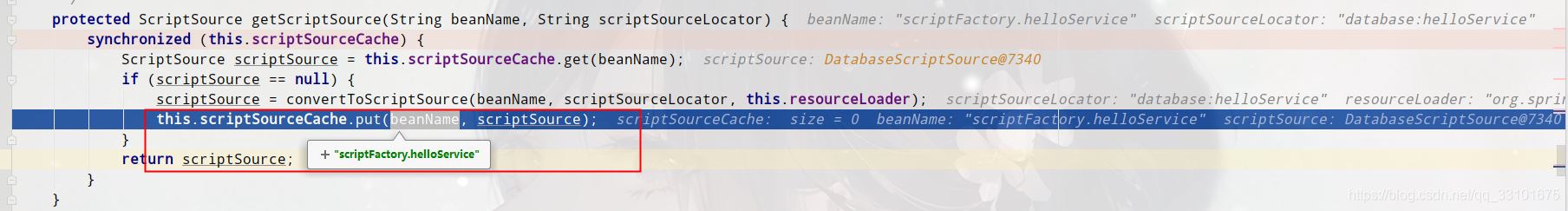
这里首先去我们下面新增的DatabaseScriptSource里拿到groovy脚本内容,并放进map里,返回DatabaseScriptSource
4、新增DatabaseScriptSource类
package com.maple.database.groovy;
import com.maple.database.groovy.cache.GroovyCache;
import org.springframework.scripting.ScriptSource;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author: maple
* @version: DatabaseScriptSource.java, v 0.1 2020年09月26日 15:37 maple Exp $
*/
public final class DatabaseScriptSource implements ScriptSource {
/**
* 脚本名称
*/
private String scriptName;
/**
* 构造函数
*
* @param scriptName
*/
public DatabaseScriptSource(String scriptName) {
this.scriptName = scriptName;
}
@Override
public String getScriptAsString() throws IOException {
return GroovyCache.getByName(scriptName).getGroovyContent();
}
@Override
public boolean isModified() {
return false;
}
@Override
public String suggestedClassName() {
return StringUtils.stripFilenameExtension(this.scriptName);
}
}
5、把我们的CustomerScriptFactoryPostProcessor放进Spring的List<BeanPostProcessor>中
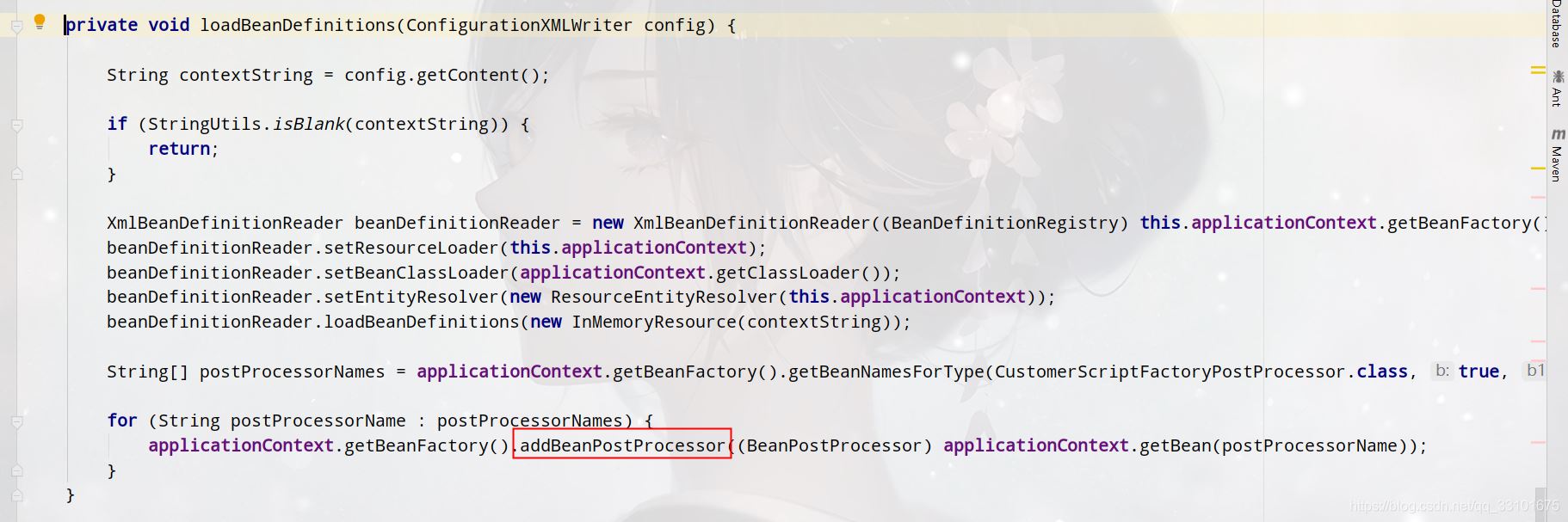
这样的话,我们就能从Spring容器中获取helloService的bean实例了,测试:
package com.maple.database.controller;
import com.maple.database.groovy.HelloService;
import com.maple.database.groovy.SpringContextUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author: maple
* @version: GroovyController.java, v 0.1 2020年09月26日 17:18 maple Exp $
*/
@RestController
public class NewGroovyController {
@GetMapping("/newGroovyTest")
private String newGroovyTest() {
HelloService helloService = SpringContextUtils.getBean("helloService");
String hello = helloService.sayHello("maple");
System.out.println(hello);
return hello;
}
}

总结:
优点:项目初始化的时候,就把DB里的groovy脚本读取到,放进本次缓存里,并交给Spring管理,减少与DB的交互次数;没有硬编码,扩展性更好。
缺点:当DB里的groovy脚本文件需要修改时,我们改完之后不能立即生效,需要重启工程或者刷新本次缓存,再次放进Spring容器里才行
附上核心处理类:GroovyDynamicLoader
package com.maple.database.manage;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper;
import com.maple.database.entity.GroovyScript;
import com.maple.database.groovy.cache.GroovyCache;
import com.maple.database.groovy.cache.GroovyInfo;
import com.maple.database.service.GroovyScriptService;
import groovy.lang.GroovyClassLoader;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.ResourceEntityResolver;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* @author: maple
* @version: GroovyDynamicLoader.java, v 0.1 2020年09月26日 20:00 maple Exp $
*/
@Configuration
public class GroovyDynamicLoader implements ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean {
private ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext;
}
@Resource
private GroovyScriptService groovyScriptService;
private static final GroovyClassLoader groovyClassLoader = new GroovyClassLoader(GroovyDynamicLoader.class.getClassLoader());
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
init();
}
private void init() {
List<GroovyScript> groovyScripts = groovyScriptService.list(new QueryWrapper<GroovyScript>().eq("status", "ENABLE"));
List<GroovyInfo> groovyInfos = groovyScripts.stream().map(groovyScript -> {
GroovyInfo groovyInfo = new GroovyInfo();
groovyInfo.setClassName(groovyScript.getScriptName());
groovyInfo.setGroovyContent(groovyScript.getScriptContent());
return groovyInfo;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(groovyInfos)) {
return;
}
ConfigurationXMLWriter config = new ConfigurationXMLWriter();
addConfiguration(config, groovyInfos);
GroovyCache.put2map(groovyInfos);
loadBeanDefinitions(config);
}
private void addConfiguration(ConfigurationXMLWriter config, List<GroovyInfo> groovyInfos) {
for (GroovyInfo groovyInfo : groovyInfos) {
writeBean(config, groovyInfo);
}
}
private void writeBean(ConfigurationXMLWriter config, GroovyInfo groovyInfo) {
if (checkSyntax(groovyInfo)) {
DynamicBean bean = composeDynamicBean(groovyInfo);
config.write(GroovyConstant.SPRING_TAG, bean);
}
}
private boolean checkSyntax(GroovyInfo groovyInfo) {
try {
groovyClassLoader.parseClass(groovyInfo.getGroovyContent());
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
private DynamicBean composeDynamicBean(GroovyInfo groovyInfo) {
DynamicBean bean = new DynamicBean();
String scriptName = groovyInfo.getClassName();
Assert.notNull(scriptName, "parser className cannot be empty!");
//设置bean的属性,这里只有id和script-source。
bean.put("id", scriptName);
bean.put("script-source", GroovyConstant.SCRIPT_SOURCE_PREFIX + scriptName);
return bean;
}
private void loadBeanDefinitions(ConfigurationXMLWriter config) {
String contextString = config.getContent();
if (StringUtils.isBlank(contextString)) {
return;
}
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader((BeanDefinitionRegistry) this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
beanDefinitionReader.setBeanClassLoader(applicationContext.getClassLoader());
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this.applicationContext));
beanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(new InMemoryResource(contextString));
String[] postProcessorNames = applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(CustomerScriptFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String postProcessorName : postProcessorNames) {
applicationContext.getBeanFactory().addBeanPostProcessor((BeanPostProcessor) applicationContext.getBean(postProcessorName));
}
}
}
到此这篇关于Spring中集成Groovy的四种方式(小结)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring集成Groovy内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

